(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023 – Inspired by the need to safeguard marine animals and promote sustainable solutions within marine environments, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia and Sofia University in Bulgaria are delving into the hydrodynamics of buoyant objects at the air-water interface.
By studying these dynamics, their goal is to expand the understanding of fluid hydrodynamics and complex surface interactions – and advance fields such as the design and performance of marine engineering systems, buoy systems, and underwater vehicles.
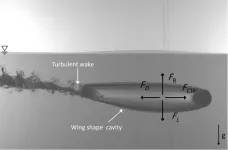
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, the team presents a study of the dynamics of buoyant spheres (think skipping stones) at the air-water interface. Their work revealed complex hydrodynamics involved in forming horizontal air cavities and the transition between floating and skipping.
The study of fluidics and physics within the context of buoyancy involves several key principles: buoyancy, hydrodynamics, fluid resistance, and a Reynolds number.
Buoyancy refers to the upward force exerted on an object immersed within a fluid, while hydrodynamics focuses on the motion of the fluid and its interactions with solid objects.
Fluid resistance, or drag, occurs when an object moving through a fluid experiences resistance due to the friction between its surface and the fluid. This resistance depends on factors such as an object’s shape, size, speed, and fluid properties.
To further analyze fluid behavior, scientists use a dimensionless parameter, a Reynolds number, to determine the type of flow around an object.
One of the team’s key findings is that as the pulling force and speed of the spheres increase, their behavior becomes more irregular. “The spheres exhibit oscillatory motions, diving into the water, rising toward and piercing the water surface, and attaching underwater air cavities in a horizontal direction,” said co-author Farrukh Kamoliddinov of KAUST.
They also discovered larger pulling angles result in different air-cavity lengths, larger skipping distances, and earlier water exit behavior – meaning that the pulling angle plays a significant role in shaping the hydrodynamics of the buoyant spheres.
And the cavity maintains a steady horizontal motion at a constant velocity over a certain distance. The air cavity formation exhibits distinct features, including an inverted wing shape and a turbulent wake behind it. This steady and controlled horizontal motion of the cavity provides insight into complex fluid dynamics and opens the door to further exploration and applications.
“Understanding buoyant sphere dynamics and cavity formation can inspire new designs and innovations in fields beyond marine engineering,” said Kamoliddinov. “It can potentially lead to new novel propulsion systems, drag reduction strategies, fluidic propulsion systems, and fluidic devices that harness the characteristics of buoyant spheres.”
###
The article “Skipping under water: Buoyant sphere hydrodynamics at the air-water interface” is authored by Farrukh Kamoliddinov, Ivan U. Vakarelski, Sigurdur T. Thoroddsen, and Tadd T. Truscott. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on July 11, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0153610). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0153610.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pof.
###
END
The science behind skipping stones
Researchers uncover dynamics of buoyant spheres and the formation of horizontal air cavities at the air-water interface.
2023-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Association of racial discrimination with obesity in children and adolescents
2023-07-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that personally mediated racial discrimination may be a risk factor for developing obesity in children and adolescents, above and beyond socioeconomic status. The results highlight the need for a multifaceted approach to address racial discrimination and its impact on the health of children and adolescents.
Authors: Adolfo G. Cuevas, Ph.D., of the New York University School of Global Public Health in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.22839)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Association between historical neighborhood redlining and cardiovascular outcomes among veterans
2023-07-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. veterans, the findings suggest that those with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who reside in historically redlined neighborhoods continue to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and higher cardiovascular risk. Even close to a century after this practice was discontinued, redlining appears to still be adversely associated with adverse cardiovascular events.
Authors: Sadeer Al-Kindi, M.D., of University Hospitals in Cleveland, and Salil V. Deo, ...
Genome sequencing nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene-sequencing test at diagnosing genetic disorders in newborns and infants
2023-07-11
July 11, 2023 (BOSTON) – A new national study, led by researchers at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, has found whole genome sequencing (WGS) to be nearly twice as effective as a targeted gene sequencing test at identifying abnormalities responsible for genetic disorders in newborns and infants. The study, “A Comparative Analysis of Rapid Whole Genomic Sequencing and a Targeted Neonatal Gene Panel in Infants with a Suspected Genetic Disorder: The Genomic Medicine for Ill Neonates and Infants ...
Racial discrimination increases risk for childhood obesity
2023-07-11
Children who experience racial discrimination are more likely to later have a higher body mass index (BMI) and larger waistline, according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open. The findings illustrate that racial discrimination may be a risk factor for young people developing obesity—above and beyond other socioeconomic factors such as family income.
“Exposure to racial discrimination must be acknowledged as both a social determinant of obesity and a significant contributor to obesity disparities among children and adolescents,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor of social and behavioral sciences at the NYU School of Global Public Health and the study’s ...
First large US clinical trial of cytisinicline finds the smoking cessation medication effective and well tolerated
2023-07-11
BOSTON – The first large-scale U.S. clinical trial of cytisinicline, led by a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigator, found the smoking cessation medication to be effective and well tolerated in adults who wished to break their nicotine dependence. In the Phase 3 study published in JAMA, researchers reported that cytisinicline could offer adults who smoke a potential new treatment option.
“Cigarette smoking remains the leading preventable cause of death worldwide, yet no new smoking cessation medication has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for nearly two decades,” says Nancy Rigotti, MD, director of MGH’s ...
A varied life boosts the brain’s functional networks
2023-07-11
That experiences leave their trace in the connectivity of the brain has been known for a while, but a pioneering study by researchers at the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and TUD Dresden University of Technology now shows how massive these effects really are. The findings in mice provide unprecedented insights into the complexity of large-scale neural networks and brain plasticity. Moreover, they could pave the way for new brain-inspired artificial intelligence methods. The results, based on an innovative “brain-on-chip” technology, are published in the scientific journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
The Dresden researchers explored ...
You’re not getting sleepy: Six myths and misconceptions about hypnosis from an expert
2023-07-11
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A strange mystic swings a pocket watch back and forth, repeating the phrase “You’re getting sleepy, very sleepy,” giving them absolute command over their subject. That’s not how hypnotism really works, but it’s the way it’s often depicted in pop culture. Even some clinicians and hypnosis educators propagate harmful myths about hypnosis.
Steven Jay Lynn, a professor of psychology at Binghamton University, State University of New York, is an expert on hypnosis who has made major contributions to the judicial system ...
Obesity and high weight linked to adverse outcomes in leukemia treatment
2023-07-11
(WASHINGTON, July 11, 2023) – As the United States faces a growing obesity epidemic, scientists are taking a closer look at how body weight can affect health outcomes. New research published in Blood Advances highlights the potential association of elevated body mass index (BMI) with inferior outcomes to treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in adolescents and young adults (AYAs). This study sheds light on the impact of weight on treatment toxicities and outcomes and calls for further study of the impact of weight on response to different ALL chemotherapy regimens.
Obesity is a growing public health threat in the United States, affecting approximately ...
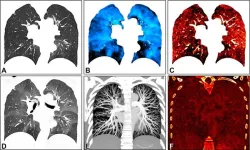
Photon-counting CT can evaluate lung function
2023-07-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New CT technology allows for a comprehensive, simultaneous evaluation of lung structure and function, something not possible with standard CT, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Chest CT is the imaging method of choice for analyzing lung disease and tracking changes over time. However, CT studies of lung function and perfusion, or blood flow, require dedicated protocols that cannot be combined.
Researchers in Germany and the Netherlands developed a chest imaging protocol that yields ...
Penn Medicine researchers to lead $40 million, multisite study of Alzheimer’s disease in Asian Americans and Asian Canadians
2023-07-11
PHILADELPHIA – A $40.5 million grant from the National Institute on Aging (NIA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), will fund the Asian Cohort for Alzheimer’s Disease (ACAD) study at Penn Medicine and 15 other academic research centers across the United States and Canada. Led by Li-San Wang, PhD, the Peter C. Nowell, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the project represents the first major Alzheimer’s disease genetics cohort for Asian Americans and Asian Canadians, populations currently underrepresented in Alzheimer’s disease research. The other principal investigators ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] The science behind skipping stonesResearchers uncover dynamics of buoyant spheres and the formation of horizontal air cavities at the air-water interface.