(Press-News.org)
On July 12, 2023, a new research paper was published in Aging, titled, “Chemically induced reprogramming to reverse cellular aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 12, 2023 – In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unlocked a new frontier in the fight against aging and age-related diseases. The study, conducted by a team of scientists at Harvard Medical School, has published the first chemical approach to reprogram cells to a younger state. Previously, this was only achievable using a powerful gene therapy.
On July 12, 2023, researchers Jae-Hyun Yang, Christopher A. Petty, Thomas Dixon-McDougall, Maria Vina Lopez, Alexander Tyshkovskiy, Sun Maybury-Lewis, Xiao Tian, Nabilah Ibrahim, Zhili Chen, Patrick T. Griffin, Matthew Arnold, Jien Li, Oswaldo A. Martinez, Alexander Behn, Ryan Rogers-Hammond, Suzanne Angeli, Vadim N. Gladyshev, and David A. Sinclair from Harvard Medical School, University of Maine and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) published a new research paper in Aging, titled, “Chemically induced reprogramming to reverse cellular aging.”
The team's findings build upon the discovery that the expression of specific genes, called Yamanaka factors, could convert adult cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This Nobel Prize-winning discovery raised the question of whether it might be possible to reverse cellular aging without causing cells to become too young and turn cancerous.
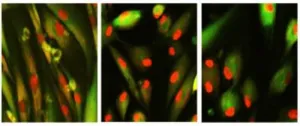
In this new study, the researchers screened for molecules that could, in combination, reverse cellular aging and rejuvenate human cells. They developed high-throughput cell-based assays to distinguish young cells from old and senescent cells, including transcription-based aging clocks and a real-time nucleocytoplasmic protein compartmentalization (NCC) assay. In an exciting discovery, the team has identified six chemical cocktails that restore NCC and genome-wide transcript profiles to youthful states and reverse transcriptomic age in less than a week.
The Harvard researchers previously demonstrated that it is indeed possible to reverse cellular aging without uncontrolled cell growth by virally-introducing specific Yamanaka genes into cells. Studies on the optic nerve, brain tissue, kidney, and muscle have shown promising results, with improved vision and extended lifespan observed in mice and, recently, a report of improved vision in monkeys.
The implications of this new discovery are far-reaching, opening avenues for regenerative medicine and, potentially, whole-body rejuvenation. By developing a chemical alternative to age reversal via gene therapy, this research could revolutionize the treatment of aging, injuries and age-related diseases and offers the potential for lower costs and shorter timelines in development. On the heels of positive results in reversing blindness in monkeys in April 2023, preparations for human clinical trials of the lab’s age reversal gene therapy are in progress.
“Until recently, the best we could do was slow aging. New discoveries suggest we can now reverse it,” said David A. Sinclair, A.O., Ph.D., Professor in the Department of Genetics and co-Director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for Biology of Aging Research at Harvard Medical School and lead scientist on the project. “This process has previously required gene therapy, limiting its widespread use.”
The team at Harvard envisions a future where age-related diseases can be effectively treated, injuries can be repaired more efficiently, and the dream of whole-body rejuvenation becomes a reality. “This new discovery offers the potential to reverse aging with a single pill, with applications ranging from improving eyesight to effectively treating numerous age-related diseases,” Sinclair said.
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204896
Corresponding Author: David A. Sinclair
Corresponding Email: david_sinclair@hms.harvard.edu
Keywords: reprogramming, rejuvenation medicine, information theory of aging, small molecules, epigenetics
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204896
About Aging: Launched in 2009, Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, epigenetic reprogramming, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
The Naval Innovation Center (NIC) at the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) in Monterey, Calif., is part of the Secretary of the Navy’s initiative to leverage the power of American innovation for national security. Integral to the function of the NIC is the Naval Innovation Exchange (NIX), a new program that organizes and empowers multidisciplinary teams of NPS students and faculty focused on developing prototype research solutions.
While in its early stages, the NIC at NPS will leverage and empower ...
At a glance:
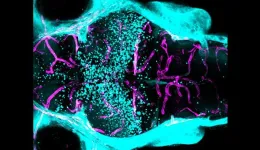
Working with mice and zebrafish, researchers identify a gene, expressed in neurons, that produces a signal needed for development and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier.
When mutated, the gene makes certain regions of the blood-brain barrier more permeable.
The findings could help scientists control the blood-brain barrier — important for delivering drugs into the central nervous system or countering damage from neurodegenerative disease
What makes the vital layer of protective cells around the brain and spinal cord — ...
Psychedelic-based therapies are poised to change the treatments that psychiatrists can offer patients.
“I often talk about psychedelic treatments as catalysts for change, for both the individual and the field of psychiatry,” said Medical University of South Carolina psychiatrist Jennifer Jones, M.D., who conducts research on these treatments.
The highly anticipated approval of MDMA, or “ecstasy,” to treat post-traumatic stress disorder would be the first for a psychedelic drug, ushering in changes for patients, mental health providers and society. The Food and Drug Administration is expected to issue a decision on MDMA-assisted ...
Cancer therapies that target specific genetic abnormalities in tumors have revolutionized treatment possibilities over the past two decades. While quality of life and survival are improved with targeted therapies, relapse is common due to the evolution of new tumor cells that are resistant to the targeted therapy. A new study by investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals how lung tumors may develop drug resistance over time, pointing to a protein, called APOBEC3A, that could be a promising target. Results, published in Nature, may help researchers develop new ...
NEW YORK, NY-- A new study suggests that eye drops developed by Columbia University researchers could be a more effective–and comfortable–therapy for a common eye disease currently treated with injections into the eye.
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO), an eye disease that affects up to 2% of people over age 40, occurs when a vein in the eye’s retina becomes blocked, leading to swelling in the eye, inflammation, damage to the retina, and vision loss.
Standard therapy involves injecting into the eye a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (anti-VEGF) that reduces swelling. ...
Scientists at the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics (UTIG) have developed a radar technique that lets them image hidden features within the upper few feet of ice sheets. The researchers behind the technique said that it can be used to investigate melting glaciers on Earth as well as detect potentially habitable environments on Jupiter’s moon Europa.
The near-surface layers of ice sheets are difficult to study with airborne or satellite ice-penetrating radar because much of what’s scientifically important happens too close to the surface to be accurately imaged. ...
New Haven, Conn. — Simply the smell of seafood can make those with an allergy to it violently ill — and therefore more likely to avoid it. The same avoidance behavior is exhibited by people who develop food poisoning after eating a certain meal.
Scientists have long known that the immune system played a key role in our reactions to allergens and pathogens in the environment, but it was unclear whether it played any role in prompting these types of behaviors towards allergic triggers.
According to Yale-led research published July ...
NEWPORT, Ore. – Rates of Chinook salmon bycatch in the Pacific hake fishery rise during years when ocean temperatures are warmer, a signal that climate change and increased frequency of marine heatwaves could lead to higher bycatch rates, new research indicates.
During years when sea surface temperatures were higher, including during a marine heatwave, Chinook salmon were more likely to overlap with the Pacific hake and raise the risk of bycatch as they sought refuge from higher temperatures.
The findings, based on ...
July 12, 2023
Bacterium Associated With Disease Found in N.C. Chiggers
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL NOON EDT ON WEDNESDAY, JULY 12
A bacterium that causes a disease called scrub typhus – a disease not previously reported in the United States – has been detected in North Carolina, according to a new study by researchers at North Carolina State University and UNC-Greensboro.
The researchers stress that scrub typhus, which can cause fever, headache and body aches – and can be fatal if left untreated by antibiotics – has not yet been ...
Researchers at McLean and Mass General Hospital demonstrated that a transplant surgical procedure (called “needle trauma”) triggers a profound immune response and causes the death of most grafted dopamine neurons
They also found that co-transplantation of neuronal cell therapy with host regulatory T cells resulted in effective suppression of needle trauma and significant improvement in the survival and recovery of grafts
Findings suggest a path for the ‘realistic’ use of cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative disorders
Cell therapy holds promise as a new treatment for Parkinson’s disease but, in many trials to date, most transplanted dopamine ...