(Press-News.org) Laptops and schoolwork on kitchen tables, a deserted playground, face masks on a washing line, an empty church, a walk in the woods.
As the UK Covid inquiry continues for a fifth week, researchers at the University of East Anglia have created a unique snapshot of lockdown life.
When the pandemic first hit, the team embarked on a project to track the physical and mental health of the nation. More than a thousand participants signed up and up and they were followed every day for three months in the first study of its kind.
As well as keeping daily lifestyle diaries about their physical activity, diet and mood, the participants were asked to submit photographs that captured their life in lockdown.
The research team studied these images, and a new paper published today reveals just how much people lost during Covid.
The images illustrate an “unequal pandemic”, the researchers say.
But they also reveal how and why some people fared better than others during lockdowns and beyond.
Lead researcher Prof Caitlin Notley, from UEA’s Norwich Medical School, said: “People around the world had to change their lifestyles very quickly in response to the Covid pandemic.
“We set out to track people’s health and lifestyle behaviours to help answer important questions about the overall impact of the pandemic on health.
“To help us really understand what life was like, we asked our participants to submit photographs that captured their experiences of lockdown.”
Almost 400 photos were submitted, along with short descriptions to accompany them, giving testimony to people’s lived experiences.
Dr Sarah Hanson, from UEA’s School of Health Sciences, said: “A recurrent theme through the images is one of loss – of both freedoms, and lives.
“But the photographs also illustrate people’s starkly different experiences of life in lockdown - it was a very unequal pandemic.
“For those with limited control over their lives and in poorer circumstances the pandemic exacerbated already difficult lives and communities that are struggling to recover.
“The pandemic has been devastating to many people and social groups and our findings show the many unintended social consequences of lockdown.
“It is right that lives return to normality but there are still people shielding, communities have suffered and people are still deeply affected by what happened during those times and the sense of loss by many is profound.
“Those who had more resources and more control over their lives were more easily able to find comfort, find a way to be socially connected and to develop a sense of resilience. It tended to be those who were better off financially, had gardens, had a computer and internet at home, and who were able to work from home, that were able to cope with it better.
“We should also be mindful that even for those who appeared to cope well, the trauma can be covert and issues can emerge as significant psychological issues later on,” she added.
‘Lest we Forget. Illuminating lived experience of the Covid-19 pandemic and lockdown’ is published in the journal Social Science & Medicine.
END
Poignant photo project reveals all we lost in lockdown
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Butterfly species’ big brains adapted giving them a survival edge, study finds
2023-07-13
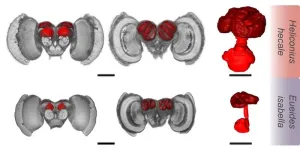
Heliconius butterflies’ brains grew as they adopted a novel foraging behaviour, scientists at the University of Bristol have found.
A region of their brain, known as the mushroom body due to its shape, are two to four times larger than those of their close relatives.
The findings, published today in Nature Communications, suggest that the structure and function of the nervous system are closely linked to an organism's ecological niche and behaviour.
Dr Stephen Montgomery of Bristol’s School of Biological Sciences explained: “Heliconius are the only butterflies known to collect and digest pollen, which gives them an adult source ...
Combination cancer therapies can shrink tumors and improve survival outcomes for patients with advanced non-small lung cancer
2023-07-13
New Haven, Conn. — While pembrolizumab is an approved treatment for patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), only some patients respond to this therapy. Treatment failure, researchers say, is often caused by differences in the tumor microenvironment. An ongoing phase II study (KEYNOTE-495/KeyImPaCT) led by a researcher at Yale Cancer Center reveals that combining pembrolizumab with other treatments reduced the size of target tumors, resulting in a higher response rate for patients with advanced NSCLC.
The new research was published July 10 in Nature Medicine.
“We are excited to share these new ...
NSF CAREER award invests in the future of stable computing
2023-07-12
Every night, uncounted numbers of devices across the globe update their operating systems (OS), and everyday users log on expecting fast, secure connections and services to keep their increasingly online lives moving forward. But as artificial intelligence and other more complex systems come online, the foundation of all them is teetering.
Every aspect of society — from government and industry to education and entertainment — relies on devices with stable operating systems. And every OS relies on ...
Collaborative seed grants nurture high-impact social and environmental research
2023-07-12
The National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration have collectively awarded millions of dollars in grant funding to numerous Virginia Tech researchers who all have one thing in common.
They were awarded Emerging Social Aspects of Global Change seed funding.
Since 2015, this funding has led to faculty from seven colleges and 15 departments collaborating and engaging in 10 research projects that address the social or policy aspects of major global environmental issues.
Sponsored by Fralin Life Sciences Institute’s Global Change Center and the Institute ...
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics
2023-07-12
Imagine you just swallowed a pill containing a miniature camera that will help your doctor collect images to diagnose a condition you’ve been battling for years. No, it’s not something from the latest science fiction or Marvel Comics movie – it’s a technique called bioimaging.
While traditional methods of bioimaging such as an MRI, CT scan, or an X-ray are more commonly known, the use of nanodevices is becoming more popular. They are less invasive and provide health care professionals with a closer look deep inside tissue.
Researchers from Virginia Tech’s College of Engineering and College of Science are using their expertise ...
Virginia Tech awarded $3.4 million grant to study the environmental effects of utility-scale solar installations
2023-07-12
As utility-scale solar farms become more widespread as a source of renewable energy, Virginia Tech scientists are researching environmental consequences with respect to stormwater and the sediment and nutrients transported in runoff.
With a $3.4 million grant from the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality, researchers from the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences will lead a comprehensive six-year study to determine how utility-scale solar farms impact stormwater runoff and local soil and water quality throughout the state.
“Solar is probably going to be the No. 1 land use change that will occur over the next decade in many parts of Virginia, particularly in existing ...
Rare brain tumor responds to targeted tumor treatment with ‘unprecedented’ success
2023-07-12
Papillary craniopharyngiomas (PCPs) are a rare type of brain tumor that cause substantial morbidity for patients. While surgery and radiation are often used to treat PCPs, incomplete removal of the tumor and toxicity from radiation can leave patients with life-long health challenges after treatment, including neuroendocrine dysfunction or vision or memory loss. Investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, led the first multicenter treatment protocol in this rare tumor. The study was based on laboratory discoveries by Mass General Brigham researchers who studied the genetic drivers of PCP growth, ...
Salinity changes threatening marine ecosystems, new UNF study shows
2023-07-12
A groundbreaking study published today reveals the critical yet severely understudied factor of salinity changes in ocean and coastlines caused by climate change. The study was co-authored by an international team of researchers, including Dr. Cliff Ross, University of North Florida biology chair/professor, and Dr. Stacey Trevathan-Tackett, UNF biology graduate program alum and research faculty member at Deakin University in Australia.
Changes in salinity, or salt content, due to climate change and land use can have potentially devastating impacts on vital coastal and estuarine ecosystems, yet this has rarely been studied until now. This new research provides valuable ...
Two UTA professors selected as Fulbright scholars
2023-07-12
Two University of Texas at Arlington faculty members have received Fulbright U.S. Scholar Program awards from the U.S. Department of State and the Fulbright Foreign Scholarship Board.
Kevin Schug, Shimadzu Distinguished Professor of Analytical Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, will travel to Palacky University in Olomouc, Czech Republic, continuing a decades-long relationship that began during his days as a graduate student.
Ling Xu, associate professor in the School of Social Work, will use the award to travel to Taiwan and embark on 10-month project to raise awareness about the ...
Daughters breastfed longer, and women accumulated greater wealth in ancient California matriarchal society
2023-07-12
In a new study, researchers and members of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area are the first to publish evidence of wealth-driven patterns in maternal investment among ancient populations.
Ancestors of the Muwekma Ohlone living 2,000 years ago at Kalawwasa Rummeytak in present-day Silicon Valley in California’s San Francisco Bay Area, placed high value on women’s economic contributions to their communities, according to the study. Women stayed in the villages in which they were born, and their male partners moved from their birth communities to join their wives’ families. Women’s intimate knowledge of the local ecology and female ...