DBST: a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic S-box
2023-07-14
(Press-News.org)
Block ciphers, a branch of modern cryptography, are playing a more prominent role in protecting information security as 5G technology develops. Although encryption algorithms of the traditional Feistel structure have great advantages in terms of consistent encryption and decryption, they have poor diffusion effects. Besides, they cannot adapt to the high throughput communication environment and resource-constrained devices. The S-box is the crucial nonlinear component in the block cipher and significantly determines the security of an algorithm. Unfortunately, the vast proportion of S-boxes exist in a static manner, which makes it difficult to effectively resist cryptographic attacks based on specific S-boxes.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Lang LI published their new research in Frontiers of Computer Science (2023, Vol. 17, Issue 3) co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer·Nature.
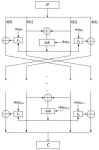
The team proposed a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic s-box named DBST for devices with limited hardware resources and high throughput requirements. The round function of DBST employs a novel generalized Feistel variant structure, which dramatically improves the diffusivity of the traditional Feistel structure. The S-box in the algorithm integrates bit-slice technology with subkeys to create a key-dependent dynamic S-box model that compensates for the shortcomings of static S-boxes.
In the research, they perform security analysis and hardware experiment on DBST. The experimental data demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has high security, high throughput rate and low hardware resources. Furthermore, differential analysis of the S-boxes proves that DBST's S-boxes have fewer differential properties than RECTANGLE's S-boxes.
###
Research Article, Published: 15 June 2023
Liuyan YAN, Lang LI, Ying GUO. DBST: a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic S-box. Front. Comput. Sci., 2023, 17(3): 173805, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-1677-5
About Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)
FCS was launched in 2007. It is published bimonthly both online and in print by HEP and Springer. Prof. Zhi-Hua Zhou from Nanjing University serves as the Editor-in-Chief. It aims to provide a forum for the publication of peer-reviewed papers to promote rapid communication and exchange between computer scientists. FCS covers all major branches of computer science, including: architecture, software, artificial intelligence, theoretical computer science, networks and communication, information systems, multimedia and graphics, information security, interdisciplinary, etc. The readers may be interested in the special columns "Perspective" and "Excellent Young Scholars Forum".
FCS is indexed by SCI(E), EI, DBLP, Scopus, etc. The latest IF is 2.669. FCS solicits the following article types: Review, Research Article, Letter.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-14
CHICAGO --- Aerobic glycolysis, the process by which cells transform glucose into lactate, is key for eye development in mammals, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study published in Nature Communications.
While it has been well known that retinal cells use lactate during cell differentiation, the exact role that this process plays in early eye development was not previously understood.
The findings further the field’s understanding of the metabolic pathways underlying organ development, according to ...
2023-07-14
July 14, 2023 – High rates of smoking among people with HIV are associated with high rates of comorbid health problems – which are associated with characteristics including gender, race/ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, according to a study in the July issue of The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (JANAC). The official journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care, JANAC is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"People with HIV who smoke are at high risk of accompanying physical and mental health conditions," comments lead author Jessica L. Elf, PhD, of Colorado ...
2023-07-14
“[...] in many cases [of chronic sinusitis] only symptom control is achieved.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 14, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on May 27, 2023, entitled, “Think outside the box – atypical infections in chronic sinusitis.”
Inflammations of the paranasal sinuses represent a common clinical picture. The annual prevalence of chronic sinusitis in Europe is up to 10%. Sinusitis can be divided into acute and chronic forms. In particular, the chronic forms (>12 weeks duration) are often challenging in the context of therapy.
Generally, all ventilation disorders of the paranasal sinuses (concha bullosa, ...
2023-07-14
CLEVELAND – A new study from University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health describes the scope and integration of their music therapy program within10 UH medical centers. The study, entitled “Effectiveness of Medical Music Therapy Practice: Integrative Research using the Electronic Health Record (EMMPIRE): Rationale, Design, and Population Characteristics” is the largest such observational study of medical music therapy practice to date. Unlike other music therapy programs, which may be limited to specific hospital units, the program at UH Connor ...
2023-07-14
A team of scientists led by researchers from the University of Leicester have discovered that the genes required for learning, memory, aggression and other complex behaviours originated around 650 million years ago.
The findings led by Dr Roberto Feuda, from the Neurogenetic group in the Department of Genetics and Genome Biology and other colleagues from the University of Leicester and the University of Fribourg (Switzerland), have now been published in Nature Communications.
Dr Feuda said: “We’ve known for a long ...
2023-07-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Monitoring dairy calves with precision technologies based on the “internet of things,” or IoT, leads to the earlier diagnosis of calf-killing bovine respiratory disease, according to a new study. The novel approach — a result of crosscutting collaboration by a team of researchers from Penn State, University of Kentucky and University of Vermont —will offer dairy producers an opportunity to improve the economies of their farms, according to researchers.
This ...
2023-07-14
An estimated 1,200 Americans, on average, are diagnosed with Lyme disease each day. Some of those patients continue to experience negative effects, even after treatment.
Lyme disease researcher Brandon Jutras, associate professor in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences and affiliated faculty of the Fralin Life Sciences Institute, recently received a $2.7 million grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health, to study what causes the disease to linger long after treatment.
“Using a series of sophisticated molecular techniques, in combination with both bacterial and host genetics, we’re working ...
2023-07-14
(Boston)—Noyan Gokce, MD, professor of medicine at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been awarded a $453,750 National Institutes of Health (NIH) R-21 grant for his research study “Impact of Per/Polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS) pollutants on vascular disease mechanisms.” This work will be performed in collaboration with co-investigator Jennifer Schlezinger, PhD from the Boston University School of Public Health.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are manmade chemicals that are extensively used in industrial and consumer products such as stain- and ...
2023-07-14
Professor Matt Rosseinsky, from the University’s Department of Chemistry and Materials Innovation Factory, has won the 2023 Eni Energy Frontiers Award for the digital design and discovery of next-generation energy materials.
A globally-prestigious prize for research in the fields of energy and environment, previous Eni Award winners include Nobel laureates such as Harold W. Kroto and Alan Heeger.
Professor Rosseinsky’s research is pushing new boundaries in how new energy materials are designed and discovered through the use of digital tools.
For the past 50 years, the scientific approach ...
2023-07-14
A study led by a Florida State University researcher that was published in Nature Human Behavior shows how colonization has contributed to the distribution of plants specimens stored in herbaria collections around the world.
Plant diversity in nature is generally highest in tropical regions around the equator, with decreasing diversity closer to the poles. FSU Department of Geography Assistant Professor Xiao Feng and Purdue University Assistant Professor Daniel Park showed that the plant specimens housed in herbaria in Europe and North America are more comprehensive and diverse than the collections housed in the countries ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DBST: a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic S-box