(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (July 18, 2023) – Rice University bioengineer Gang Bao and his team have won a 4-year, $2.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to address critical questions surrounding the safety and efficacy of using gene editing to treat sickle cell disease.
Because it is caused by a mutation in a single gene, sickle cell disease is a prime candidate for gene editing treatments using tools such as CRISPR-Cas9.
“Sickle cell disease affects over five million people worldwide, and life expectancy ranges from approximately five years in low-resource settings to 40-45 in countries like the U.S.,” Bao said.
Previously, the Bao lab has found that CRISPR-Cas9 does not work as expected, resulting in unintended large deletions and insertions at the Cas9 cut site. He and his team will now direct their efforts to figuring out why these gene modifications occur, what their biological consequences are and what can be done to fix the issue.
“We want to understand the mechanisms that cause these large gene modifications,” Bao said. “For many years, we believed that a CRISPR-Cas9-induced DNA double-strand break only results in small deletions or insertions of less than 50 nucleotides. But we found that these modifications are in fact much larger ⎯ ranging from about 200 to several thousand nucleotides.”
A Cas9 enzyme relies on a CRISPR guide RNA to target the site in the genome where it performs its cut.
“We tested three guide RNA molecules designed to treat sickle cell disease and found that they all had large deletions and insertions at the Cas9 cut-sites in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from patients with sickle cell disease,” Bao said. “We also tested a guide RNA designed for editing T cells for immunotherapy, and we found the same thing happens in that context.”
The discovery that CRISPR-Cas9 generates large, unintended gene modifications prompts the question of how these changes affect messenger RNA and proteins, where messenger RNA is a molecule that helps translate the genetic information encoded in genes into proteins which, in turn, are made up of subunits known as domains.
“Now we have a good picture of what happens in terms of the DNA,” Bao said. “Next, we want to understand what happens at the level of messenger RNA and proteins. Does a large DNA deletion lead to disruption of the gene or to a large deletion in the messenger RNA that will in turn produce an incomplete protein? Alternatively, does a large DNA insertion get translated by messenger RNA into a protein with an extra domain?”
Researchers will study how the changes to gene expression and/or protein structure affect stem cell differentiation and function.
“We believe some of the large deletions actually could be beneficial,” Bao said. “Some of these larger deletions could, for instance, induce the expression of fetal hemoglobin, which would help cure sickle cell disease. But we need to do more work to figure out which large deletions might achieve this and how to utilize them for curing sickle cell disease.
“We need to understand the major biological consequences of having these unintended large gene modifications and then figure out how to best address this problem.”
So-Hyun (Julie) Park, a Rice doctoral alum and assistant research professor of bioengineering, made a significant contribution to obtaining the NIH grant. Dr. Cecile Karsenty, clinical fellow in the Department of Pediatrics at the Baylor College of Medicine and at Texas Children’s Hospital, and bioengineering doctoral students Mingming Cao and ByoungYong Yoo generated some of the data for the grant proposal.
Bao is the department chair and Foyt Family Professor of Bioengineering, a professor of chemistry, materials science and nanoengineering, and mechanical engineering, and a CPRIT Scholar in Cancer Research.
-30-
This release can be found online at news.rice.edu.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Image Downloads:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/JF6_6267.jpg
CAPTION: So-Hyun (Julie) Park (from left), Mingming Cao, Gang Bao, Cecile Karsenty and ByoungYong Yoo. (Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/JF6_6235.jpg
CAPTION: Cecile Karsenty (from left), Gang Bao, ByoungYong Yoo and So-Hyun (Julie) Park. (Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/JF6_6221.jpg
CAPTION: Gang Bao is department chair and Foyt Family Professor of Bioengineering, a professor of chemistry, materials science and nanoengineering, and mechanical engineering, and a CPRIT Scholar in Cancer Research. (Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
Related stories:
Even good gene edits can go bad:
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/even-good-gene-edits-can-go-bad
New genetic weapons challenge sickle cell disease:
https://news2.rice.edu/2019/06/03/new-genetic-weapons-challenge-sickle-cell-disease-2/
Links:
Bao Lab: http://bao.rice.edu
Rice Department of Bioengineering: https://bioengineering.rice.edu
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 4,552 undergraduates and 3,998 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
END
Despite having worse stroke symptoms and living within comparable distances to comprehensive stroke centers, women with large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke are less likely to be routed to the centers compared to men, according to a new study from UTHealth Houston.
Led by corresponding author Sunil Sheth, MD, associate professor of neurology and director of the vascular neurology program with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and senior author Youngran Kim, PhD, assistant professor of management, policy, and community health with UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, the study was published today in the Journal of the American ...
IOP Publishing’s (IOPP) new environmental research journals are now open for submissions. Announced earlier this year, the two new open access (OA) journals: Environmental Research: Energy and Environmental Research: Food Systems are the latest additions to IOPP’s expanding Environmental Research Series which now includes eight open access titles.
IOPP’s Environmental Research series builds on the established reputation of the journal Environmental Research Letters (ERL) and shares the same outstanding levels of author service, inclusive editorial policies, strict quality assurance and has open science principles at its core.
IOP ...
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – July 18, 2023 –Research from Sanford Burnham Prebys and the Osaka International Cancer Institute has shed new light on the anti-cancer properties of mannose, a sugar that is crucial to many physiological processes in humans and is also known to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. The findings, published in the journal eLife, suggest that mannose could be a helpful secondary treatment for cancer.
“This sugar could give cancer an extra punch alongside other treatments,” says study co-author Hudson Freeze, Ph.D., director of the Human Genetics ...
Brushing twice a day keeps the dentist away – but can we improve on the toothpaste we use to maintain clean teeth, preventing medical issues that spiral from poor dental health? Most toothpastes use fluoride, a powerful tool for oral hygiene. However, fluoride can pose health problems in some cases, especially for children who consume too much fluoride by swallowing most of their toothpaste: children normally use only a tiny dose of toothpaste to avoid these problems, but that reduces toothbrushing efficacy. In the search for alternatives, a team of international scientists and Polish clinicians have identified a hydroxyapatite toothpaste that works just as well as fluoride toothpaste ...
The Horizon 2020 BiCIKL Project is proud to announce that the Biodiversity Knowledge Hub (BKH) is now online.
BKH is a one-stop portal that allows users to access FAIR and interlinked biodiversity data and services in a few clicks. BKH was designed to support a new emerging community of users over time and across the entire biodiversity research cycle providing its services to anybody, anywhere and anytime.
“The Knowledge Hub is the main product from our BiCIKL consortium, and we are delighted with the result! BKH can easily be seen as the beginning of the major shift in the way we search interlinked biodiversity information,”
says Prof. Lyubomir ...
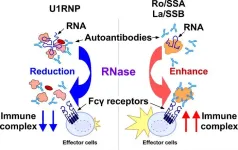
Osaka, Japan – Systemic autoimmune diseases are characterized by inflammation of multiple organs and can have devastating consequences for patients. There is a dire need for treatments against these diseases. RNase treatments seem promising in some clinical trials but not all. Researchers from Japan have uncovered the reasons for this variability.
In a study recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight (JCI Insight), researchers from Osaka University have provided new insights into the opposite effects of RNase ...
Researchers from the Center of Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems within the Institute for Basic Science (PCS-IBS) made an important discovery that describes the relationship between synchronization and thermodynamics in quantum systems.
The question of how order arises from disorder has captivated humanity for centuries. One fascinating example of such emergence is synchronization, where multiple oscillators initialized randomly could end up oscillating in harmony. Synchronization exists in our everyday lives, e.g. the sound of clapping hands or the simultaneous flashing of fireflies. Remarkably, scientists have discovered ...
The study is led by Prof. Chilai Chen (Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences).
The detection of dissolved gases in the deep sea is of great significance in exploring the origin and early evolution of life, understanding the interaction between the Earth's spheres, studying the geological profile of the Earth, searching for underwater oil, gas, and mineral resources, and researching global climate change. Changes in the concentrations of dissolved oxygen and nitrogen can indirectly or directly reflect the activity patterns ...
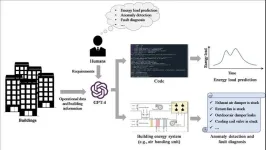
The building sector is a significant contributor to global energy consumption, accounting for approximately 33% of the world's final energy usage. Recently, data mining technologies have showed powerful capacities for revealing energy waste and providing energy-saving tips to building owners. These technologies have the ability to save approximately 15%-30% of the energy consumed in buildings. However, the practical application of data mining technologies has been limited due to its labor-intensive nature, resulting in a scarcity of real-world use cases.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Energy and Built Environment, ...
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – July 17, 2023 – By identifying genes in patients and testing their effects in fruit flies, researchers from Sanford Burnham Prebys have found new genes that contribute to hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), a rare, life-threatening heart disease that occurs in infants. The findings, published in the journal eLife, bring scientists one step closer to unraveling the biology of this complex disease.
“Every case of HLHS is unique because there are many different things that can go wrong during the early development of the heart,” ...