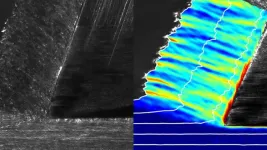
(Press-News.org) Scientists have combined two light wavelengths to deactivate a bacterium that is invulnerable to some of the world’s most widely used antibiotics, giving hope that the regime could be adapted as a potential disinfectant treatment.
Under the guidance of project leader Dr Gale Brightwell, scientists at New Zealand’s AgResearch demonstrated the novel antimicrobial efficiency of a combination of two light wavelengths against a ‘superbug’ known as antibiotic-resistant extended-spectrum beta-lactamase E. coli.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major global threat of increasing concern to human and animal health, with 10M deaths due to AMR forecast to occur every year after 2050. There is now a critical need to develop safe and effective antimicrobial technologies that do not result in new and emerging resistance, corresponding author Amanda Gardner explained.
A combination of far UVC (222 nm) and blue Led (405 nm) light have been shown to be effective in the inactivation of a wide range of microorganisms while being much safer to use and handle as compared to traditional UVC at 254 nm, she said.
“The E. coli we chose for this investigation were extended-spectrum beta- lactamases producing E. coli (ESBL-Ec) as these bacteria produce enzymes that break down and destroy commonly used antibiotics, including penicillins and cephalosporins, making these drugs ineffective for treating infections,” she said.
“This intrinsic resistance means that there are fewer antibiotic options available to treat ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae infections. In many cases, even common infections such as urinary tract infections require more complex treatments. Instead of taking oral antibiotics at home, patients with these infections might require hospitalisation and intravenous (IV) carbapenem antibiotics.
“The coupling of far-UVC and blue Led light together increases the effectiveness of the two individual lights through the deployment of different mechanisms of microorganism inactivation. There is great potential for these two light wavelengths to be used together in many applications where safety to the end user is of most importance,” she said.
The team found that a combination of dual far-UVC and blue Led light could be used to disinfect both antibiotic resistant and antibiotic sensitive E. coli, offering a non-thermal technology that may not drive further antibiotic resistance.
However, if exposed to sub-lethal levels of dual and far-UVC light, the antibiotic resistant E. coli tested did exhibit light tolerance. One surprising finding was that this light tolerance was only exhibited by the antibiotic resistant E. coli and not the antibiotic sensitive E. coli that was also tested.
Gardner says further work is needed to understand whether the light tolerance is due to a genetic change, or some other mechanism.
“It is also important to investigate the development of light tolerance in other antimicrobial-resistant bacteria and to determine the minimum dose of far-UVC light that can create light tolerance as well as the potential of further resistance development to other things such as sanitizers, heat, and pH in bacteria for application purposes,” she said.
The study was reported in the paper ‘Light Tolerance of Extended Spectrum β-lactamase Producing Escherichia coli Strains After Repetitive Exposure to Far-UVC and Blue LED Light’, which is publishedn by the Journal of Applied Microbiology, an Applied Microbiology International publication.
To find out more about AMI’s journals, visit HERE.
Notes to editors
Applied Microbiology International (AMI) is the oldest microbiology society in the UK and with more than half of its membership outside the UK, is truly global, serving microbiologists based in universities, private industry and research institutes around the world.AMI provides funding to encourage research and broad participation at its events and to ensure diverse voices are around the table working together to solve the sustainability development goals it has chosen to support.
AMI publishes leading industry magazine, The Microbiologist, and in partnership with Wiley and Oxford University Press, publishes six internationally acclaimed journals. It gives a voice to applied microbiologists around the world, amplifying their collective influence and informing international, evidence-based, decision making.
Oxford University Press (OUP) is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. OUP is the world's largest university press with the widest global presence.
OUP publishes more than 500 academic and research journals covering a broad range of subject areas, two-thirds of which are published in collaboration with learned societies and other international organizations. It has been publishing journals for more than a century and, as the world’s largest university press, has more than 500 years of publishing expertise. END
Dual wavelengths of light effective against antibiotic-resistant bacterium
Scientists have combined two light wavelengths to deactivate a bacterium that is invulnerable to some of the world’s most widely used antibiotics, giving hope that the regime could be adapted as a potential disinfectant treatment.
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Learning from superheroes and AI: UW researchers study how a chatbot can teach kids supportive self-talk
2023-07-19
At first, some parents were wary: An audio chatbot was supposed to teach their kids to speak positively to themselves through lessons about a superhero named Zip. In a world of Siri and Alexa, many people are skeptical that the makers of such technologies are putting children’s welfare first.
Researchers at the University of Washington created a new web app aimed to help children develop skills like self-awareness and emotional management. In Self-Talk with Superhero Zip, a chatbot guided pairs of siblings ...
Consortium explores energy-efficient electronics and photonics
2023-07-19
The University of Texas at Arlington is part of a new consortium funded by the Department of Energy that involves the development of new technologies and college courses covering everything from radiation detection to nuclear engineering.
The grant also will help UTA develop 2D materials that can be integrated into new hand-held photonic technologies with multiple uses.
Electrical Engineering Professor Weidong Zhou and Associate Professor Alice Sun will use the five-year, $1.8 million grant to work with collaborators at UT Arlington, University of North Texas, University of Arkansas Pine Bluff, ...
Staying sharp: Researchers turn to an everyday shop tool to study how materials behave
2023-07-19
Researchers at Texas A&M University are taking a traditional manufacturing tool — metal cutting — and developing a more accessible method for understanding the behavior of metals under extreme conditions.
Metal cutting – scraping a thin layer of material from a metal’s surface using a sharp knife (not unlike how we scrape butter) – might not be the first thing that comes to mind for studying material properties. However, Drs. Dinakar Sagapuram and Hrayer Aprahamian, assistant professors ...
Bipolar disorder linked to 6-fold heightened risk of early death from external causes
2023-07-19
People with bipolar disorder—characterised by extreme mood swings—are 6 times more likely to die before their time from external causes, such as accidents, violence, and suicide, than those without the condition, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
And they are twice as likely to die from somatic (physical) causes, with alcohol a major contributing factor, the findings show.
A heightened risk of an early death from any cause has been consistently reported in those with ...
Tripling in proportion of smokers’ duty free tobacco purchases in England since 2019
2023-07-19
The proportion of smokers’ duty free tobacco purchases in England has tripled since 2019, rising from just over 5% to just over 16%, but there’s been no reported change in black market purchases, reveals a time-trends analysis published online in the journal Tobacco Control.
Between 2002 and 2014, between 12% and 20% of UK adult smokers said their last tobacco purchase had been from a low or untaxed source. And smokers who buy their tobacco from low/untaxed sources—and those who switch to cheaper products—are less likely to try to quit smoking than those ...
Explore psilocybin and other psychedelics for women’s cancer distress, urge doctors
2023-07-19
It’s time to stop prevaricating and explore the use of psilocybin—the active ingredient in ‘magic mushrooms’—and other psychedelics to ease the often overwhelming distress faced by women with late stage gynaecological cancers, urge doctors in a commentary published online in the International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.
Conventional ‘gold standard’ psychotherapeutic approaches, such as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), take too long to change old habits and require too much stamina, suggest the authors from the University of Texas ...
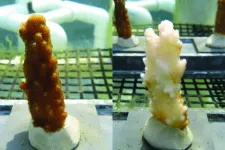
Some corals may survive climate change without paying a metabolic price
2023-07-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — If, as the saying goes, ‘nothing in life is free,’ then corals might pay a price for being resilient to climate change. Indeed, the prevailing belief among scientists has been that corals must suffer reduced growth or other tradeoffs when they partner with symbiotic algae that help them tolerate warmer water. Yet, new research led by Penn State demonstrates that certain corals can have their cake and eat it too, and as a result, these coral-symbiont partnerships may come to dominate ...
Study shows differences in how patients with heroin use disorder process drug and reward cues
2023-07-18
An Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai study sheds new light on some of the underlying neurobiological mechanisms of opioid addiction, which accounted for three-quarters of the more than 100,000 fatal drug overdoses in the United States in 2021.
The Mount Sinai researchers found that inpatients with heroin use disorder exhibited a bias in favor of processing drug cues over cues related to natural, non-drug rewards, as observed during passive viewing of the cues and when the patients were asked to try two emotional regulation strategies. Results of the study were published in the July 12 issue of the American Journal ...
How to track animal of legend? Look to the poop
2023-07-18
How do you study a predator with both camouflage and stealth that make it virtually invisible in the forest?
Even jaguars poop.
A team of researchers led by the University of Cincinnati applied genetic and isotopic analyses to jaguar scat to investigate the habitat needs of the big cats in the Mountain Pine Ridge Forest Preserve of Belize in Central America. The study demonstrates a novel and noninvasive technique for identifying the landscape use and conservation needs of elusive wildlife.
Researchers used scat-detecting dogs named Billy and Bruiser to find telltale evidence left behind by jaguars ...
Researchers identify new method to reverse effects of fentanyl
2023-07-18
According to the Centers for Disease Control, 100,000 Americans die each year from an overdose, most due to the use of synthetic opiates like fentanyl. While naloxone, currently the only an antidote for opiate overdose, has become more common, it is less effective against fentanyl-class synthetic opioids.
Researchers at Indiana University have identified a new method of reversing the effects of fentanyl, which is 50 to 100 times stronger than morphine. Their study, published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, could lead to a new way to reverse overdoses either through a new product or working synchronously with naloxone.
"The synthetic opiates bind very ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Dual wavelengths of light effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteriumScientists have combined two light wavelengths to deactivate a bacterium that is invulnerable to some of the world’s most widely used antibiotics, giving hope that the regime could be adapted as a potential disinfectant treatment.