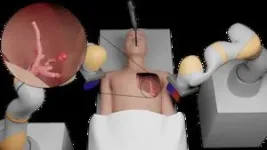
(Press-News.org) The ultra-soft tentacle, which measures just 2 millimetres in diameter and is controlled by magnets, can reach some of the smallest bronchial tubes and could transform the treatment of lung cancer.
It paves the way for a more accurate, tailored, and far less invasive approach to treatment and has been developed by engineers, scientists and clinicians based at the STORM Lab in Leeds.
The researchers tested the magnetic tentacle robot on the lungs of a cadaver and found that it can travel 37% deeper than the standard equipment and leads to less tissue damage.
The results of their investigations, which were funded by the European Research Council, are published today in Nature Engineering Communications.
Professor Pietro Valdastri, Director of the STORM Lab and research supervisor, said: “This is a really exciting development.
“This new approach has the advantage of being specific to the anatomy, softer than the anatomy and fully-shape controllable via magnetics. These three main features have the potential to revolutionize navigation inside the body.”
Lung cancer has the highest worldwide cancer mortality rate. In early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, which accounts for around 84% of cases, surgical intervention is the standard of care. However, this is typically highly invasive and leads to the significant removal of tissue. This approach is not suitable for all patients and can have an impact on lung function.
Lung cancer screening programmes have led to better survival rates but have also highlighted the urgent need to find non-invasive ways to diagnose and treat patients early.
As well as improving navigation within the lungs during biopsies, the magnetic tentacle robot could pave the way for far less invasive treatment, allowing clinicians to target only malicious cells while allowing healthy tissue and organs to continue normal function.
The report’s co-author, Dr Giovanni Pittiglio, who carried out the research while conducting his PHD at the University of Leeds’s School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, added: “Our goal was, and is, to bring curative aid with minimal pain for the patient.
“Remote magnetic actuation enabled us to do this using ultra-soft tentacles which can reach deeper, while shaping to the anatomy and reducing trauma.”
The team will now set about collecting all the data that will allow them to start human trials
How magnetic tentacle robots can work together
Researchers at the STORM Lab have also been investigating ways of controlling two independent magnetic robots so that they can work together in a confined area of the human anatomy, allowing one to move a camera and the other to control a laser to remove tumours.
The devices are made of silicone to minimise tissue damage and are steered by magnets mounted on robotic arms outside the patient’s body.
Using a replica of a skull, the team successfully trialled the use of two robots to carry out endonasal brain surgery, a technique which allows a surgeon to go through the nose to operate on areas at the front of the brain and the top of the spine.
The researchers needed the magnetic robots to move independently of each other so that one could move the camera, while the other could direct a laser onto a tumour.
Normally, two magnets placed closely together would attract each other, creating a challenge for the researchers. They overcame it by designing the bodies of the tentacles in a way that they can bend only in specific directions and by relocating the north and south poles in each magnetic robot tentacle.
They were then able to simulate the removal of a benign tumour on the pituitary gland at the base of the cranium, proving for the first time ever that it is possible to control two of the robots in one confined area of the body.
The findings of their research, which was jointly funded by the European Research Council and the Physical Sciences Research Council, is published today in Advanced Intelligent Systems.
The paper’s lead author, Zaneta Koszowska, a researcher in the University of Leeds School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, said: “This is a significant contribution to the field of magnetically controlled robotics.
“Our findings show that diagnostic procedures with a camera, as well as full surgical procedures, can be performed in small anatomical spaces.”
END
Tiny surgical robots could transform detection and treatment of cancers
A tiny robot which can travel deep into the lungs to detect and treat the first signs of cancer has been developed by researchers at the University of Leeds
2023-07-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fusion model hot off the wall
2023-07-27
Kyoto, Japan -- Humans may never be able to tame the Sun, but hydrogen plasma -- making up most of the Sun's interior -- can be confined in a magnetic field as part of fusion power generation: with a caveat.
The extremely high temperature plasmas, typically as high as 100 million degrees Celsius, confined in the tokamaks -- donut-shaped fusion reactors -- cause damage to the containment walls of these mega devices. Researchers inject hydrogen and inert gases near the device wall to cool the plasma by radiation and recombination, ...
Stockholm University leads Bio-LUSH for development of new sustainable bio-based fibers for a circular bioeconomy
2023-07-27
Bio-LUSH, a Horizon Europe project led by Stockholm University, extracts high-quality fibers from diverse plants, maximizing resource utilization for sustainable bio-based innovation. Supported by the EU-call Circular Bio-based Europe Joint Undertaking (CBE JU), the research project establishes a value chain for sustainable products such as textiles, food packaging and reinforced composites ready for the consumer market, thus driving plant-based solutions for a circular bioeconomy.
The four-year Bio-LUSH project, launched in May 2023, supports the establishment of a ...
Low fiber intake during pregnancy may delay development in infants’ brains
2023-07-27
Undernutrition during pregnancy is one of the factors linked to an increased risk of diseases in children as they grow older. Yet, maternal malnutrition remains a problem for women worldwide.
Animal studies have shown that a low-fiber diet during pregnancy impairs brain nerve function in offspring. Now, in the first human cohort study on the relation of maternal nutritional imbalance and infants’ brain development, researchers in Japan have investigated if the same effects can be found in humans.
“Most pregnant women in Japan consume far less dietary ...
Cannabis poisonings rise after legalization, new review concludes
2023-07-27
A new meta-analysis (an analysis of past research) published by the scientific journal Addiction has found that cannabis legalisation is associated with increased rates of cannabis poisoning. The risk of cannabis poisoning was higher among studies that focused on children.
Cannabis poisoning occurs when too much cannabis is consumed at one time. The effects of cannabis poisoning include lethargy, drowsiness, dizziness, hypertension, palpitations, tachycardia (elevated heart rate), nausea, vomiting, irritability, agitation, coma, and slowing of the central nervous system. Cannabis use in children ...
New On Our Sleeves® survey highlights top stressors as students prepare to head back to school
2023-07-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio (July 27, 2023) — Preparing to head back to school can be a time of many emotions, from excitement to nerves. But for children who found the previous school year to be challenging, it can be an especially stressful experience.
In a new national survey conducted online by The Harris Poll on behalf of The On Our Sleeves Movement for Children’s Mental Health, 71% of American parents say their children experienced challenges last school year.
The top factors identified by parents included safety concerns (37%), academic challenges (26%), bullying (24%), ongoing social challenges ...
New research method determines health impacts of heat and air quality
2023-07-27
The planet experienced the hottest day on record earlier this month and climate projections estimate the intensity of heat waves and poor air quality will increase and continue to cause severe impacts. Researchers from the University of Waterloo and Toronto Metropolitan University have refined and expanded a method of data collection to assess their health impacts.
They discovered that even moderate temperature increases, for example night-time temperatures starting at 18.4 degrees Celsius, can lead to increased hospital ...
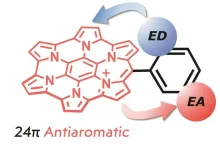
A demonstration of substituent effects in anti-aromatic compounds
2023-07-27
Circularly conjugated compounds with 4n+2 pi-electrons are known as aromatic compounds. They are generally stable and are therefore found in our surroundings. On the other hand, anti-aromatic compounds with 4n pi-electrons have been conventionally considered unstable, and the creation of stable anti-aromatic compounds has been one of the challenging issues in organic chemistry. Several studies on the synthesis, isolation, and characterization of stable and clearly anti-aromatic compounds have been reported in recent years. In general, anti-aromatic compounds are considered to be more susceptible to substituents than aromatic compounds because of their narrower HOMO-LUMO gap. However, ...
Older women at risk for Alzheimer’s disease may benefit from yoga
2023-07-27
Kundalini yoga, a form of yoga that focuses on breathing, meditation, and mental visualization, appeared beneficial for older women who had risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and concerns about episodes of memory decline, according to a UCLA Health study.
Researchers at UCLA Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior, using a type of MRI that measures activity in regions and subregions of the brain, found that Kundalini yoga, which combines movement and meditation and focuses on breathing, mantra recitation and mental visualization, increased connectivity in an area of the brain that can be impacted by stress and ...
Cigarette smokers more at risk for tobacco dependence than users of smokeless tobacco or multiple tobacco products
2023-07-27
New York, NY (July 27, 2023) – Cigarette smokers have higher odds of tobacco dependence than those who vape or use a variety of types of tobacco products, according to a Mount Sinai study published in July in Nicotine & Tobacco Research.
The findings suggest that tailored tobacco cessation programs are needed for people with different tobacco use habits. The researchers identified three clear types of tobacco users: those who predominantly smoke cigarettes, those who predominantly use smokeless tobacco, and those who predominantly use a combination of cigarettes, e-cigarettes, and cigars.
This discovery is important for tailoring tobacco use reduction ...
Identification of genetic drivers for esophageal cancer creates new opportunity for screening, treatment
2023-07-27
Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) is a highly lethal cancer, with a five-year survival rate of less than 20 percent. Although a precursor lesion to EAC, called Barrett's esophagus (BE), is present in roughly seven percent of middle-aged adults, less than one percent of BE patients will progress to EAC, making it difficult to determine which individuals are at risk of developing this deadly cancer. To better understand why only a small fraction of individuals with BE develop EAC, investigators from the Mass ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Tiny surgical robots could transform detection and treatment of cancersA tiny robot which can travel deep into the lungs to detect and treat the first signs of cancer has been developed by researchers at the University of Leeds