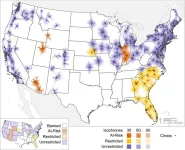
(Press-News.org) DALLAS, August 2, 2023 — The American Heart Association, a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives, has recognized 2,671 health care and emergency response organizations — nearly 145 more than in 2022 — for their commitment to improving health outcomes for cardiovascular patients through evidence-based efficient and coordinated care.
The American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines® and Mission: Lifeline® are hospital-based quality improvement recognition programs that use the latest evidence-based scientific guidelines to save lives and hasten health care recovery times. Through these programs, the American Heart Association recognizes participating hospitals, clinics and emergency medical services systems for demonstrating their dedication to improving quality care and reducing barriers to prompt treatment, ultimately leading to more lives saved, shorter recovery times and fewer returns to the hospital.
Get With The Guidelines and Mission: Lifeline award categories cover treatment for stroke, high cholesterol, cardiac arrest, heart failure, ST-elevation myocardial infarction heart attack, Type 2 diabetes and atrial fibrillation. Award levels range from gold plus to bronze status depending on the number of requirements met for each designation.
“Patients experiencing cardiovascular events depend on efficient, coordinated care to survive,” said Joseph Wu, M.D., PhD, FAHA, volunteer president of the American Heart Association, director of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute and Simon H. Stertzer, MD, Professor of Medicine and Radiology at Stanford University. “The American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines® and Mission: Lifeline® programs help hospitals follow the latest, research-based standards to ensure each of their patients has the best chance of survival and the highest quality of life possible.”
For the fourth year, award recipients include health care systems from all 50 states and Washington, D.C., Guam and Puerto Rico. Approximately 13,000 quality improvement awards were earned this year, with many organizations earning more than one award.*
“For more than 20 years, the American Heart Association had championed quality improvement in health and health care, and these awardees put in the work to ensure equitable, quality care in communities across the nation,” Wu said. “Thousands of health care organizations see the value these programs bring and how the American Heart Association supports their commitment to quality health care.”
Every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke or heart attack, and heart disease and stroke are the No. 1 and No. 5 causes of death in the United States, respectively, according to the American Heart Association 2022 Statistical Update. Studies show patients can recover better when providers consistently follow treatment guidelines.
Visit U.S. News & World Report to view the full list of recipients by state and award. Learn more about Get With The Guidelines or Mission: Lifeline at www.heart.org/quality.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of the release link.
Spanish news release will be added as available.
Get With The Guidelines website
Mission: Lifeline website
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
About Mission: Lifeline
The American Heart Association’s Mission: Lifeline program helps hospitals and emergency medical services develop systems of care that follow proven standards and procedures for STEMI patients. The program works by mobilizing teams across the continuum of care to implement American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Foundation clinical treatment guidelines. For more information, visit heart.org.
About Get With The Guidelines
Get With The Guidelines® is the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s hospital-based quality improvement program that provides hospitals with the latest research-based guidelines. Developed with the goal of saving lives and hastening recovery, Get With The Guidelines has touched the lives of more than 12 million patients since 2001. For more information, visit heart.org.
END
More than 2,600 health care organizations recognized for commitment to high-quality cardiovascular care
The American Heart Association honors hospitals, clinics and EMS systems in all 50 states and Washington, D.C.
2023-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stalking a silent killer
2023-08-02
With a survival rate in the single digits, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is highly lethal. In fact, by the time PDAC is clinically diagnosed, it is already considered incurable via surgery or other means in up to 90% of patients.
Yangzom D. Bhutia, D.V.M., Ph.D., from the Department of Cell Biology and Biochemistry at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine, has for years focused her research on PDAC. To bolster her efforts, the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health recently awarded Bhutia a five-year, $1.76 million grant (“SLC6A14 as a unique ...
Many people feel their jobs are pointless
2023-08-02
A sociological study by the University of Zurich confirms that a considerable proportion of employees perceive their work as socially useless. Employees in financial, sales and management occupations are more likely to conclude that their jobs are of little use to society.
In recent years, research showed that many professionals consider their work to be socially useless. Various explanations have been proposed for the phenomenon. The much-discussed “bullshit jobs theory” by the American anthropologist David Graeber, for example, states that some jobs are objectively useless and that this occurs more frequently ...
Abortion facility access means long drives for 41.8% of women
2023-08-02
SPOKANE, Wash. – One year after the Dobbs decision, 41.8% of U.S. women of reproductive age have to drive 30 minutes or more to reach an abortion care facility, according to a study of data as of June 2, 2023. Researchers predicted that number would rise to 53.5% if other state bills under consideration are passed.
The study estimated longer drives as well, finding that 29.3% of women didn’t have access to a facility within a 60-minute drive and 23.6% lacked access even within a 90-minute drive. Those figures would jump to 45.6% ...
Unhappy family or trauma in youth leads to poor health in old age
2023-08-02
Adverse childhood experiences have impacts deep into old age, especially for those who experienced violence, and include both physical and cognitive impairments.
It’s known that a difficult childhood can lead to a host of health issues as a young or midlife adult, but now, for the first time, researchers at UC San Franciso have linked adverse experiences early in life to lifelong health consequences.
They found that older U.S. adults with a history of stressful or traumatic experiences as children were more likely to experience both physical and cognitive impairments in their senior years. Stressful childhood experiences could include exposure to ...
Extroverts more likely to resist vaccines, study shows
2023-08-02
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 2, 2023) – Which types of personalities were more hesitant about COVID-19 vaccination during the pandemic’s peak? Extroverts — according to a new study on more than 40,000 Canadians.
“We expected that people who were especially high in extroversion would be more likely to get the vaccine,” said Melissa Baker, Ph.D., lead author and assistant professor at The University of Texas at El Paso. “We figured those people would want to get back out in the world and socialize, right? It’s actually the opposite.”
The findings, ...
UTokyo researchers imagine future see-through objects
2023-08-02
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science(IIS), The University of Tokyo, conducts a wide range of research, including physics, chemistry and biology. In this context, DLX Design Lab carries out activities aimed at fusing science, technology, and design. One of these activities is the Treasure Hunting Project, which aims to inform the general public about the value and potential of scientific research. As part of this project, in 2022-2023, DLX Design Lab produced a video introducing future ...
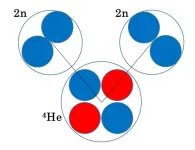
Correlation between neutron pairs observed in helium-8 nuclei
2023-08-02
Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons such as protons and neutrons, which are bound together by nuclear force or strong interaction. This force allows protons and neutrons to form bound states; however, when only two neutrons are involved, the attractive force is slightly insufficient to create such a state. This prompts the question: would four neutrons be adequate? This question has captivated atom physicists, who have actively sought to unlock this mystery in both the theoretical and experimental realms.
With ...
Training on LSA lifeboat operation using Mixed Reality
2023-08-02
Research Background
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has identified the human element as one of the key attributes for the safety of life at sea and a contributing factor to most of the casualties in the shipping sector. The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty which requires signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with minimum safety standards in construction, equipment and operation. As part of the SOLAS code, there is the requirement that all personnel on vessels at sea must undertake Standards of Training, ...
Humble feijoa to help prevent type 2 diabetes?
2023-08-02
Can the humble feijoa help the world tackle type 2 diabetes? University of Auckland scientists are investigating.
With more than 200,000 people in New Zealand living with type 2 diabetes, prevention is key to tackling this important health issue. Could a solution be found growing in New Zealand backyards?
The feijoa study, named FERDINAND, is a six-month weight-loss and maintenance programme, during which adults with raised blood sugar will be given about a gram of whole-fruit feijoa powder (or a placebo) each ...
Irregular sleep patterns associated with harmful gut bacteria
2023-08-02
New research has found irregular sleep patterns are associated with harmful bacteria in your gut.
The study, published today in The European Journal of Nutrition, by researchers from King’s College London and ZOE, the personalised nutrition company, is the first to find multiple associations between social jet lag – the shift in your internal body clock when your sleeping patterns change between workdays and free days - and diet quality, diet habits, inflammation and gut microbiome composition in a single cohort.
Previous research has shown that working shifts disrupts the body clock and can increase risk ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] More than 2,600 health care organizations recognized for commitment to high-quality cardiovascular careThe American Heart Association honors hospitals, clinics and EMS systems in all 50 states and Washington, D.C.