Researchers develop smartphone app that reliably recognizes physical signs of stroke
2023-08-02
(Press-News.org) CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
SAN DIEGO—Today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting, researchers discussed a smartphone app created that reliably recognizes patients’ physical signs of stroke with the power of machine learning.
In the study, “Smartphone-Enabled Machine Learning Algorithms for Autonomous Stroke Detection,” researchers from the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and multiple medical institutions in Bulgaria used data from 240 patients with stroke at four metropolitan stroke centers. Within 72 hours of the start of the patients’ symptoms, researchers used smartphones to record videos of patients and test their arm strength in order to detect patients’ facial asymmetry, arm weakness, and speech changes—all classic stroke signs.
To evaluate facial asymmetry, the study authors used machine learning to analyze 68 facial landmark points. To test arm weakness, the team used data from a smartphone’s standard internal 3D accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. To determine speech changes, researchers used mel-frequency cepstral coefficients, a typical sound recognition method that translates sound waves into images, to compare normal and slurred speech patterns. They then tested the app using neurologists’ reports and brain scan data, finding that the app was sensitive and specific enough to diagnose stroke accurately in nearly all cases.
“It’s exciting to think how this app and the emerging technology of machine learning will help more patients identify stroke symptoms upon onset,” said Dr. Radoslav Raychev, a vascular and interventional neurologist from UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine. “Quickly and accurately assessing symptoms is imperative to ensure that people with stroke survive and regain independence. We hope the deployment of this app changes lives and the field of stroke care.”
To receive a copy of this abstract or to speak with the study authors, please contact Camille Jewell at cjewell@vancomm.com or at 202-248-5460.
About the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery
The Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery (SNIS) is a scientific and educational association dedicated to advancing the specialty of neurointerventional surgery through research, standard-setting, and education and advocacy to provide the highest quality of patient care in diagnosing and treating diseases of the brain, spine, head, and neck. Visit www.snisonline.org and follow us on Twitter (@SNISinfo) and Facebook (@SNISOnline).
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-02
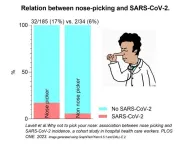
Nose-picking healthcare workers were more likely to catch COVID-19 during the pandemic than their colleagues who refrained, per Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0288352
Article Title: Why not to pick your nose: Association between nose picking and SARS-CoV-2 incidence, a cohort study in hospital health care workers
Author Countries: The Netherlands
Funding: This work was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development ZonMw (S3 study, grant agreement no. 10430022010023 to M.K.B.) and the Corona ...
2023-08-02
Half of popular TikTok videos about Baby Boomers portray older adults negatively, risking reinforcing stereotypes and creating intergenerational conflict
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285987
Article Title: Videos about older adults on TikTok
Author Countries: Singapore
Funding: We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Social Science Research Council SSHR Fellowship (MOE2018-SSHR-004). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to ...
2023-08-02
Extreme climates may have driven Middle Pleistocene hominins towards (positive) assortative mating and evolution of bigger brains, according to economic model of climate change impacts
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287964
Article Title: An economic model and evidence of the evolution of human intelligence in the Middle Pleistocene: Climate change and assortative mating
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work. END ...
2023-08-02
Interest in local bird feeding appears to have ramped up in countries all over the world during the pandemic lockdowns, even in countries not historically noted for bird feeding practices, according to a study published August 2, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Jacqueline Doremus from California Polytechnic State University and Liqing Li from Texas A&M University College Station, US, and Darryl Jones from Griffith University, Australia.
Feeding wild birds is a popular nature-based pastime because of its simplicity, low cost, and accessibility in even urban environments. ...
2023-08-02
In an analysis of more than 5,000 people, frequently working in teams was associated with a greater tendency for women and white men to put in extra effort at work, while other links between job conditions and effort varied between genders and ethnoracial groups. Wei-hsin Yu of the University of California, Los Angeles, US, and Janet Chen-Lan Kuo of National Taiwan University, Taiwan, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 2, 2023.
Popular media has recently featured discussion of “quiet ...
2023-08-02
In a study involving more than 500 people, participants correctly identified speech deepfakes only 73 percent of the time, and efforts to train participants to detect deepfakes had minimal effects. Kimberly Mai and colleagues at University College London, UK, presented these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 2, 2023.
Speech deepfakes are synthetic voices produced by machine-learning models. Deepfakes may resemble a specific real person’s voice, or they may be unique. Tools for making speech deepfakes have recently improved, raising concerns about security threats. For instance, they have already ...
2023-08-02
A single accessory – an ornate necklace from a child’s grave in ancient Jordan – provides new insights into social complexity of Neolithic culture, according to a study published August 2, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Hala Alarashi of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and the Université Côte d’Azur, France and colleagues.
Body adornments are powerful symbols that communicate cultural values and personal identities, and they are therefore highly valuable in the study of ancient cultures. In this study, Alarashi and colleagues analyze materials that adorned ...
2023-08-02
In the August 02, 2023 issue of Science Translational Medicine, University of California San Diego researchers lead a team that has published new insights on pelvic floor muscle (PFM) dysfunction, which is one of the key risk factors for pelvic floor disorders, a set of morbid conditions that include pelvic organ prolapse and urinary and fecal incontinence, that impact close to a quarter of women in the U.S. and have a strong association with vaginal childbirth. The work is part of a larger effort to advance understanding, treatment and prevention of pelvic floor muscle dysfunction in humans.
The ...
2023-08-02
The study, published today in PLOS ONE, is the first to assess human ability to detect artificially generated speech in a language other than English.
Deepfakes are synthetic media intended to resemble a real person’s voice or appearance. They fall under the category of generative artificial intelligence (AI), a type of machine learning (ML) that trains an algorithm to learn the patterns and characteristics of a dataset, such as video or audio of a real person, so that it can reproduce original sound or imagery.
While early deepfake speech algorithms may have required thousands of samples of a person’s voice to be able ...
2023-08-02
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A study examining the effects of deportation on the health and wellbeing of noncitizen veterans who served in the United States military has found that this group is a vulnerable and often unrecognized health disparity population.
Overseen by Ann Cheney, an associate professor of social medicine, population, and public health in the School of Medicine at the University of California, Riverside, the study reports the post-deportation economic, social, and political conditions of living abroad harm veterans’ physical and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop smartphone app that reliably recognizes physical signs of stroke