Diagnosing pediatric Crohn disease with radiomic and clinical data
AJR found that deploying a radiomic-based model with T2-weighted MRI data could increase diagnostic accuracy for pediatric Crohn disease
2023-08-04
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, August 4, 2023—An accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) found that deploying a radiomic-based model with T2-weighted MRI data could increase diagnostic accuracy for pediatric Crohn disease (CD).
Noting that ileal-wall radiomic features were strongly predictive of CD—and that model performance improved when ensembled with clinical data—“a radiomic machine learning model predicted CD diagnosis with better performance than two of three expert radiologists,” wrote corresponding author and AJR Pediatric Imaging Section Editor Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc.
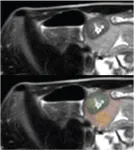
Dillman et al.’s manuscript identified patients who underwent MR enterography (MRE) for suspected ileal CD—enrolling participants with newly diagnosed ileal CD or serving as healthy controls from December 2018 to October 2021. Using axial T2-weighted SSFSE images, one radiologist selected two slices showing the greatest terminal ileal wall thickening. Four ROIs were then segmented, radiomic features were extracted from each, and support-vector machine models were trained to catalog the presence of ileal CD. Three fellowship-trained pediatric abdominal radiologists independently classified the presence of ileal CD on SSFSE images, with clinical diagnosis following positive endoscopy and biopsy serving as the reference standard.
Ultimately, the best-performing radiomic-only model in this AJR accepted manuscript used a round bowel-wall ROI in the area of greatest terminal ileum thickening, having AUC of 0.95 and accuracy of 89.6%. Ensembling this radiomic-only model with a clinical-only model achieved AUC of 0.98 and accuracy of 93.5%. Meanwhile, the three specialized radiologists achieved accuracies of 83.7%, 86.7%, and 88.1%.
An electronic supplement to this AJR accepted manuscript is available here.
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
MEDIA CONTACT:
Logan K. Young, PIO
44211 Slatestone Court
Leesburg, VA 20176
lyoung@arrs.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-04
Childhood trauma, such as abuse, emotional neglect, and exposure to domestic violence, may heighten a woman’s subsequent risk of pregnancy complications, and of giving birth to a low birthweight or premature baby, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The risks of pregnancy related diabetes, high blood pressure, depression/anxiety and of giving birth to underweight and or premature babies may all be significantly higher, the analysis suggests.
While previously ...
2023-08-04
The use of essential peppermint oil aromatherapy may ease pain severity after open heart surgery and enhance sleep quality as well, suggest the results of a small comparative clinical trial, published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
Heart surgery is a major procedure, necessitating the separation of the breastbone (sternum) as well as mechanical breathing support, both of which are associated with a high risk of severe pain, stress, and sleeplessness, note the researchers.
Effective pain relief allows patients to recover more quickly and may reduce the risk of postoperative complications, ...
2023-08-04
SEATTLE, Wash. August 3, 2023 – An analysis of 19 causes of death in the United States revealed persistent disparities and a familiar pattern across five racial-ethnic groups and 3,110 counties from 2000 to 2019. That’s according to the most comprehensive peer-reviewed research published today in The Lancet.
The mortality rates among American Indian or Alaska Native (AIAN) and Black populations were substantially higher than among White populations nationally and in most counties. For example, mortality was higher among the AIAN population than the White population in nearly all counties for skin and ...
2023-08-04
As little as 25 minutes a day of slow walking seems to be enough to counter the detrimental physical effects of bedrest on older hospital patients, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And for optimal improvements in physical function, around 50 mins/day of slow walking or around 40 mins of combined physical activities, such as 20 mins of resistance bands with around 20 mins of aerobic activity, are the most effective, the analysis indicates.
But there may be a threshold effect, with no clear benefit for ‘doses’ of more than 90 mins/day ...
2023-08-04
An international team of scientists have discovered an unusual Jupiter-sized planet orbiting a low-mass star called TOI-4860, located in the Corvus constellation.
The newly discovered gas giant, named TOI-4860 b, is an unusual planet for two reasons: stars of such low mass are not expected to host planets like Jupiter, and the planet appears to be particularly enriched by heavy elements.
The study, led by University of Birmingham astronomers, is published today (Friday 4th August) in a letter published within the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The planet was initially identified using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet ...
2023-08-04
Novel blood testing technology being developed by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center that combines genome-wide sequencing of single molecules of DNA shed from tumors and machine learning may allow earlier detection of lung and other cancers.
The test, called GEMINI (Genome-wide Mutational Incidence for Non-Invasive detection of cancer), looks for changes to DNA throughout the genome. First, a blood sample is collected from a person at risk for developing cancer. Then, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) shed by tumors is extracted from the plasma and sequenced using cost-efficient ...
2023-08-04
Kamaʻehuakanaloa (formerly Lōʻihi Seamount), a submarine Hawaiian volcano located about 20 miles off the south coast of the Big Island of Hawai‘i, has erupted at least five times in the last 150 years, according to new research led by Earth scientists at the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa. For the first time, scientists were able to estimate the ages of the most recent eruptions of Kamaʻehu, as well as the ages of eight additional older eruptions at this volcano going back about 2,000 years. Their findings were published recently in Geology.
Hawaiian volcanoes are thought to transition through a series of growth stages. ...
2023-08-04
Research from the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience has identified a mechanism through which insulin-like growth factors facilitate brain plasticity.
The insulin superfamily of hormones, including insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), play a crucial role not only in regulating blood sugar, metabolism, and growth, but also in healthy brain development and function, including learning and memory. These hormones can enter the brain through the bloodstream from the liver or can be synthesized directly in neurons and glial cells within the brain. They bind to receptors, ...
2023-08-04
Mothers who eat apples and herbs in early pregnancy could be protecting the brain health of their children and grandchildren, a Monash University study using genetic models has found.
The discovery is part of a project that found a mother’s diet can affect not just her child’s brain but also those of her grandchildren.
Published in Nature Cell Biology, the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute study found that certain foods could help protect against the deterioration of brain function.
More specifically, the study used roundworms (Caenorhabditis elegans) as the genetic model because many of ...
2023-08-04
In a new study published in Nature Geosciences, researchers, led by a Tulane University sedimentologist , investigated why the paths of meandering rivers change over time and how they could be affected by climate change.
Chenliang Wu, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at Tulane University School of Science and Engineering, began this research by looking at the Mississippi River before adding other rivers on Earth and ancient riverbeds on Mars to the study.
The study specifically looks at river sinuosity, or how much rivers curve. The sinuosity of rivers changes over time, depending on the age of the river and environmental changes. Some of these changes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diagnosing pediatric Crohn disease with radiomic and clinical data
AJR found that deploying a radiomic-based model with T2-weighted MRI data could increase diagnostic accuracy for pediatric Crohn disease