(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study of 18.4 million patients in the U.S. with overweight and obesity indicate that the annual probability of 5% or greater weight loss was low (1 in 10) despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss, but 5% or greater weight loss was more likely than body mass index (BMI) reduction to the healthy weight category, especially for patients with the highest initial BMIs.
Authors: Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27358)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27358?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=080723
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Probability of 5% or greater weight loss or BMI reduction among adults with overweight or obesity
JAMA Network Open
2023-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effects of cuff size on the accuracy of blood pressure readings
2023-08-07
About The Study: Using a regular blood pressure (BP) cuff size for all individuals regardless of arm size resulted in strikingly inaccurate BP readings with an automated device in this randomized crossover trial including 195 adults. This is particularly concerning for settings where one regular BP cuff size is routinely used in all individuals, regardless of arm size. A renewed emphasis on individualized BP cuff selection is warranted.
Authors: Tammy M. Brady, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3264)
Editor’s ...
Associations of different combinations of aerobic and muscle-strengthening activity with mortality
2023-08-07
About The Study: This study of 500,000 participants demonstrated that balanced levels of moderate aerobic physical activity, vigorous aerobic physical activity, and muscle strengthening activity combined may be associated with optimal reductions of mortality risk. Higher-than-recommended levels of moderate aerobic physical activity and vigorous aerobic physical activity may further lower the risk of cancer and all-cause mortality, respectively.
Authors: Rubén López-Bueno, Ph.D., of the University of Zaragoza in Zaragoza, Spain, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
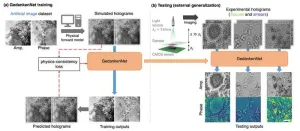
Self-supervised AI learns physics to reconstruct microscopic images from holograms
2023-08-07
Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have unveiled an artificial intelligence-based model for computational imaging and microscopy without training with experimental objects or real data.
In a recent paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, UCLA’s Volgenau Professor for Engineering Innovation Aydogan Ozcan and his research team introduced a self-supervised AI model nicknamed GedankenNet that learns from physics laws and thought experiments.
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the imaging process across ...
Butterflies can remember where things are over sizeable spaces, new study finds
2023-08-07
Heliconius butterflies are capable of spatial learning, scientists have discovered.
The results provide the first experimental evidence of spatial learning in any butterfly or moth species.
The findings, published today in Current Biology, also suggest Heliconius butterflies may be able to learn spatial information at large scales, consistent with the apparent importance of long-range spatial learning for traplining, which involves foraging within a home range of a few hundred square metres.
Spatial learning is known in insects, but much of the research has focused on ant and bee species which live socially ...
AI model can help determine where a patient’s cancer arose
2023-08-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- For a small percentage of cancer patients, doctors are unable to determine where their cancer originated. This makes it much more difficult to choose a treatment for those patients, because many cancer drugs are typically developed for specific cancer types.
A new approach developed by researchers at MIT and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute may make it easier to identify the sites of origin for those enigmatic cancers. Using machine learning, the researchers created a computational model that ...
Using social media to raise awareness of women’s resources
2023-08-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA The Covid-19 pandemic created a global increase in domestic violence against women. Now, an MIT-led experiment designed with that fact in mind shows that some forms of social media can increase awareness among women about where to find resources and support for addressing domestic violence.
In the randomized experiment, set in Egypt, women recruited via Facebook were sent videos via social media as well as reminders to watch television programming from a well-known Egyptian human rights lawyer focused on gender norms and violence. The study found that receiving the videos or reminders increased consumption of media content about the issue, increased knowledge ...
Dana-Farber AI-model predicts primary source of cancer using gene sequencing data
2023-08-07
BOSTON – Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have created an AI-based tool that uses tumor gene sequencing data to predict the primary source of a patient’s cancer. The study, published in in Nature Medicine, suggests that this predictive tool, called OncoNPC, could help guide treatment of cancer and improve outcomes in difficult to diagnose cases.
The primary source of cancer is traditionally diagnosed by a standardized diagnostic work-up, including radiology and pathology assessments based on slides of cells taken from a tumor biopsy. In 3-5% of cancer ...
Game-changing potential for drug testing and cardiovascular disease treatments - Tiny Heart Model Carries Massive Implications
2023-08-07
A remarkable breakthrough, a collaborative team of researchers, led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, and Tissue Dynamics Ltd., has unveiled a miniature human heart model that could potentially transform drug testing and cardiovascular research. This study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, introduces a self-paced multi-chambered human heart model, no larger than a grain of rice, which promises to revolutionize the way we study the heart and its functions.
Cardiovascular ...
Fanning the flames
2023-08-07
As Canadian wildfire smoke continues to impact large swaths of the United States, resulting in poor air quality and negative health outcomes for millions of Americans, more people than ever are feeling the effects of longer fire seasons and a changing climate. Now, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered that wildfires may have even bigger climate impacts than previously thought.
In a new study published Aug. 7 in Nature Geoscience, researchers led by Rajan Chakrabarty, the Harold D. Jolley Career Development Associate Professor in the ...
Effective medications for opioid use disorder rarely used
2023-08-07
Most individuals diagnosed with opioid use disorder are not on recommended medications and even fewer remain in care, according to a research letter published today in JAMA Internal Medicine by lead author Ashley Leech, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Health Policy at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC).
In 2021, there were more than 100,000 overdose deaths in the United States, with the highest rates among those ages 25-54.
Just 22% of the 40,000 individuals with opioid use disorder studied by VUMC researchers continuously used ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Probability of 5% or greater weight loss or BMI reduction among adults with overweight or obesityJAMA Network Open