(Press-News.org) Groundbreaking new research has uncovered a potential route to developing the first ever drug treatments for vascular dementia, that directly target a cause of the condition. The research, funded by the British Heart Foundation and published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, [1] has shed light on how high blood pressure causes changes to arteries in the brain, a process that leads to the devastating condition.
High blood pressure is a main cause of vascular dementia, a condition characterised by poor blood flow to the brain. The reduced blood supply starves brain cells of nutrients and over time they become damaged and die. Symptoms of vascular dementia include loss of energy, lack of concentration and poor memory.
It's normal for the brain’s arteries to narrow and widen in response to changes in blood pressure. However, consistently high blood pressure causes arteries to stay narrow and restrict the brain’s blood supply. Until now, it was not known how.
The study, from researchers at the Geoffrey Jefferson Brain Research Centre at The University of Manchester, reveals that – in mice – high blood pressure disrupts messaging within artery cells in the brain. They found that this occurs when two cell structures, that normally help transmit messages that tell arteries to dilate, move further apart. This stops the messages reaching their target, which causes the arteries to remain permanently constricted, limiting blood flow to the brain.
By identifying drugs that could restore this communication, the researchers hope to soon be able to improve blood supply to affected areas of the brain and slow the progression of vascular dementia.
While the findings are yet to be confirmed in humans, the processes of blood vessel narrowing and widening are very similar in mice and humans. The researchers are now investigating drugs that could restore this signalling, which they hope, in future will lead to human studies that aim to restore healthy brain blood flow in vascular dementia.
Professor Adam Greenstein, a clinician scientist specialising in high blood pressure at the University of Manchester and one of the leaders of the research, said:
“By uncovering how high blood pressure causes arteries in the brain to remain constricted, our research reveals a new avenue for drug discovery that may help to find the first treatment for vascular dementia. Allowing blood to return as normal to damaged areas of the brain will be crucial to stopping this devastating condition in its tracks.
“Any drugs that are discovered to improve brain blood supply may also be able to open a new line of attack in treating Alzheimer’s disease, which causes very similar damage to blood vessels as vascular dementia. Drugs to restore healthy blood flow could make current treatments, which focus on removing harmful amyloid plaques in the brain, more effective.“
Professor Sir Nilesh Samani, Medical Director at the British Heart Foundation, who funded the research, said:
“Vascular dementia affects around 150,000 people in the UK, and this number is going up. There are no treatments to slow or stop the disease, but we know that high blood pressure is an important risk factor. The incurable symptoms are hugely distressing for patients and those close to them.
“This exciting research reveals a specific mechanism by which high blood pressure might increase the risk of vascular dementia. Pinpointing how arteries remain permanently narrowed in vascular dementia could lead to the development of new effective treatments, raising hope that there may soon be a way to prevent this illness from destroying more lives.”
ENDS
To request interviews or for more information please call the BHF press office on 020 7554 0164 or email newsdesk at newsdesk@bhf.org.uk.
Notes to editors
[1] Taylor JL et al (2023). Uncoupling of Ca2+ sparks from BK channels in cerebral arteries underlies hypoperfusion in hypertension-induced vascular dementia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Full paper available via EurekAlert https://www.eurekalert.org/tipsheet-item/view-document/64354
About the British Heart Foundation
It is only with donations from the public that the BHF can keep its life saving research going. Help us turn science fiction into reality. With donations from the public, the BHF funds ground-breaking research that will get us closer than ever to a world free from the fear of heart and circulatory diseases. A world where broken hearts are mended, where millions more people survive a heart attack, where the number of people dying from or disabled by a stroke is slashed in half. A world where people affected by heart and circulatory diseases get the support they need. And a world of cures and treatments we can’t even imagine today. Find out more at bhf.org.uk
About The University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is recognised globally for its pioneering research, outstanding teaching and learning, and commitment to social responsibility. The Russell Group institution is ranked the 6th best university in the UK and 38th in the world (Academic Ranking of World Universities).
A truly international university, its community includes more than 44,000 students, 12,000 staff, and 500,000 alumni from 190 countries. Together, they are tackling the world’s biggest challenges – the University’s social and environmental impact is ranked in the top ten globally (Times Higher Education Impact Rankings).
The University is a powerhouse of research and discovery; 25 Nobel laureates are among its former staff and students; and it was ranked fifth for research power – the quality and scale of research and impact – in the UK government’s Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2021.
The institution is the most popular in the UK for undergraduate applications (UCAS 2021 cycle), and it is the it is the most targeted university by the UK’s leading employers (The Graduate Market, 2023).
END
Engineers have developed nanoscale tattoos—dots and wires that adhere to live cells—in a breakthrough that puts researchers one step closer to tracking the health of individual cells.
The new technology allows for the first time the placement of optical elements or electronics on live cells with tattoo-like arrays that stick on cells while flexing and conforming to the cells’wet and fluid outer structure.
“If you imagine where this is all going in the future, we would like to have sensors to remotely monitor and ...
ATLANTA — Catherine Perkins, a clinical professor in the College of Education & Human Development at Georgia State University, has been awarded a five-year, $3.6 million grant by the U.S. Department of Education to expand quality school-based mental health (SBMH) services for underserved populations in high-need schools.
The Expanding Quality SBMH Services for Underserved Populations with Inclusive Practices (GSU-EQUIP) grant will have a direct impact in metro Atlanta by increasing access to school-based programs and strengthening the candidate pool of mental ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – There is more to a harmful algal bloom than the green stuff in water that meets the eye – specifically, a changing hazard level of toxins produced by the microbes that make up the scummy mess.
A new study analyzing toxins produced by Microcystis, the main type of cyanobacteria that compose the annual harmful algal bloom (HAB) in Lake Erie, suggests that the toxicity of the bloom may be overestimated in earlier warm months and underestimated later in the summer.
The research is part of a large project, led by The Ohio State University, designed to develop a more accurate harmful algal bloom toxicity forecast ...
WASHINGTON (August 7, 2023) – The domestication of canines and their co-evolution with humans has fostered an incredibly unique relationship with these animals. Over time, our four-legged friends have adapted well to understanding human modes of communication, both verbal and nonverbal. However, researchers at the George Washington University say humans could do more to better understand our furry companions, and a dogs’ facial markings may be one key to meeting them halfway.
In a new paper published in the journal Animals, ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (8/7/2023) - The Pacific Ocean’s western boundary current, which forms a critical regulator of sea surface temperature and weather patterns, has significantly strengthened as the planet warms, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
The study provides the first evidence that the western boundary current in the South Pacific has significantly strengthened during the 20th century in response to global warming, contributing to an intensified equatorial undercurrent, according to Boston College Assistant Professor of Earth and Environmental Sciences Xingchen (Tony) Wang, a co-author ...
Academic performance has long been linked to how supported students feel at school. Now, a Rutgers study suggests this sentiment is also essential to preventing suicides.
A Rutgers researcher found that having a strong sense of school belonging – the subjective feeling of being accepted, valued, included and encouraged in the school community – could mitigate suicidal tendencies among Black adolescents.
“Having a supportive teacher or other nonparent adult can change a child’s life because they will want to go to school,” said Adrian Gale, an assistant professor at the Rutgers School of Social Work and co-author of the study ...
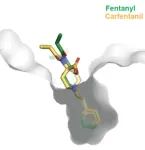
LA JOLLA, CA—An antibody in single-chain fragment variable (scFv) format that binds to the powerful opioid carfentanil was shown to reverse signs of carfentanil overdose in preclinical tests conducted by scientists at Scripps Research.
Carfentanil is a variant of the synthetic opioid fentanyl, and about 100 times as potent as its chemical cousin. Along with fentanyl and other fentanyl variants, it is commonly mixed with illegal drugs such as heroin and cocaine to enhance their euphoric effects, resulting in many fatal overdoses.
In the study, published in ACS ...
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has announced the renewal of the Midwest Integrated Center for Computational Materials (MICCoM) for another three years at $3 million per year. Founded in 2015, the Center is headquartered at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory. Partnering universities include the University of Chicago, University of Notre Dame and University of California, Davis.
“The MICCoM team has been at the forefront of developing simulation methods and codes and solving cutting-edge materials science problems,” said Center director Giulia Galli. She is also a senior scientist in Argonne’s Materials Science division and professor in the ...
Key Takeaways
A new method derived from standard blood pressure assessments can improve monitoring of critically ill patients with circulatory shock
The method accurately predicts risk of death, length of hospital stay, and blood lactate levels (an indicator of tissue perfusion and oxygenation).
BOSTON – Critically ill patients with circulatory shock—when the heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to the rest of the body, often as a result of heart failure, sepsis, or hemorrhage—require close monitoring and treatment, especially to maintain adequate blood pressure to prevent injury to important organs. ...
Researchers have successfully grown bacterial cells in potential sand-based construction materials, as detailed in a paper published by Research Directions: Biotechnology Design, a new journal from Cambridge University Press.
This achievement marks a substantial contribution to the field of biodesign, which seeks to incorporate living organisms into building materials as a means of making architecture more sustainable. It is effectively a fusion of biological and architectural expertise, with the shared goal of building better.
Cyanobacteria could enable the solidification of inorganic materials such as CO2, ...