(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES (August 8, 2023) — Whatever the opioid crisis calls to mind, it likely isn’t pacifiers and diapers. But when 1 out of every 5 hospitalized infants receives opioids, and when some infants require methadone treatment, it’s time to widen the scope. A new study led by pediatric surgeons at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles shows that methadone use after surgery can prolong a baby’s recovery and increase an infant’s dependence on ventilators and intravenous (IV) nutrition.
To call the opioid problem in the United States a crisis is not hyperbole. The rate of death due to opioid overdose has risen exponentially in the last 10 years, reaching 80,000 in 2021 alone. But the dangers of opioids are not limited to overdose.
Opioids are highly addictive—and withdrawal can be severe. “It seems unbelievable, but the same thing happens to babies,” says Lorraine Kelley-Quon, MD, MSHS, a pediatric surgeon at CHLA. “If you abruptly stop opioids in babies, they can show signs of withdrawal—irritability, intestinal problems or even seizures.” For this reason, babies receiving a prolonged course of opioids may need to be weaned off of them with methadone, a longer-acting, weaker opioid.
In her latest study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Kelley-Quon examined how methadone use impacted recovery in infants. The study included over 2,000 babies from 48 children’s hospitals who were surgically treated for necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a life-threatening inflammatory condition that can develop in premature newborns. While rare, NEC is the most common reason for emergency surgery in newborn babies.
The findings: Babies who required methadone needed to stay in the hospital an average of 21 days longer after surgery. They also required more days on the ventilator and longer reliance on IV nutrition.
“It ends up being a snowball effect,” she says. “The longer a baby is on opioids, the more likely the need for methadone, which is still an opioid.” Side effects of opioids are respiratory depression and decreased intestinal motility.
So why are opioids given to babies in the first place? The answer is simple: babies in the hospital may need surgery or painful interventions, and opioids are effective at treating their pain. However, babies can’t take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen for pain, like older children can. “Nobody wants a baby to be in pain,” says Dr. Kelley-Quon. “We don’t want to stop using opioids, especially when a baby is undergoing an operation. What we do want is to understand the impact of opioids and use them more judiciously.”
More judicious use of opioids doesn’t just mean limiting prescriptions. It also means standardizing opioid use. "We found such a wide range in what hospitals were doing,” she says. “In some hospitals, over 40% of infants received methadone. In other hospitals, methadone isn’t used at all.” This wide variability points to the need to standardize opioid and methadone use among hospitals.
Dr. Kelley-Quon has spent the last several years uncovering how widespread the impact of the opioid epidemic fallout has become for children. A few years ago, she established the first evidence-based guidelines for safer pain management in children and adolescents. Her work continues to uncover the need for what she calls “opioid stewardship.”
Other authors on the study include first author Olivia A. Keane, MD; Abigail K. Zamora, MD; Shadassa Ourshalimian, MPH; Elaa M. Mahdi, MD, MPH; Ashley Y. Song, MPH, PhD; Eugene Kim, MD and Ashwini Lakshmanan, MD, MPH.
The study was supported by grant KL2TR001854 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS) and grant R01HD105656 from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
About Children’s Hospital Los Angeles
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles is at the forefront of pediatric medicine, offering acclaimed care to children from across the world, the country and the greater Southern California region. Founded in 1901, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles is the largest provider of care for children in Los Angeles County and the No. 1 pediatric hospital in California and the Pacific region, and is consistently ranked in the top 10 in the nation on U.S. News & World Report’s Honor Roll of Best Children’s Hospitals. Clinical expertise spans the pediatric care continuum from newborns to young adults, from everyday preventive medicine to the most medically complex cases. Inclusive, compassionate, child- and family-friendly clinical care is led by physicians who are faculty members of the Keck School of Medicine of USC. Physicians translate the new discoveries, treatments and cures proven through the work of scientists in The Saban Research Institute of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles—among the top 10 children’s hospitals for National Institutes of Health funding—to bring answers to families faster. The hospital also is home to one of the largest training programs for pediatricians in the United States. To learn more, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube and Twitter, and visit our blog at CHLA.org/blog.
END
Opioids, methadone and babies
A Children’s Hospital Los Angeles study shows that methadone use following surgery in infants can increase hospital stay and delay recovery.
2023-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Investors force Black families out of home ownership, new research shows
2023-08-08
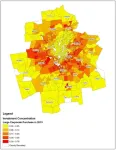
Investors have been buying houses at a steady rate since the last recession, but how much does it affect availability in the housing market? New research from the Georgia Institute of Technology shows investors are most likely to push out Black, middle-class homeowners from neighborhoods.
Data from 800 neighborhoods in the Atlanta metropolitan area between 2007 and 2016 revealed that major investors bought homes in majority-minority neighborhoods far from downtowns and in lower-income areas. These homes were often undervalued because of their minority populations, but they remained desirable and offered good market value.
The neighborhoods ...
Cybersecurity project plans to connect researchers across the country
2023-08-08
From building fighter jets to automobiles, the manufacturing world is increasingly adapting digital instruction as technology advances. Mechanical parts can be designed on a computer and shipped over the network to a manufacturing machine that follows digital instructions to produce a specific part. The move into the digital world makes securing online information a national interest.
Dr. Narasimha Reddy, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Texas A&M University, recently received a National Science Foundation grant to research cybersecurity ...
The “unknome”: a database of human genes we know almost nothing about
2023-08-08
Researchers from the United Kingdom hope that a new, publicly available database they have created will shrink, not grow, over time. That’s because it is a compendium of the thousands of understudied proteins encoded by genes in the human genome, whose existence is known but whose functions are mostly not. The database, dubbed the “unknome”, is the work of Matthew Freeman of the Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, England, and Sean Munro of MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England, and ...
Texas A&M's McKay receives NSF CAREER Award
2023-08-08
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) can be found in every water body on Earth, encompassing both saltwater and freshwater. It is a significant carbon source and is critical in environmental carbon cycling, which is the circulation of carbon in various forms through the environment and nature that makes the Earth sustainable for life.
The interaction between DOM and sunlight is essential for the carbon cycle to function effectively. However, the chemical structure of light-absorbing compounds, also known as chromophores, in DOM remains limited.
Dr. Garrett McKay, principal investigator of the Aquatic Chemistry Lab and assistant professor ...
Researchers use SPAD detector to achieve 3D quantum ghost imaging
2023-08-08
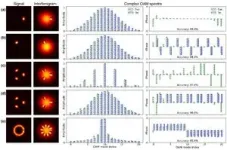
WASHINGTON — Researchers have reported the first 3D measurements acquired with quantum ghost imaging. The new technique enables 3D imaging on a single photon level, yielding the lowest photon dose possible for any measurement.
“3D imaging with single photons could be used for various biomedical applications, such as eye care diagnostics,” said researcher Carsten Pitsch from the Fraunhofer Institute of Optronics, System Technologies and Image Exploitation and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, both in Germany. “It can be applied to image materials and tissues that are sensitive to light or drugs that become toxic when exposed ...
NASA announces monthly themes to celebrate the Heliophysics Big Year
2023-08-08
This October, NASA is launching the Heliophysics Big Year – a global celebration of solar science and the Sun’s influence on Earth and the entire solar system. Modeled after the “Big Year” concept from citizen scientists in the bird-watching community, the Heliophysics Big Year challenges everyone to get involved with fun Sun-related activities.
For each month from October 2023 to December 2024, the Heliophysics Big Year will celebrate under a theme, sharing opportunities to participate in many solar science events from watching eclipses to joining citizen science projects. During ...
Stroke rehab at home is near
2023-08-08
The world of at-home stroke rehabilitation is growing near, incredible news for the 795,000 people in the United States who annually suffer a stroke. A new low cost, portable brain-computer interface that connects the brain of stroke patients to powered exoskeletons for rehabilitation purposes has been validated and tested at the University of Houston.
“We designed and validated a wireless, easy-to-use, mobile, dry-electrode headset for scalp electroencephalography (EEG) recordings for closed-loop brain–computer ...
People’s everyday pleasures may improve cognitive arousal and performance
2023-08-08
Listening to music and drinking coffee are the sorts of everyday pleasures that can impact a person’s brain activity in ways that improve cognitive performance, including in tasks requiring concentration and memory.
That’s a finding of a new NYU Tandon School of Engineering study involving MINDWATCH, a groundbreaking brain-monitoring technology.
Developed over the past six years by NYU Tandon's Biomedical Engineering Associate Professor Rose Faghih, MINDWATCH is an algorithm that analyzes a person's brain activity from data collected via any wearable device that can monitor electrodermal activity ...
Nitrogen runoff strategies complicated by climate change
2023-08-08
Washington, DC— As climate change progresses, rising temperatures may impact nitrogen runoff from land to lakes and streams more than projected increases in total and extreme precipitation for most of the continental United States, according to new research from a team of Carnegie climate scientists led by Gang Zhao and Anna Michalak published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The conditions predicted by these findings are opposite to recent decades, when increasing precipitation has outpaced warming and led to more aquatic nitrogen pollution. Understanding the relative roles of changes in temperature and rainfall is critical for designing ...
Wearables will transform health, but change brings challenges say researchers
2023-08-08
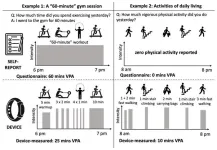
In a series of three editorials published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, the international team of scientists discuss issues facing the wearables field including lack of standardisation of devices and data, disconnects between research and industry and the impact of inequality in ownership.
Currently around a third of UK adults own a smartwatch or fitness tracker. A 2021 Australian-based survey reported 24 percent used fitness trackers and 23 percent used smartwatches.
Some use them to track their steps, others their sleep, but few understand the potential of these devices to transform our understanding of how everyday activity influences health.
“If you ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Opioids, methadone and babiesA Children’s Hospital Los Angeles study shows that methadone use following surgery in infants can increase hospital stay and delay recovery.