(Press-News.org) The Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP) has published the new call for the 2024 HFSP Nakasone Award. Until September 30th, the global scientific community is invited to submit their nominations for this prestigious award.
The HFSP Nakasone Award recognizes groundbreaking contributions and breakthrough discoveries in the life sciences. The award celebrates exceptional achievements in scientific excellence, particularly those that have propelled the boundaries of biological knowledge forward.
In its 13th year, the scope of the HFSP Nakasone Award extends to all levels of complexity, encompassing mechanisms of biological phenomena and interactions between organisms and their environments. Breakthrough discoveries can cover a broad spectrum, ranging from molecular and cellular approaches to biological functions to systems neuroscience including cognitive functions.
Nominations will be accepted until September 30th. Nominators have the option to nominate an individual or a pair of scientists jointly for the same award. The nominated scientists should be co-authors of groundbreaking publications or collaborators in key discoveries. Both the nominators and nominees are welcome from any country, and prior engagement with HFSP programs is not a prerequisite for consideration. HFSP is deeply committed to promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion, and strongly encourages the nomination of female scientists, early career researchers, individuals from underrepresented ethnic and racial backgrounds in the scientific community, as well as those from equity-seeking countries.
The selection of the 2024 HFSP Nakasone Awardee will be undertaken by the HFSP Council of Scientists, with the announcement of the winner(s) early 2024.
Recipients of the award will receive a small unrestricted research grant of 15,000 USD, an commemorative medal, and a certificate of recognition. Furthermore, the awardee(s) will deliver the HFSP Nakasone Lecture at the 2024 HFSP Awardees Meeting.
The HFSP Nakasone Award was established in 2010, honoring the vision of former Japanese Prime Minister Yasuhiro Nakasone, who played a pivotal role in conceiving and establishing the International Human Frontier Science Program. Past awardees of the Nakasone Award include distinguished scientists such Karl Deisseroth (2010), Michael Elowitz (2011), Gina Turrigiano (2012), Stephen Quake (2013), Uri Alon (2014), James Collins (2015), Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier (2016), David Julius (2017), Svante Pääbo (2018), Michael Hall (2019), Angelika Amon (2020), Anthony Hyman and Clifford Brangwynne (2021), Aviv Regev, Franz-Ulrich Hartl and Arthur L. Horwich (2022).The 2023 awardee was Rotem Sorek (2023).
####
HFSPO was established by the G7 countries at the initiative of former Prime Minister Yasuhiro Nakasone of Japan at the 1987 Venice Summit. Open to scientists of every nation, HFSPO is supported by 17 Members, Australia, Canada, France, Germany, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Korea, New Zealand, Norway, Singapore, South Africa, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, the United States of America and the European Commission. The mission of HFSPO is to foster bold, basic, frontier research in the life sciences and interdisciplinary collaborations around the world. Since 1990, close to 8,000 researchers from more than 70 countries have been supported. Of these, 28 HFSP awardees have gone on to win the Nobel Prize.
END
For all the astonishing things artificial intelligence can do, it has a particular blind spot that one University of Virginia researcher seeks to remedy.
It can’t recognize all shapes.
“Current machine-learning models lack the capability to analyze and quantify the shape of objects presented in images with complex structures and large variations, especially in the context of medical imaging,” said Miaomiao Zhang, an assistant professor in the UVA School of Engineering and Applied Science.
The models are biased toward “seeing” image textures and have limited ability ...
Osaka, Japan – You’re likely familiar with RNA, the molecule that plays an important role in protein production and gene expression control. Perhaps you’re less familiar, however, with PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA), a special type of RNA that protects the genome from mutations. Now, researchers in Japan have shed light on how these critical molecules are formed by the dynamics of several associated proteins in the germline of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster.
In a new study published in the Journal of Cell Biology, researchers from Osaka University have clarified how the proteins Tejas (Tej), Vasa (Vas), and Spindle-E ...
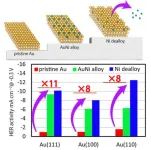
In recent years, hydrogen gas has gained momentum as the fuel for a clean and green future. This carbon-neutral fuel source releases huge amounts of energy via combustion in the presence of oxygen with water vapor as the by-product. One of the most popular methods of hydrogen production is the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity.
An electrochemical cell is used to split water, and the hydrogen gas gets released at the negatively charged electrode in hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). Catalysts are used to lower the ...
Breastfeeding has long been used as a method to help keep newborns healthy and protected against a variety of diseases. But certain sugars naturally found in breastmilk could also help prevent infections before a baby arrives. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have found that these sugars can stop a common prenatal infection in human tissues and pregnant mice. This could someday help avoid preterm births or complications without the need for additional antibiotics.
One of the most common bacteria that can affect pregnancies is Group B streptococcus (GBS). If left untreated, ...
By some estimates, the human nose can detect up to a trillion different smells with its hundreds of scent receptors. But even just catching a quick whiff of certain chemicals known as nerve agents can be lethal, even in tiny amounts. Researchers now reporting in ACS Sensors have developed a sensitive and selective nerve gas sensor using these human scent receptors. It reliably detected a substitute for deadly sarin gas in simulated tests.
Nerve gases are often very potent, requiring highly sensitive sensors to detect them ...
Everywhere scientists look for microplastics, they’ve found them — food, water, air and some parts of the human body. But examinations of our innermost organs that aren’t directly exposed to the environment are still limited. Now, in a pilot study of people who underwent heart surgery, researchers in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology report that they have found microplastics in many heart tissues. They also report evidence suggesting that microplastics were unexpectedly introduced during the procedures.
Microplastics ...
Conditions are ripe for an accelerated transition to electric vehicle (EV) use in the United States. The Biden-Harris administration has set a target that 50 percent of newly purchased cars in 2030 be electric. In addition, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provides significant tax incentives for purchasing electric vehicles and for companies that produce them.
And that is good news for environmental justice (EJ), says Lisa Benjamin, author of a paper called “EVs as EJ?” forthcoming in Harvard Environment Law Review. Benjamin, associate professor of law at Lewis & Clark Law School, details all of the positive impacts of EVs ...
Alzheimer’s disease, one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, leads to progressive loss of memory and autonomy. It is characterised by the accumulation of neurotoxic proteins in the brain, namely amyloid plaques and tau tangles. Due to the silent development of pathology over decades, very early diagnosis is of utmost importance to be able to take action as early as possible in the disease process. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) has demonstrated ...
A new DNA study has nuanced the picture of how different groups intermingled during the European Stone Age, but also how certain groups of people were actually isolated. The study was carried out by researchers at Uppsala University working with an international team of researchers, who produced new genetic data from 56 Central and Eastern European individuals from the Stone Age. The results have been published in the journal Communications Biology.
“Conducting studies like this one requires a broad interdisciplinary discussion. In this study, this discussion has been exceptionally fruitful,” says Tiina Mattila, population geneticist at Uppsala ...
Odorants are widely used in natural gas for leak detection, however, few studies have examined their potential effects on public health. A new peer-reviewed publication in Current Environmental Health Reports, suggests that some commonly-used natural gas odorants may induce a range of adverse health symptoms at very low concentrations, ranging from headaches to respiratory inflammation and skin rashes.
“Our sense of smell is the first line of defense in detecting gas leaks, but few studies have examined how odorants in gas may adversely affect our health or well-being,” said the review’s lead author, PSE Healthy Energy Senior Scientist Drew Michanowicz. “The ...