(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 14, 2023 — Imagine using insects as a source of chemicals to make plastics that can biodegrade later — with the help of that very same type of bug. That concept is closer to reality than you might expect. Today, researchers will describe their progress to date, including isolation and purification of insect-derived chemicals and their conversion into functional bioplastics.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 13–17, and features about 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“For 20 years, my group has been developing methods to transform natural products — such as glucose obtained from sugar cane or trees — into degradable, digestible polymers that don’t persist in the environment,” says Karen Wooley, Ph.D., the project’s principal investigator. “But those natural products are harvested from resources that are also used for food, fuel, construction and transportation.”
So Wooley began searching for alternative sources that wouldn’t have these competing applications. Her colleague Jeffery Tomberlin, Ph.D., suggested she could use waste products left over from farming black soldier flies, an expanding industry that he has been helping to develop.
The larvae of these flies contain many proteins and other nutritious compounds, so the immature insects are increasingly being raised for animal feed and to consume wastes. However, the adults have a short life span after their breeding days are over and are then discarded. At Tomberlin’s suggestion, those adult carcasses became the new starting material for Wooley’s team. “We’re taking something that’s quite literally garbage and making something useful out of it,” says Cassidy Tibbetts, a graduate student working on the project in Wooley’s lab at Texas A&M University.
When Tibbetts examined the dead flies, she determined that chitin is a major component. This nontoxic, biodegradable, sugar-based polymer strengthens the shell, or exoskeleton, of insects and crustaceans. Manufacturers already extract chitin from shrimp and crab shells for various applications, and Tibbetts has been applying similar techniques using ethanol rinses, acidic demineralization, basic deproteinization and bleach decolorization to extract and purify it from the insect carcasses. She says her fly-sourced chitin powder is probably purer, since it lacks the yellowish color and clumpy texture of the traditional product. She also notes that obtaining chitin from flies could avoid possible concerns over some seafood allergies. Some other researchers isolate chitin or proteins from fly larvae, but Wooley says her team is the first that she knows of to use chitin from discarded adult flies, which — unlike the larvae — aren’t used for feed.
While Tibbetts continues to refine her extraction techniques, Hongming Guo, another graduate student in Wooley’s lab, has been converting the purified fly chitin into a similar polymer known as chitosan. He does this by stripping off chitin’s acetyl groups. That exposes chemically reactive amino groups that can be functionalized and then crosslinked. These steps transform chitosan into useful bioplastics such as superabsorbent hydrogels, which are 3D polymer networks that absorb water.
Guo has produced a hydrogel that can absorb 47 times its weight in water in just one minute. This product could potentially be used in cropland soil to capture floodwater and then slowly release moisture during subsequent droughts, Wooley says. “Here in Texas, we’re constantly either in a flood or drought situation,” she explains, “so I've been trying to think of how we can make a superabsorbent hydrogel that could address this.” And because the hydrogel is biodegradable, she says it should gradually release its molecular components as nutrients for crops.
This summer, the team is starting a project to break down chitin into its monomeric glucosamines. These small sugar molecules will then be used to make bioplastics, such as polycarbonates or polyurethanes, which are traditionally made from petrochemicals. Black soldier flies also contain many other useful compounds that the group plans to use as starting materials, including proteins, DNA, fatty acids, lipids and vitamins.
The products made from these chemical building blocks are intended to degrade or digest when they’re discarded, so they won’t contribute to the current plastic pollution problem. Wooley’s vision for that process would align it with the sustainable, circular economy concept: “Ultimately, we'd like the insects to eat the waste plastic as their food source, and then we would harvest them again and collect their components to make new plastics,” she says. “So the insects would not only be the source, but they would also then consume the discarded plastics.”
The researchers acknowledge support and funding from the Welch Foundation and a private donation.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Monday, Aug. 14, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsfall2023briefings. Reporters can request access to media briefings during the embargo period by contacting newsroom@acs.org.
For health and safety information for ACS Fall 2023, please visit the FAQ webpage.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Harvesting of building blocks from insect feedstocks for transformation into carbohydrate-derived superabsorbent hydrogels
Abstract
A primary interest in the Wooley laboratory is the production of functional polymers from renewable sources that are capable of reverting to those natural products once their purpose has been served. As scaled-up production of biomass-based biodegradable polymers continues to grow, we’ve recognized a need to avoid competition with resources that are important to food, fuel, construction and other societal demands. Therefore, we’re turning to unique supply chains, including harvesting of naturally-derived building blocks from black soldier flies (BSF), a rapidly growing feed crop industry. This presentation will highlight efforts to isolate carbohydrate feedstocks from BSF and transform them into superabsorbent hydrogel materials, which are designed to address global challenges with flooding and drought associated with climate change.
Title
Harvesting of naturally-derived building blocks from adult black soldier flies
Abstract
The urgent threat to our environment created by plastic pollution has continued to grow and develop as we face the well-established problems arising from traditional plastic production using petrochemicals and their accumulation. Polymeric materials constructed from natural building blocks are promising candidates to displace environmentally-persistent petrochemical counterparts, due to their similar thermal and mechanical properties and greater breadth of compositions, structures and properties, sustainability and degradability, thereby redefining the current plastic economy. A key goal in the exploration of building blocks from natural polymers is to avoid competition with resources critical to food, fuel, construction and other societal demands. This requires turning to unique supply chains, such as black soldier flies (BSF).
BSF provides an immense array of potential utility to society, ranging from being a protein source for animal feed to composting waste. However, the larvae are almost exclusively of use for these processes and the adults serve the sole purpose of reproducing. Once the adults die, they are currently considered as waste and disposed of. Intrigued with the opportunity to create a value chain using the adult BSF, studies focusing on optimization and scalability for the digestion of adult black soldier flies to produce high quality chitin and utilize it as a feedstock for the production of super-absorbent hydrogel networks will be discussed.
END
Transforming flies into degradable plastics
2023-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Irrigating more US crops by mid-century will be worth the investment
2023-08-14
With climate change, irrigating more crops in the United States will be critical to sustaining future yields, as drought conditions are likely to increase due to warmer temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns. Yet less than 20% of croplands are equipped for irrigation.
A Dartmouth-led study finds that by the middle of the 21st century under a moderate greenhouse gas emissions scenario, the benefits of expanded irrigation will outweigh the costs of installation and operation over an expanded portion of current U.S. ...
New statement urges engaging patients in their care, collaborating on treatment decisions
2023-08-14
DALLAS, Aug. 14, 2023 - A new American Heart Association scientific statement highlights evidence that supports shared decision-making, a term that describes the process of ensuring patients have the knowledge and tools to make decisions about their health in collaboration with their professional health care team. The statement publishes today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
More than 100 trials have demonstrated that shared decision-making ...
Making plant-based meat alternatives more palatable
2023-08-14
New colloidal technique could give a juicy sensation without adding fat
Switch to plant-based diets needed to hit climate change targets
One of the biggest obstacles to the uptake of plant-based alternatives to meat is their very dry and astringent feel when they are eaten.
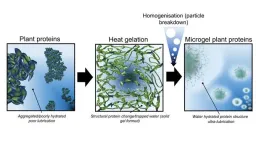
Scientists, led by Professor Anwesha Sarkar at the University of Leeds, are revolutionising the sensation of plant proteins, transforming them from a substance that can be experienced as gloopy and dry to one that is juicy and fat like.
And the only substance they are adding to the plant proteins is water.
Plant protein microgels
To ...
3D-printed vegan seafood could someday be what’s for dinner (video)
2023-08-13
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 13, 2023 — In the refrigerated grocery store aisle, meat alternatives greatly outnumber plant-based seafoods. But more mock seafood options are needed because of unsustainable fishing and aquaculture practices, which can deplete the supply and harm the environment. Today, researchers present a new approach for creating desirable vegan seafood mimics that taste good, while maintaining the healthful profile of real fish. They 3D-printed an ink made from microalgae protein and mung bean protein, and their proof-of-concept calamari rings can even be air-fried for a quick, tasty snack.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American ...
ORNL buildings researchers earn top ASHRAE honors
2023-08-12
Kashif Nawaz and Mahabir Bhandari, building technologies researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, were recognized for research achievements in support of ASHRAE during the 2023 annual conference of the national heating, refrigerating, and air-conditioning engineering society.
Nawaz, a distinguished researcher and head of ORNL’s Buildings Technologies Research Section, received the Crosby Field Award, which honors the highest-rated paper presented before a technical session, a symposium or poster session ...
Raising awareness of Long Covid ‘blue legs’ symptom
2023-08-12
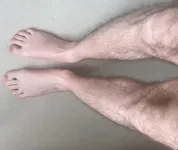
An unusual case of a Long Covid patient’s legs turning blue after 10 minutes of standing highlights the need for greater awareness of this symptom among people with the condition, according to new research published in the Lancet.
The paper, authored by Dr Manoj Sivan at the University of Leeds, focuses on the case of one 33-year man who developed with acrocyanosis – venous pooling of blood in the legs.
A minute after standing, the patient’s legs began to redden and became increasingly blue over time, with veins becoming more prominent. After 10 minutes the colour was much more pronounced, with the patient ...
For labrum tears, regrowth rather than repair
2023-08-12
Tears to the glenoid labrum—cartilage tissue that lines the shoulder where the arm joins—can be repaired with arthroscopic surgery, which significantly weakens the joint and involves a lengthy recovery.
Liping Tang, a bioengineering professor at The University of Texas at Arlington, is developing a new method to repair labrum tears that would enable the body to regenerate tissue to completely reattach the sides of the tear. He recently received a five-year, $2.1 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases for the research, which would improve the current standard of care ...
Call for papers: Special theme issue: Artificial intelligence (AI) and ChatGPT in Asian and Pacific Islander (API) health
2023-08-11
Asian/Pacific Island Nursing Journal (APINJ) Editor-in-Chief: Hyochol (Brian) Ahn, PhD, MSN, MS-ECE, MS-CTS, APRN, ANP-BC, FAAN and guest editor Shu-Fen Wung, Ph.D., RN, ACNP-BC, FAAN welcome submissions to a special theme issue examining "Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ChatGPT in Asian and Pacific Islander (API) Health."
Generative AI, like ChatGPT, can have many applications in health care and medicine, particularly in addressing the unique needs and challenges faced by API communities. Potential topics related to the use of generative AI in health care and nursing care specific to API health that we ...
SLU ethicists, leading scholars publish guidance for parents, physicians making medical decisions for children
2023-08-11
ST. LOUIS – How should others make decisions for pediatric patients?
For decades, there has been debate in academic literature about the ethical principles that govern medical decision-making for children. In response to this, a group of leading scholars in pediatric ethics participated in a June 2022 symposium, “Best Interests and Beyond: Standards of Decision Making in Pediatrics,” at Saint Louis University. Over the course of three days, the 17 scholars debated one question – in the context of U.S. pediatric care, what moral precepts ought to guide parents and clinicians in medical decision-making for children?
A group of ...
Hundred-year storms? That's how long they last on Saturn.
2023-08-11
The largest storm in the solar system, a 10,000-mile-wide anticyclone called the Great Red Spot, has decorated Jupiter's surface for hundreds of years.
A new study now shows that Saturn — though much blander and less colorful than Jupiter — also has long-lasting megastorms with impacts deep in the atmosphere that persist for centuries.
The study was conducted by astronomers from the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who looked at radio emissions from the planet, which come from below the surface, and found long-term disruptions in the distribution ...