(Press-News.org)
Inoue Receives Funding For Mason CARES Plus
Megumi Inoue, Associate Professor, Social Work, received funding for: "Mason CARES Plus."
Mason CARES Plus is an expansion study to Mason CARES that will focus on conducting in-depth focus groups and online semi-structured interviews to assess which specific aspects of the Stress Busting Program (SBP) and the Music and Memory program (M&M) were most (and least) impactful in reducing care partner stress and identify effective strategies to improve care partner engagement with the M&M program among Mason CARES participants.
Preliminary results from the Mason CARES study show a high average baseline stress level among care partners before the program started. They also show a significant reduction in caregiver stress levels among spouse caregivers compared to non-spouse caregivers five weeks after the SBP intervention.
Results also show those caring for adults living with moderate dementia experienced a greater reduction in stress levels than those caring for adults with severe dementia.
These findings suggest that SBP effectiveness varied based on the care partner’s baseline stress level, spousal relationship, and dementia severity of the care receiver.
Through the implementation of Mason CARES Plus, researchers will:
examine which elements of the Stress Busting Program (SBP) sessions were most effective (and least effective) among care partners with mild to moderate stress levels compared to those with very high stress levels;
understand the specific elements of the SBP program that are more (and less) effective in reducing stress levels for different types of care partners;
identify best practices for targeting and adopting the use of stress management techniques to improve effectiveness in reducing stress among different types of care partners; and
examine how a structured social support system can reduce the stress levels of different care partners.
They will also:
assess which factors were associated with higher levels of engagement and adoption of the Music and Memory (M&M) program from the perspectives of care partners AND that of older adults with early-to-moderate stage dementia;
explore the perceived efficacy of the M&M program using a novel approach of interviewing older adults living with mild to moderate dementia;
compare the perceived efficacy of the M&M intervention among care partners with mild to moderate stress levels compared to those with high-stress levels; and
strategize best practices for utilizing M&M to ultimately reduce care partner stress.
Inoue received $89,995 from RRF Foundation for Aging for this project. Funding began in July 2023 and will end in late June 2024.
The significance of the study is that Mason CARES Plus will provide new practical insights to improve the targeting and effectiveness of this dual intervention (SBP and M&M), with the goal of improving its adoption by care partners and in turn, reducing care partner stress.
The research team also includes: Emily Ihara, Professor and Chair. Social Work; Cathy Tompkins, Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs, Social Work, College of Public Health; Gilbert Gimm, Associate Professor, Health Administration and Policy; and Shannon Layman, Adjunct Faculty, Psychology.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls 38,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the last half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity and commitment to accessibility. Learn more at http://www.gmu.edu.
END
Hopping in the shower, we anticipate the warm water to be cleansing and renewing after a long, hard day — but there may be something dangerous lurking in the showerhead.
Showers can expose us to many types of bacteria cells. Most are harmless, but some – called drinking water-associated pathogens of the immunocompromised (DWPIs) – can pose a serious risk to our health, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
Sarah Haig, Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, received $420,000 from the National Science Foundation ...
Boston, MA - New research led by Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Public Health found that children who received integrated mental health care showed improvements in both mental health and school performance. These findings, published in the Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, examined changes over time in outcomes among 6-12-year-old children receiving integrated behavioral health care at three federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) that implemented the TEAM UP Model of care.
The study, which included 51 children serviced ...
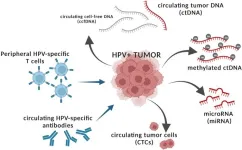
“We discuss existing clinical data on these surrogates of tumor burden and their potential in evaluating efficacy of immunotherapy in HPV-associated malignancies.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 14, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on August 10, 2023, entitled, “Peripheral surrogates of tumor burden to guide chemotherapeutic and immunotherapeutic strategies for HPV-associated malignancies.”
With the rapid adoption of immunotherapy into clinical practice for HPV-associated ...
When it comes to translational medicine, Robert Gourdie is among the 2 percent of “super-producers,” National Institutes of Health-funded scientists at U.S. biomedical institutions who hold 10 or more issued patents.
Super-producers were responsible for half of all patents issued according to research published Aug. 11 in Nature Biotechnology. The objective of the research was to create a tool to better quantify bridges and barriers to clinical translation of biomedical discoveries.
The research marks a novel area of inquiry for Gourdie, a professor and cell biologist at the Fralin Biomedical ...
In the rush to harness artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to make care more efficient at hospitals nationwide, a new study points to another possible use: identifying patients with non-medical needs that could affect their health and ability to receive care.
These social determinants of health – everything from transportation and housing to food supply and availability of family and friends as supports – can play a major role in a patient’s health and use of health care services.
The new study ...
A new study from clinicians and researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center, U-M Department of Pathology and the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology reveals findings from over 800 clinical assays performed for kidney patients with MiTF family gene mutations. This study, published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology¸ is the largest series of its kind in kidney cancer and carries deep clinical and diagnostics implications.
The team, led by Rohit Mehra, M.D., performed over 800 clinical assays on the MiTF family genes TFE3 and TFEB in renal tumors with morphologic and biomarker alterations considered suspicious for MiTF family genetic mutations.
The ...
The latest study about of proboscideans (elephants and their ancient relatives) from the University of Helsinki provides proof that some proboscideans started to adapt to locally grass-rich environments in East Africa first by changing their behavior and starting to feed more on grasses. This happened in some lineages of proboscideans, such as choerolophodonts, much earlier than has been thought until now, about 23 to 11 million years ago in parts of East Africa
Also, around 7 million years ago in the lake Turkana region, increasingly grass-rich diets of the earliest true ...
CLEVELAND: A first-in-human trial of deep brain stimulation (DBS) for post-stroke rehabilitation patients by Cleveland Clinic researchers has shown that using DBS to target the dentate nucleus – which regulates fine-control of voluntary movements, cognition, language, and sensory functions in the brain – is safe and feasible.
The EDEN trial (Electrical Stimulation of the Dentate Nucleus for Upper Extremity Hemiparesis Due to Ischemic Stroke) also shows that the majority of participants (nine out of 12) demonstrated ...
What drives us to develop new ideas rather than settling for standard methods and processes? What triggers the desire to innovate at the risk of sacrificing time, energy, and reputation for a resounding failure? Creativity is based on complex mechanisms that we are only beginning to understand and in which motivation plays a central role. But pursuing a goal is not enough to explain why we favor some ideas over others and whether that choice benefits the success of our actions.
"Creativity can be defined as the ability to produce original ...
Megumi Inoue, Associate Professor, Social Work, received funding for: "Group Digital Gaming: Experiences of Older Adults Living with Dementia in an Activity for Cognitive Impairment."
The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of a group digital gaming intervention on cognitive function, mood, and behaviors in people with early to moderate levels of dementia. A group digital gaming company, called Obie Technology, was developed to facilitate cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, and group interactions simultaneously. ...