(Press-News.org) The Moral Difference between Faces and FaceTime
Kyle E. Karches
Although telemedicine can be useful in certain situations, physicians should not consider it an adequate substitute for the office visit, writes Karches, an associate professor of health care ethics and internal medicine at St. Louis University. While seeing the potential for telemedicine to improve care for certain patients, he is concerned about what may be lost if telemedicine comes to replace many in-person visits. Telemedicine rules out an embodied encounter between physician and patient, in which the sense of touch has special importance.
Another Voice
Facing Progress with Pragmatism: Telemedicine and Family Medicine
Marc Tunzi
The singular expertise of family physicians is the ability to manage complexity with pragmatism, both clinically and ethically. Telemedicine raises multiple questions about the nature of the patient-physician relationship as manifested in clinical encounters. Some of these questions are concerning, underscoring the need to assess whether medical care is better with this new technology—or if it is just different or maybe even worse. It seems clear, however, that, regardless of its limitations, telemedicine is here to stay. The pragmatic complex ethical question, then, is how all of us together—both medical professionals and society at large—will manage it.
The Moral Value of Telemedicine to the Physician‐Patient Relationship
Benjamin S. Wilfond
Wilfond, a pediatric pulmonologist who cares for extremely premature babies, writes that his experience as a clinician was very positive and learning how to use telemedicine has made him a better doctor. An appointment can be a virtual house call that takes less time for his patient’s family and allows him to learn even more about their home. While there are limitations of telemedicine, there are good ethical reasons for clinicians to support the broader use of telehealth, including equity, efficiency, effectiveness, and respecting preferences. Empirical health-services research that assesses satisfaction, quality, and health outcomes will be necessary to determine the impact of telehealth on a population level to ensure that is used in a way that promotes equity in care.
Also in this issue:
Essay—Case Study
Smuggled Doughnuts and Forbidden Fried Chicken: Addressing Tensions around Family and Food Restrictions in Hospitals
Megan A. Dean and Laura Guidry-Grimes
It is a common practice for family members to bring food to hospitalized loved ones. However, in some cases, this food contravenes a patient's dietary plan. Such situations can create significant tension and distrust between health care professionals and families and may lead the former to doubt a family's willingness or ability to support patient recovery. This case-study essay offers an ethical analysis of these situations and offers strategies for creative problem-solving that center diet as a subject for shared decision-making and regular, ongoing communication among health care professionals, patients, and families.
Table of Contents Hastings Center Report: Vol 53, No 4 (wiley.com)
For more information, contact:
Susan Gilbert
Director of Communications
The Hastings Center
845-424-4040 x244
gilberts@thehastingscenter.org.
END
Hastings Center Report, July-August 2023 Issue
2023-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Department of Energy grant supports inclusive high energy physics research
2023-08-15
The new project creates opportunities for researchers from historically underrepresented groups to develop technology that will help us understand the forces behind an expanding universe.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the Missouri University of Science and Technology (Missouri S&T) have been awarded funding for a program that aims to generate insights about the universe while expanding diversity in the high energy physics field.
Through the $589,000, three-year grant from DOE’s Funding for Accelerated, Inclusive Research (FAIR) initiative, ...
Could exposure to chemicals in plastics predispose you and your children to cardiovascular disease?
2023-08-15
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Exposure to environmental chemicals, including those in common plastic products, has been linked with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or CVD, the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019.
Changcheng Zhou, a professor of biomedical sciences in the School of Medicine at the University of California, Riverside, has received an eight-year award of nearly $6.8 million from the Revolutionizing Innovative, Visionary Environmental Health Research (RIVER) program of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, or NIEHS, to investigate how ...
Cancer organizations recommend mindfulness-based interventions to treat anxiety and depression in patients
2023-08-15
WASHINGTON, D.C. (August 15, 2023) — The Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) and the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) formally recommend mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) and other integrative therapies to manage anxiety and depression symptoms in adults living with cancer. The guideline, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, reviews the effectiveness of integrative therapies such as yoga, relaxation, hypnosis, acupuncture, and music therapy in treating anxiety and depression symptoms during ...
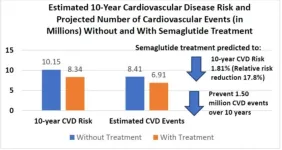
Recent study at UC Irvine found that semaglutide medication may benefit 93 million U.S. adults
2023-08-15
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have just published a study that projects 93 million U.S. adults that are overweight and obese may be suitable for the 2.4 mg dosage of semaglutide, a weight loss medication known under the brand name Wegovy.
They projected based on the known weight loss effects (15% average weight loss) of this therapy that its use could result in 43 million fewer people with obesity, and prevent up to 1.5 million heart attacks, strokes, and other adverse cardiovascular events over 10 years.
The study, US Population Eligibility and Estimated Impact of ...
Carnegie Mellon University developed AI method uses transformer models to study human cells
2023-08-15
Researchers in Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science have developed a method that uses artificial intelligence to augment how cells are studied and could help scientists better understand and eventually treat disease.
Images of organ or tissue samples contain millions of cells. And while analyzing these cells in situ is an important part of biological research, such images make it nearly impossible to identify individual cells, determine their function and understand their organization. A technique called spatial transcriptomics ...
Kessler Foundation receives 4 grants totaling nearly $1.7 million from New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research
2023-08-15
East Hanover, NJ – August 15, 2023 – Kessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI). Researchers will use funds to address identity reconstruction, physical and mental fatigue, and upper limb (UL) function.
Helen Genova, PhD, associate director, Center for Autism Research, received $528,824 for her study, “Using my Strengths: Evaluation of a Strength-Based Intervention in Adults with TBl.” ...
CHOP researchers develop versatile and low-cost technology for targeted long-read RNA sequencing
2023-08-15
Philadelphia, August 15, 2023—In a development that could accelerate the discovery of new diagnostics and treatments, researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a versatile and low-cost technology for targeted sequencing of full-length RNA molecules. The technology, called TEQUILA-seq, is highly cost-effective compared to commercially available solutions for targeted RNA sequencing and can be adapted for different research and clinical purposes. The details were described in a paper in Nature Communications.
On the journey ...
New kidney function equation may reduce health disparities by improving access to heart failure therapy in previously ineligible patients
2023-08-15
Physician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine recently conducted a large-scale analysis to assess the impact of a newly introduced equation used to evaluate one’s heart failure risk. The study, published in the Journal of Cardiac Failure, showed that the new and old kidney function equations had comparable values in predicting the risk of heart failure.
Naman Shetty, M.D., a clinical research fellow in the UAB Division of Cardiovascular Disease and ...
NIH supports UCF scientist to develop new antibiotic for TB
2023-08-15
BY SUHTLING WONG | AUGUST 15, 2023
A College of Medicine researcher is developing a new antibiotic related to penicillin to treat tuberculosis (TB) and related lung infections.
Dr. Kyle Rohde, an infectious disease expert, recently received a $3.4 million, five-year grant from the National Institutes of Health to create new antibiotics that target mycobacterial infections caused by pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium abscessus.
TB infected 11 million people in 2021, ranking it 13th as the leading cause of ...
An AI coach that improves your golf swing
2023-08-15
A University of Texas at Arlington researcher is working on the prototype of a golf swing training system that combines artificial intelligence (AI) with portability and can be used at home or on the driving range.
Nicholas Gans, a UT Arlington principal research scientist and division head for the UT Arlington Research Institute (UTARI), leads the project, which is funded by a nearly $53,000 grant from the University and Fort Worth-based IGSC.AI LLC. Gans’ initial work is considered a preliminary proof of concept.
“We’ll use a camera-based ...