Websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone Tests
JAMA Network Open
2023-08-21
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: In this study including content analysis of 27 websites across multiple countries, most websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) tests included false and misleading claims which might lead consumers to purchase an AMH test in the belief that it can reliably predict fertility potential and age of menopause. Depending on the test result, this may in turn lead to misplaced anxiety or reassurance about one’s fertility and modifications to subsequent conception or contraceptive plans and behavior.
Authors: Tessa Copp, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30192)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30192?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=082123
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-21
With the advent of ChatGPT4, the use of artificial intelligence in medicine has absorbed the public’s attention, dominated news headlines, and sparked vigorous debates about the promise and peril of medical AI.
But the potential of AI reaches far beyond the frontlines of medicine.
AI is already changing the way scientists discover and design drugs. It is predicting how molecules interact and proteins fold with never-before-seen speed and accuracy. One day, AI may even be used routinely to safeguard the function of nuclear reactors.
These are but a few of the exciting applications of AI in the natural sciences, ...
2023-08-21
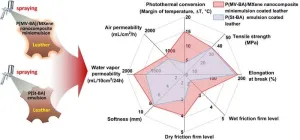
A study published in the journal of Engineering reveals a remarkable development in the field of green coating materials for leather. Researchers have successfully synthesized a solvent-free, bio-based antibacterial agent and aromatic monomer called methacrylated vanillin (MV). This innovative compound not only imparts antibacterial properties to leather coatings but also serves as an eco-friendly alternative to the petroleum-based carcinogen styrene (St).
In this research article, titled "Bio-based ...
2023-08-21
Clopidogrel is a commonly prescribed medication used to prevent further heart attacks after an initial event. It needs to be activated in the body to be effective. Studies of European populations show that 30% of individuals have genetic variants that reduce or prevent activation through the production of an enzyme called CYP2C19. People of South Asian ancestry have high rates of cardiovascular disease, but previous studies have not looked for these variants in UK South Asian populations or linked these variants with risk of recurrent heart attacks if prescribed clopidogrel in South Asian ancestry ...
2023-08-21
As our planet undergoes significant transformations due to climate change, habitats are being altered, appearing, disappearing, or changing in quality. Understanding the impact of these changes on the geographic distributions of species is of great significance. The shrinking ranges of protected organisms and the expanding ranges of noxious species, such as pests and pathogens, highlight the urgent need to monitor range movements precisely. However, this task poses challenges as the available observation time is often short compared to the pace of underlying population processes, making it difficult to distinguish between directional shifts and random fluctuations.
Addressing ...
2023-08-21
People who have recovered from a major depressive episode, when compared with individuals who have never experienced one, tend to spend more time processing negative information and less time processing positive information, putting them at risk for a relapse, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our findings suggest that people who have a history of depression spend more time processing negative information, such as sad faces, than positive information, such as happy faces, and that this difference is greater compared to healthy people with no history,” said lead author Alainna Wen, PhD, ...
2023-08-21
INDIANAPOLIS – Social risk factors such as financial instability and housing insecurity are increasingly recognized as influencing health. But unlike diagnosis codes, prescription information, lab or other test reports, social risk factors do not adhere to standardized, controlled terminology in a patient’s electronic medical record, making this information difficult to extract from the clinical notes where they typically are found.
A new study has found that a natural language processing (NLP) system developed by Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health informaticians showed excellent performance when ported ...
2023-08-21
Ames, IA — Twenty years ago, the National Football League adopted the Rooney Rule. It attempted to address racial disparity in top positions by requiring teams to interview at least one person of color for every head coach opening.
But newly published research suggests the gap will persist unless it’s closed at the bottom. The NFL has a hierarchal labor pool, explains Andreas Schwab, co-author and associate professor of entrepreneurship at Iowa State University. Under the head coach are two coordinators who oversee defense and offense. These coordinators supervise position-specific coaches who may have their own assistant coaches.
“To become ...
2023-08-21
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For Immediate Release
August 21, 2023
In 2006, the Tripod Complex Fire burned more than 175,000 acres in north-central Washington. The fire, which was within the Okanogan-Wenatchee National Forest, was more than three times the size of Seattle. Yet while considered severe at the time, even larger wildfires in 2014, 2015 and 2021 have since dwarfed Tripod.
Past research shows that large and severe wildfires like these were much rarer in the western U.S. and Canada prior to the late ...
2023-08-21
AMES, Iowa – Yan Zhao gestured toward the trees outside his campus window on a rainy afternoon.
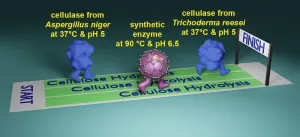
The professor of chemistry at Iowa State University is developing new synthetic catalysts to break down cellulose, the plant fibers that make those trees tall and strong.
“Cellulose is built to last – a tree doesn’t just disappear after rain,” Zhao said. “Cellulose is a huge challenge to break down.”
Zhao thinks he has an idea and a technology that can get the job done, making plant biomass a practical source of sugars that can be converted to many applications, including ...
2023-08-21
Nearly one million people in the United States are living with Parkinson’s disease, making it the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Current medical treatments for Parkinson’s are focused on helping people manage symptoms. But the underlying mechanisms of the neurological disorder remain poorly understood.
Tamily Weissman, associate professor of biology and department chair, is working to change that. Parkinson’s symptoms occur because of a drop in dopamine levels when ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone Tests
JAMA Network Open