(Press-News.org)
Everyday symbols like &?!#@$ are highly memorable, according to new research.
The new study led by the University of Waterloo aimed to investigate how well symbols are remembered compared to words with the same meaning.
“Our work is ground-breaking as it highlights how humans remember graphic symbols and logos,” said Myra Fernandes, co-author and professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at Waterloo. “Symbols are particularly useful as they can be used as logos in advertising, as well as offer a faster means of communication through emojis. Our studies examining memory for symbols offer insight into ways to maximize retention and refine communication.”
Across five studies, the researchers surveyed over 1100 adults to examine the role of symbols in memory. In the studies, participants were presented with either a symbol or its word counterpart, e.g., ‘$’ or ‘dollar’, and tested on how many symbols or words they could remember.
In all studies, the researchers found that participants were able to memorize symbols better than words with the same meaning.
“Symbols might be more easily remembered because they give concrete visuals to abstract ideas,” said Brady Roberts, lead author and PhD candidate in Cognitive Neuroscience. “When we think about abstract concepts, like love, it can be difficult to visualize clearly. But with symbols, we can use a sort of image that represents the concept – like a heart for love – which makes the abstract idea more concrete and therefore easier to remember.”
Roberts adds that symbols may also be easier to remember because they are unique and tend to represent a single concept, whereas words can have multiple meanings. Consider the play symbol [▷]. It only has one meaning: to start a piece of media. But its word counterpart ‘play’ has many other meanings, such as a game or theatrical performance, and there are many synonyms for the word, such as commence, begin, and start.
The authors hope that their work will aid in the future of visual design to help plainly communicate complicated or abstract ideas.
The paper, Symbol superiority: Why $ is better remembered than ‘dollar’, authored by Roberts, Fernandes, and Colin MacLeod, appears in the psychology journal Cognition.
END
In 2010, the U.S. government announced a multi-billion-dollar plan to improve the energy efficiency of its buildings, including a focus on LEED certification. Used worldwide, LEED—Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design—is a system that rates buildings on energy efficiency. A new study examined the effects of LEED certification on energy efficiency in federal buildings. The study found no effect on average energy consumption, primarily because many other factors come into play when rating energy.
The study, by researchers ...
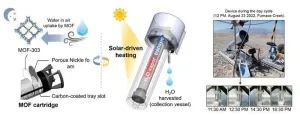
Korea is regarded as a “water-stressed nation.” Although the country receives an annual precipitation of approximately 1,300mm, it is characterized by concentrated periods and specific regions, thereby giving rise to challenges stemming from water scarcity. The lack of drinking water extends beyond mere inconvenience, posing life-threatening implications for certain individuals. In March 2023, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) released a report highlighting the plight of roughly 190 million children in Africa who suffer from an absence of safe water, resulting in the tragic daily loss of 1,000 children under the age of five.
Nations across the globe ...
Early data on activities that will be unsafe to undertake in automated vehicles has been released. From doing work to watching the world, from social media to resting – preliminary results are in.
Research led by RMIT University looked at what happens if a driver is suddenly required to take control of an automated vehicle, such as in an emergency.
The series of papers examines how experience and three types of distractions (work, social media and rest) impacted on the driver’s ability to respond.
Study lead author in the School of Engineering, Dr Neng Zhang, said ...
The REIMAGINE study, published today in BMJ Oncology, is the first study to use MRI scans with prostate specific antigen (PSA) density to assess the need for further standard NHS tests. Of the 29 participants found to have serious prostate cancer, 15 had a ‘low’ PSA score that would have meant they were not referred for further investigation under the current system.
Currently, men over 50 in the UK can ask for a PSA test if they are experiencing symptoms or are concerned about prostate cancer. ...
Relatively short-term use of immunosuppressant medications to control an inflammatory disease was not associated with an increased risk of later developing cancer, according to new research led by scientists at the University of Pittsburgh and Mass Eye and Ear, a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, and published today in the journal BMJ Oncology.
The findings should provide reassurance to patients and clinicians who may hesitate to prescribe the medications because they are known to increase the risk of cancer in people who ...
**Embargoed until 23.30 [UK time] / 6.30pm [ET] Monday, August 21, 2023** Peer-reviewed / Systematic review and meta-analysis
The Lancet: New study reveals the most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, affects 15% of the global population over the age of 30
Aging, population growth, and obesity are key drivers
● By 2050, nearly 1 billion people are projected to have osteoarthritis.
● Obesity is a major contributor to osteoarthritis. In 2020, obesity was responsible
for approximately 20% of the disability of osteoarthritis.
● Osteoarthritis increases with age. For ages 70+, the condition ranked seventh
among causes ...
Researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute identified potential new treatment options for people with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and high levels of estrogen promote its development. The study, published in Molecular Cancer Research discovered that estrogen receptor mutations found in endometrial cancers cause large changes in endometrial cancer cells.
Estrogen is a reproductive hormone that binds and activates estrogen receptors. Cancer can cause estrogen receptors to remain in a state of constant activity. That increases shedding of the endometrial ...
UC Davis MIND Institute researchers have received a $4.7 million, five-year grant from the National Institutes of Mental Health to study a child-focused autism intervention in community agencies. The Early Start Denver Model (ESDM) is a comprehensive intervention for autistic children ages 1-4. It addresses all areas of development and emphasizes communication and social interaction through everyday activities.
ESDM was tested in research studies at the MIND Institute and shown to improve communication skills and daily living skills. The new grant will allow MIND Institute experts to train behavior analysts in community agencies to use the model, to see if it is effective ...
A University of Texas at Arlington researcher is constructing an open-networked airborne computing platform to enable unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to help first responders better coordinate their efforts during emergency or disaster responses.
UT Arlington also is developing a universal plug-in hardware unit that can fit into any UAV to allow for this computing platform to be used.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is funding the research through a $1.8 million grant to UTA, University of ...
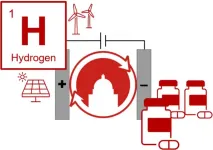
MADISON – The world needs greener ways to make chemicals. In a new study, University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers demonstrate one potential path toward this goal by adapting hydrogen fuel cell technologies. These technologies are already used to power some electric vehicles, laptops and cell phones.
"The chemical industry is a massive energy consumer, and there is a big push to decarbonize the industry,” says Shannon Stahl, a professor in the UW–Madison Department of Chemistry who guided much of the research. “Renewable electricity can provide energy to produce chemicals with a much lower carbon footprint than burning fossil fuels.”
The ...