(Press-News.org) The Aging Research and Drug Discovery (ARDD) conference, being held at the University of Copenhagen Aug. 28-Sept. 1, is celebrating 10 years of convening top scientists, venture capitalists, business leaders, and journals engaged in aging research, medicine, and emerging technology.
The conference has grown significantly over its decade-long history. This year’s event kicks off with Longevity Medicine Day which will include speakers like Evelyne Bischof, MD, an expert in internal medicine, oncology, and longevity from Renji Hospital, Shanghai; Michael Basson, Senior Editor of Nature Medicine; Thomas A. Rando, MD, PhD, Deputy Director of the Stanford Center on Longevity; and Michael Ringel, Managing Director and Senior Partner at BCG. Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine and one of the founders and co-chairs of the ARDD, is also a featured presenter.
“ARDD provides real value for the biopharmaceutical industry,” says Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD. “This conference allows the pharmaceutical industry to actively engage in and incorporate the latest discoveries in credible aging research into every aspect of their internal R&D strategy.”
Professor Morten Scheibye-Knudsen, MD, PhD, head of the Biology of Aging laboratory at the University of Copenhagen and executive chair of ARDD says: “We are extremely humbled, honored and excited that so many amazing speakers will join our meeting onsite at the University of Copenhagen. This year we maintain our focus on young scientists who will be the future of our field and we have a large amount of speaker slots for these rising stars.”
The conference will involve presentations on a number of breakthrough innovations and new technologies in aging research, including advanced biological techniques for rejuvenation therapies, machine learning and quantum computing in drug discovery; aging clocks; and a presentation on Pharma.AI, Insilico Medicine’s commercially available generative AI platform for end-to-end drug discovery presented by Petrina Kamya, PhD, Head of AI Platforms at Insilico Medicine and Fran Pun, PhD, Head of Insilico’s Hong Kong office.
Based on the adoption of its AI platforms and collaborations, Insilico Medicine estimates that approximately 40% of large pharmaceutical companies have initiated exploratory research projects in aging research. Some of these projects have already transitioned into the early-stage therapeutic discovery programs.
This year's conference will again support Student Ambassadors, pairing teenage researchers interested in aging and drug discovery with expert mentors and conference registration. Two ARDD student ambassadors, Andrea Olsen and Zachary Harpaz, went on to publish their findings using Insilico’s AI platform to discover glioblastoma targets in the journal Aging, and together founded the Youth Longevity Association.
“I am truly impressed by the commitment of these young researchers,” says Dr. Zhavoronkov. “I hope their work will inspire other young people excited about science and technology to look at how they can use AI tools to discover new targets and treatments for both aging and disease.”
Details and registration: http://www.agingpharma.org
For further information, images or interviews, please contact: ardd@insilico.com
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage end-to-end artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, connects biology, chemistry, and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers, and other modern machine learning techniques to discover novel targets and to design novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine delivers breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system (CNS), and aging-related diseases.
For more information, visit www.insilico.com
END
World’s largest aging research and drug discovery conference celebrates 10 years
2023-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A calculator to predict benefit from adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma
2023-08-22
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer of the liver and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with China accounting for over half of the global annual cases and deaths. Hepatectomy is the standard curative-intent treatment option for appropriately selected patients with localized HCC. However, the high postoperative recurrence rate causes many patients to have a poor prognosis and a high incidence of cancer-specific death. This occurs in especially early recurrence within the first year after surgery, which is most likely due to occult micro-metastasis from the original tumor. Given that survival among patients with recurrence is markedly ...
Paired liver exchange developed by Boston College economists results in first four-way liver exchange
2023-08-22
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (8/22/2023) – In a breakthrough in liver transplantation that may lead to the ability to connect more living donors and patients, a new matching system designed by a team led by Boston College economists enabled the world’s first four-way liver exchange and a cascade of additional matches, researchers reported recently in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The results show that expanding the capacity of the donor-patient matching mechanism beyond the traditional 2-way change – matching two patients with two donors – can increase the number of ...
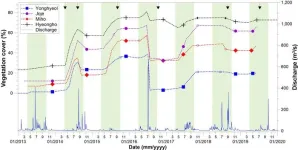
Understanding river alteration via shifting flow regime
2023-08-22
Researchers at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) published their findings on the drastic short-term alterations in rivers accompanied by shifts in vegetation and geomorphology drawn from actual on-site investigation and analyses and not from model simulations.
The alteration processes from a 'white river,' characterized by riverbeds with no vegetation including bare sandbars, to a densely vegetated 'green river' with grass and trees, have been ...
Want to increase resiliency in kids? Teach creativity
2023-08-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Train elementary school students how to be creative and you can help increase their resilience in the face of real-life problems, new research suggests.
In a small study, researchers trained third, fourth and fifth graders to use literary techniques such as perspective shifting, counter-factual (what if) thinking and causal (why) thinking to improve creativity in dealing with difficulties.
The techniques helped kids come up with new, creative and practical ways to solve problems, said Angus Fletcher, lead author of the study and a professor of English at The Ohio State University and member of the university’s Project ...
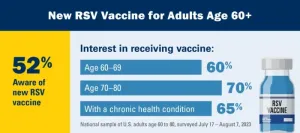
Many older adults want RSV vaccine, poll shows
2023-08-22
The first Americans over age 60 just started rolling up their sleeves to get vaccinated against respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, now that brand-new vaccines have started to arrive at pharmacies and clinics.
Millions more older adults may do the same in coming weeks and months, a new University of Michigan poll suggests, as they seek protection against a virus that is especially good at infecting older lungs.
But nearly half of older adults do not know about the new RSV vaccines that received approval earlier this year, the poll finds. And some groups of older adults show much less interest in getting ...
New test chamber created to find better ways to keep people cool
2023-08-22
PULLMAN, Wash. — A shipping container that can test passive cooling systems could help researchers and builders find carbon-free ways to keep people cool in extreme temperatures.
Washington State University researchers created the 60 square-foot chamber to test passive systems that use wind towers along with water evaporation instead of electricity to cool spaces.
Finding cooling methods that don’t require putting more greenhouse gases into the air is crucial to helping a growing population adapt to climate change, said Omar Al-Hassawi lead author of the study in the journal, Energies.
“Cooling is ...
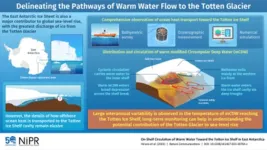
Delineating the pathways of warm water towards East Antarctica’s Totten Glacier
2023-08-22
One of the most feared effects of global warming is the rise in sea level caused by the melting of polar continental ice. In fact, polar researchers have been working towards raising the awareness of this impending threat. The scientific fraternity relies on sampling the remote regions of Artic and the Antarctic continental shelves to estimate these risks. They can then use these measurements to model and understand the processes that drive the melting of ice at these locations and determine the extent of meltwater that will eventually flow ...
Hundreds of Andean bird species at risk due to deforestation: New research shows how to protect them
2023-08-22
Birds native to the tropical Andes, many of which cannot be found anywhere else, are threatened by increasing agricultural development in the region. A new study details how the resulting habitat loss affects specific species and lays out possible ways to protect birds from human-driven disturbance.
The researchers combined a meta-analysis of papers on birds across the Andes with five years of fieldwork in Peru, revealing that open farmlands result in up to a 60% decline in the number of species in an area. Before this work, there was little data on which species were declining or by how much.
“The vast majority ...
Pacific coral reef shows historic increase in climate resistance
2023-08-22
Coral reefs in one part of the Pacific Ocean have likely adjusted to higher ocean temperatures which could reduce future bleaching impacts of climate change, new research reveals.
A Newcastle University-led study focused on the Pacific Island nation of Palau and has shown that historic increases in the thermal tolerance of coral reefs are possible. The results demonstrate how this capacity could reduce future bleaching impacts if global carbon emissions are cut down.
Drawing on decades of field observations, the scientists modelled many possible future coral bleaching trajectories for Palauan reefs, ...
Researchers extract ancient DNA from a 2,900-year-old clay brick, revealing a time capsule of plant life
2023-08-22
For the first time, a group of researchers have successfully extracted ancient DNA from a 2,900-year-old clay brick.
The analysis provides a fascinating insight into the diversity of plant species cultivated at that time and place, and could open the way to similar studies on clay material from other sites and time periods.
The results are published today in Nature Scientific Reports.
Currently housed at the National Museum of Denmark, the clay brick originates from the palace of Neo-Assyrian king Ashurnasirpal II, in the ancient city of Kalhu. Known today as the North-West palace in Nimrud (modern-day northern Iraq), its construction began around 879 BCE. ...