(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/24/2023) —Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer in the United States, and 80% of lung cancer deaths are linked to one risk factor: smoking. While lung cancer screenings are a critical part of prevention and treatment for the disease and 15 million Americans qualify for yearly screenings, over half those eligible for screenings are still actively smoking. Without standard smoking cessation measures in place, the benefits of the screenings have not been fully realized.
New research published in JAMA Pulmonary Medicine, led by the University of Minnesota Medical School, examined how different combinations of behavioral treatment and medication affect tobacco cessation and, going forward, how they can be used to increase the benefits of lung cancer screenings. Researchers from the School of Public Health, College of Liberal Arts, U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and Allina Health also contributed to the study.
The Program for Lung Cancer Screening and Tobacco Cessation (PLUTO) trial tested different adaptive interventions based on the evidence-based Tobacco Longitudinal Care (TLC) program, in part to learn how best to incorporate TLC into annual lung cancer screening as a smoking cessation standard. The trial assessed the effect of adding a referral to prescription medication therapy management to the TLC program among participants who did not respond to initial TLC treatment — i.e. did not stop smoking — as well as the effect of decreasing the intensity of TLC among participants who did respond to initial treatment.
The study found:
After initial TLC treatment, 80% of participants had not responded to treatment (were continuing to smoke cigarettes) and 20% had responded to treatment (early success with quitting).
After 18 months of follow-up, the quit rate across the TLC intervention groups was 24%.
Among participants who did not respond to initial TLC treatment, the quit rate for participants who additionally received a referral for medication therapy management was similar to the participants who received TLC without medication therapy management.
Among participants who did respond to initial TLC treatment, the quit rate for those receiving TLC quarterly was 44% compared to 59% for those receiving TLC monthly.
The findings suggest that TLC was most effective when implemented without modification and does not need additional pharmacist resources. Integrating the TLC program — which consists of frequent telephone coaching and over-the-counter combination nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) — with lung cancer screening was feasible and associated with clinically meaningful quit rates.
“If we do not help people quit smoking, we will not adequately reap the benefits of lung cancer screening,” said Steven Fu, a professor at the U of M Medical School, member of the Masonic Cancer Center and the lead author on the study. “The PLUTO trial shows that we can deliver both intensive behavioral treatment and medications to help people quit by integrating a longitudinal tobacco cessation care program into the lung cancer screening setting.”
While further work is needed to identify implementation strategies, researchers recommend that health systems consider integrating longitudinal tobacco cessation care into the lung cancer screen setting in order to improve outcomes for patients who still smoke.
-30-
About the University of Minnesota Medical School
The University of Minnesota Medical School is at the forefront of learning and discovery, transforming medical care and educating the next generation of physicians. Our graduates and faculty produce high-impact biomedical research and advance the practice of medicine. We acknowledge that the U of M Medical School, both the Twin Cities campus and Duluth campus, is located on traditional, ancestral and contemporary lands of the Dakota and the Ojibwe, and scores of other Indigenous people, and we affirm our commitment to tribal communities and their sovereignty as we seek to improve and strengthen our relations with tribal nations. Learn more at med.umn.edu.
About College of Liberal Arts
For more than 150 years, the College of Liberal Arts (CLA) has played a central and enduring role in shaping lives, for the good of Minnesota and the world. CLA is the largest college in the University of Minnesota system with nearly 500 world-class faculty instructing more than 12,000 undergraduate and 1,400 graduate students. CLA is home to 31 academic departments and 20+ interdisciplinary research centers in the arts, social sciences, and humanities. Learn more at cla.umn.edu.
About the School of Public Health
The University of Minnesota School of Public Health improves the health and wellbeing of populations and communities around the world by bringing innovative research, learning, and concrete actions to today’s biggest health challenges. We prepare some of the most influential leaders in the field, and partner with health departments, communities, and policymakers to advance health equity for all. Learn more at sph.umn.edu.
END
Optimizing tobacco cessation treatment with lung cancer screening
2023-08-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New quantum device generates single photons and encodes information
2023-08-24
A new approach to quantum light emitters generates a stream of circularly polarized single photons, or particles of light, that may be useful for a range of quantum information and communication applications. A Los Alamos National Laboratory team stacked two different, atomically thin materials to realize this chiral quantum light source.
“Our research shows that it is possible for a monolayer semiconductor to emit circularly polarized light without the help of an external magnetic field,” ...
Making materials more durable through science
2023-08-24
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories developed a molecule that helps change the way some materials react to temperature fluctuations, which makes them more durable. It’s an application that could be used in everything from plastic phone cases to missiles.
Polymers, which include various forms of plastics, are made up of many smaller molecules, bonded together. This bond makes them especially strong and an ideal product to be used to protect delicate components in a wide variety of items. But with time, use and exposure to different environments, all materials begin to deteriorate.
Hot ...
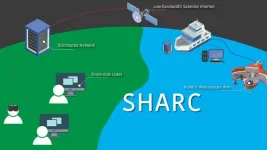
New framework for oceanographic research provides potential for broader access to deep sea scientific exploration
2023-08-24
Woods Hole, Mass. (August 23, 2023) -- Scientific exploration of the deep ocean has largely remained inaccessible to most people because of barriers to access due to infrastructure, training, and physical ability requirements for at-sea oceanographic research.
Now, a new and innovative framework for oceanographic research provides a way for shore-based scientists, citizen scientists, and the general public to seamlessly observe and control robotic sampling processes.
The Shared Autonomy for Remote Collaboration (SHARC) framework “enables remote participants to conduct shipboard operations and control ...
How pre-eclampsia accelerates aging in women
2023-08-24
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Pre-eclampsia, a life-threatening surge in blood pressure, is an enigmatic condition. Each year, it causes the deaths of more than 70,000 women worldwide. Because scientists do not know what causes it, they lack targeted strategies to treat it.
Delivery, the only available therapy, is not the cure it is often made out to be, according to Vesna D. Garovic, M.D., Ph.D., a nephrologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who has devoted her career to studying this common pregnancy complication.
"Even after delivery, women ...
Sweet corn yield at the mercy of the environment, except for one key factor
2023-08-24
URBANA, Ill. — A new analysis from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the USDA-Agricultural Research Service (ARS) has identified the top factors accounting for yield variability in processing sweet corn (used for canned and frozen products), including one within the control of processors.
“We used a very robust approach to account for sweet corn yield with field-level data across some 16,000 fields and 27 years. Year and production region were the two most important variables, which makes ...
Cambridge and ISPA scientists create a tool to identify individuals at risk of developing different myeloid leukemias
2023-08-24
Scientists have created a new test for identifying people at risk of developing acute myeloid leukaemia and related cancers, years before they do. The new platform, ‘MN-predict’, will allow doctors and scientists to identify those at risk and to design new treatments to prevent them from developing these potentially lethal cancers.
Researchers at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute (CSCI), the University of Cambridge’s Department of Haematology, and Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria del Principado de Asturias (ISPA) analysed data from more than 400,000 individuals participating ...
Repairing broken brain circuits may offer path to new Parkinson’s treatments
2023-08-24
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (August 24, 2023) — Van Andel Institute scientists have identified a series of processes that help the brain adapt to damage caused by breakdowns in circuits that govern movement, cognition and sensory perception.
Because such breakdowns contribute to Parkinson’s disease, the findings may one day help researchers optimize current treatments or develop new ones that repair or bypass the broken circuits.
A study describing the findings published this week in the journal Science Advances.
“Our work highlights the importance ...
MSK Research Highlights, August 24, 2023
2023-08-24
New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and the Sloan Kettering Institute — a hub for basic science and translational research within MSK — suggests a method for revealing DNA repair “scars” could help make treatment decisions in BRCA1- and BRCA2-deficient cancers; modified a bacteria-made compound to target mutant KRAS-driven cancers; and shed new light on brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.
New method for revealing DNA repair “scars” ...
Study uncovers genetic risk factors for heart failure
2023-08-24
In a new study co-led by investigators at the United States Department of Veterans Affairs and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, a global team of scientists conducted one of the largest genetic association studies on heart failure to date. Using genomic data from over 90,000 heart failure patients and more than a million controls, the team identified 39 genetic mutations associated with heart failure, 18 of which had not been reported previously.
The researchers also pinpointed seven druggable proteins that, when targeted with specially ...
Training immune cells to remove ‘trash’ helps resolve lung inflammation
2023-08-24
Inflammation is a standard part of our bodies’ immune system response. But sometimes this response becomes hyperactivated in our lungs, causing inflammation to continue unchecked, which can be fatal. Many deaths from COVID-19 have been due to excessive inflammation, which results in acute lung injury.
A group of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have investigated how lungs counterbalance inflammation. Their work points to cells in the lung that reduce inflammation by removing ...