(Press-News.org) Around the country, non-profits and local governments are testing the idea of food as medicine through “produce prescription programs”—with promising results, according to researchers from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.
By prescribing free, healthy foods similar to how doctors prescribe medications, clinicians and policy makers hope to remove financial barriers to accessing fruits and vegetables to individuals with diet-related illness. Specifically, produce prescriptions offer vouchers, debit cards, or loyalty cards to access free or discounted produce at grocery retail and farmer’s markets and typically enroll food-insecure households. A Tufts-led pooled analysis of nine such programs found these programs were associated with positive benefits, from halving food insecurity to lowering blood pressure. The study, which is the largest known evaluation of these programs to date, was published August 29 in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
The researchers analyzed surveys and medical records from over 1,800 children and 2,000 adults who had been identified as low-income and at risk for cardiometabolic diseases. Study participants had been enrolled in produce prescription programs operating across 22 sites in 12 U.S. states from 2014 to 2020. Each program was operated by Wholesome Wave, a national nonprofit that works to address disparities in diet-related disease and enhance nutrition equity by making fruits and vegetables more accessible and affordable to low-income community members through systems change.
The data showed an increase in fruit and vegetable intake (by about a serving per day among adults) as well as improved clinical biomarkers of cardiometabolic health for adults. For example, diabetic patients saw a 0.3 percentage point drop in hemoglobin A1C, an indicator for average blood sugar levels in the previous three months, and a decrease in body mass index by 0.4 kg/m2 among those with overweight or obesity. In patients with hypertension, blood pressure also dropped by 5-to-8 millimeters of mercury. The improvement for these clinical biomarkers of cardiometabolic health were greater among participants with uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, or stage 2 hypertension.
The study also revealed improvements in fruit and vegetable intake, food security, and self-reported health status among child participants. While body mass index was not noticeably reduced in children, the researchers say these benefits reflect critical measures for their development, long-term health and well-being.
“We were excited to see the results, which showed that participants who receive this incentive consume more fruits and vegetables, yielding clinically relevant outcomes,” says senior study author Fang Fang Zhang, a nutritional epidemiologist and Neely Family Professor at the Friedman School. “We need larger-scale implementation of these programs, which may play a role in improving care, in particular for lower-income adults with obesity, diabetes, or hypertension.”
The records reviewed were from patients who were enrolled in the nine produce prescription programs for an average of six months, usually after being referred by their physician. Most participants received a voucher or card that could be redeemed at selected grocery stores and/or farmers’ markets. Prescriptions covered an average of $43 per household per month in adult programs, and $112 per household per month in programs for children.
“Our findings provide important new evidence from a diverse set of programs for meaningful benefits of produce prescriptions, highlighting the need for clinical, policy, and healthcare payer and providers' efforts to implement produce prescription programs,” says Zhang.
"There is much we still need to learn about which programs are likely to be effective, how long they should operate, what happens to patient health outcomes when they end and more,” says first author Kurt Hager, who completed the work as a doctoral student at the Friedman School and is now an instructor at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School. “The future of Food is Medicine will likely see pilots and expansion occurring alongside ongoing evaluations that will continually improve the quality of services provided.”
Researchers across institutions have been conducting analyses of these and similar programs, with most finding net positive benefits for patients, but differences in the extent of those gains and how the programs were implemented. Such studies can help to guide the implementation of the Biden-Harris Administration’s National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition and Health, which, among other things, calls for expanded produce prescription programs for people enrolled in Medicaid, Medicare, Veterans Affairs, and the Indian Health Service.
“This research is a step in the right direction and in alignment with the comprehensive National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health,” says Alison Brown, a registered dietician and program director in the Prevention and Population Science Program in the Division of Cardiovascular Sciences at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health. “However, more rigorous ‘food is medicine’ studies are needed to add to our scientific knowledge and inform evidence-based policies.”
Further research will help to fill some existing information gaps. While the observed gains for participants were clinically and statistically meaningful, the new study lacked a control group, which means the benefits could be attributed to other factors. Some of the programs were also in place during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have impacted their efficacy, as participants were less likely to redeem their vouchers.
Research reported in this article was supported by the Rockefeller Foundation and Kaiser Permanente, and by the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute under award R01HL115189. Complete information on authors, funders, and conflicts of interest is available in the published paper. This content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
END
Produce prescription programs yield positive health benefits for participants, study finds
In the largest known such study to date, an analysis of participant records by Tufts University researchers found programs that provide free fruits and vegetables have measurable benefits for health and food security
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Innovative therapy for anorexia nervosa shows promise
2023-08-29
**EMBARGOED UNTIL 3:00am CT TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023**
Tulsa, Okla. – A trailblazing study conducted by researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) in Tulsa, Okla., has made significant strides with a novel technique for treating anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder characterized by low body weight, body image abnormalities, and anxiety. The study, “The impact of floatation therapy on body image and anxiety in anorexia nervosa: a randomized clinical efficacy ...
An investment in more research to benefit children and adolescents
2023-08-29
Launched in 2019, the Botnar Research Centre for Child Health (BRCCH) aims to drive innovative health research that benefits children and adolescents globally – especially those living in low- or middle-income countries. Within this centre, the University of Basel and ETH Zurich work in partnership with the University Children’s Hospital Basel (UKBB) and the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH).
Over the past four years, the BRCCH has supported around 80 researchers and 29 research projects worldwide. For example, researchers improved the treatment of cleft lip and palate and developed biotechnology to monitor paediatric gut ...
Maintaining stable weight increases longevity among older women
2023-08-29
Reaching the age of 90, 95 or 100, known as exceptional longevity, was more likely for women who maintained their body weight after age 60, according to a multi-institutional study led by University of California San Diego. Older women who sustained a stable weight were 1.2 to 2 times more likely to achieve longevity compared to those who experience a weigh loss of 5 percent or more.
Reporting in the Aug. 29, 2023 online issue of the Journal of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, researchers investigated the associations of weight changes later in life with exceptional longevity ...
Air pollution and its threat to health are unequally spread throughout the world, and so are the opportunities to combat it
2023-08-29
As global pollution edged upward in 2021, so did its burden on human health, according to new data from the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI). If the world were to permanently reduce fine particulate pollution (PM2.5) to meet the World Health Organization’s (WHO) guideline, the average person would add 2.3 years onto their life expectancy—or a combined 17.8 billion life-years saved worldwide.
This data makes clear that particulate pollution remains the world’s greatest external risk to human health, with the impact on life expectancy comparable to that of smoking, more than 3 times that of alcohol use and unsafe water, and more than ...
Overcoming the challenges to synthesising iron–sulfur proteins outside the glovebox
2023-08-29
Fe–S clusters, which are a part of Fe–S proteins, are found across all forms of life. They play a significant role as biological cofactors—helper molecules that assist these proteins in different biochemical transformations—that are involved in respiration and metabolism. These clusters are of keen research interest since they are considered to be a critical part of evolution. They serve as a link between pre-biotic chemistry (chemical processes that existed prior to the emergence of life forms) and the complex molecular and biological systems we know today. Put simply, they ...
Mothers in prison embrace a parenting program to strengthen bonds with separated children
2023-08-29
The number of women imprisoned in Australia has jumped by 64% in the past decade, leaving thousands of children separated from their mothers and causing huge stress to both parties.
In a bid to ease the strain of separation and maintain the mother-child bond, a new prison parenting program has been developed in close collaboration with women in prison as well as prison staff and key members of the Aboriginal community in South Australia.
The Mothers Matter program, led by University of South Australia midwife and researcher Belinda Lovell, includes direct input from Aboriginal and/or Torres ...
Resistant E. coli rises despite drop in ciprofloxacin use
2023-08-29
After a nearly threefold drop in prescriptions for the antibiotic ciprofloxacin between 2015 and 2021, the rates of ciprofloxacin-resistant E. coli bacteria circulating in the community did not decline.
In fact, a study of Seattle-area women over age 50 who had not taken any antibiotics for at least a year discovered that the incidence of gut-colonizing ciprofloxacin-resistant E. coli actually increased. About 1 in 5 women in the study were affected.
Scientists at the University of Washington School of Medicine, Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute and Seattle Children’s Hospital ...
Golden rules for building atomic blocks
2023-08-29
National University of Singapore (NUS) physicists have developed a technique to precisely control the alignment of supermoiré lattices by using a set of golden rules, paving the way for the advancement of next generation moiré quantum matter.
Moiré patterns are formed when two identical periodic structures are overlaid with a relative twist angle between them or two different periodic structures but overlaid with or without twist angle. The twist angle is the angle between the crystallographic orientations of the two structures. For example, when graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) which are layered materials are overlaid on each other, the atoms in the ...
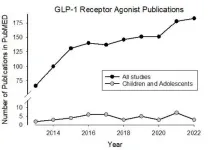
Researchers at UC Irvine issue a warning that GLP-1RA’s may be dangerous for children
2023-08-29
A team of clinicians, exercise scientists, pharmaceutical scholars, ethicists and behavioral experts at the University of California, Irvine, outlined their concerns that the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) to treat childhood obesity and type 2 diabetes may have unintended and adverse consequences for children’s health.
The commentary, Unintended Consequences of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Medication in Children and Adolescents – A Call to Action, was published as a perspective in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Science. The article was led by Dan M. Cooper, MD, distinguished professor in the Department of Pediatrics ...
Medicine: Mozart lullaby may relive pain in newborns during blood spot test
2023-08-29
Playing a Mozart lullaby may help reduce the pain experienced by newborn babies undergoing a heel prick blood test, according to a randomised, blinded clinical trial involving 100 infants published in Pediatric Research.
Saminathan Anbalagan and colleagues measured the pain levels of newborn infants undergoing a heel prick blood test as part of routine screening for conditions such as jaundice and phenylketonuria (PKU) in New York City, New York, USA between April 2019 and February 2020. Infants were, on average, two days old and born at 39 gestational weeks, while 53% were male and 61% were Hispanic. As part of standard care, all infants ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Produce prescription programs yield positive health benefits for participants, study findsIn the largest known such study to date, an analysis of participant records by Tufts University researchers found programs that provide free fruits and vegetables have measurable benefits for health and food security