(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semiannual content update with 1,945 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations exchange medical data. The release contains newly created content based on requests submitted by stakeholders from more than 100 countries.
LOINC version 2.75 is available for download from the LOINC website and via the LOINC Terminology Service using HL7® FHIR®. The updated version includes new, edited and newly mapped concepts in laboratory, clinical, survey and other domains. LOINC has users from nearly every country.
“Issuing these concepts semiannually helps support the exchange and aggregation of clinical results for the benefit of care delivery,” said Marjorie Rallins, DPM, M.S., executive director of LOINC and Health Data Standards. “The users’ ability to download LOINC or utilize HL7® FHIR® for version 2.75 concepts facilitates the seamless movement of healthcare data.”
Of the new concepts, 1,469 were laboratory-based and 476 were clinical observations and assessments.
The 2023 LOINC conference, set for October 17-20 in Atlanta, Georgia, will cover all the new concepts released in version 2.75. To register and learn more about the four-day conference, visit the LOINC website.
For any inquiries about the version 2.75 release of LOINC and to have discussions with others in the LOINC community, post the topic, question or concern in the LOINC Community Forum. This platform was recently relaunched with a new, simpler structure.
LOINC, short for Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, is a worldwide standard for identifying health measurements, observations and documents. Created and maintained at Regenstrief Institute, the code system is available to users at no cost. LOINC enables the identification, exchange and collection of data across health systems. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted and further emphasized the value of this standard and its impact on data interoperability.
About LOINC®
LOINC® was created in 1994 at Regenstrief Institute to facilitate interoperability in healthcare. There was a growing trend to send clinical data electronically between healthcare entities, a practice that has now become ubiquitous. Today, it contains more than 100,000 terms for everything from an albumin level to a zygomatic arch X-ray report. For each concept, LOINC contains many other rich details, such as synonyms, units of measure, and carefully crafted descriptions.
About Regenstrief Institute
Founded in 1969 in Indianapolis, the Regenstrief Institute is a local, national and global leader dedicated to a world where better information empowers people to end disease and realize true health. A key research partner to Indiana University, Regenstrief and its research scientists are responsible for a growing number of major healthcare innovations and studies. Examples range from the development of global health information technology standards that enable the use and interoperability of electronic health records to improving patient-physician communications, to creating models of care that inform clinical practice and improve the lives of patients around the globe.
Sam Regenstrief, a nationally successful entrepreneur from Connersville, Indiana, founded the institute with the goal of making healthcare more efficient and accessible for everyone. His vision continues to guide the institute’s research mission.
END
Partners from more than 100 countries collaborate as LOINC® issues 1,945 new concepts in semiannual release
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study will examine impact of lifestyle physical activity on cognition for older adults
2023-08-29
Jason Yang has been awarded nearly $400,000 from the National Institute on Aging to explore the role of lifestyle physical activity (light movements, walking) in cognition among insufficiently active older adults with higher risks for Alzheimer’s or related dementias. The exercise science assistant professor will use the two-year R21 grant to help determine if frequent and regular engagement in lifestyle physical activity over time may benefit cognitive function for this population.
A ...
More sleep could reduce impulsive behavior in children
2023-08-29
Sleep is a critical part of a child’s overall health, but it can also be an important factor in the way they behave.
According to a new study from the Youth Development Institute at University of Georgia, getting enough sleep can help children combat the effects of stressful environments.
“Stressful environments are shown to make adolescents seek immediate rewards rather than delayed rewards, but there are also adolescents who are in stressful environments who are not impulsive,” said lead author Linhao Zhang, a fourth-year doctoral student in UGA’s College of Family and Consumer Sciences. “We looked at what explains that link and what makes some people ...
New study sheds light on the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in abdominal aortic aneurysm
2023-08-29
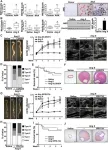
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a common degenerative vascular disease, particularly afflicts men over the age of 60, with up to 8% affected. Characterized by the abnormal dilation of the abdominal aorta, AAA risks a potentially fatal rupture. Despite increasing research efforts, effective pharmaceutical strategies to curb aneurysm growth remain elusive.
In a study published in the journal of Genes & Diseases, researchers from Sant Pau Hospital Research Institute and Biomedical Research Institute Sant Pau scrutinized the Wnt signaling pathway's deregulation in human abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). This ...
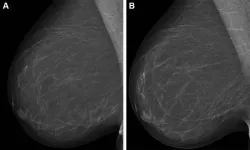
Combining AI models improves breast cancer risk assessment
2023-08-29
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Combining artificial intelligence (AI) systems for short- and long-term breast cancer risk results in an improved cancer risk assessment, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Most breast cancer screening programs take a one-size-fits-all approach and follow the same protocols when it comes to determining a woman’s lifetime risk of developing breast cancer. Using mammography-based deep learning models may improve the accuracy of breast cancer risk assessment and can also lead to earlier ...
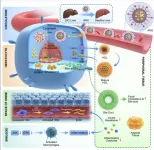
Anionic nanogel delivers effective anti-obesity drug to mouse livers
2023-08-29
An anti-obesity drug can be delivered selectively to the liver using a nanogel-based carrier, according to a study. Synthetic thyroid hormone mimics are promising treatments for metabolic diseases including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and inflammatory liver disease; however, the molecules are not highly bioavailable or potent, which are necessary to see significant weight loss. S. Thayumanavan and colleagues designed a nanogel-based carrier with anionic moieties on the surface ...
Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) selects Symplectic Elements to enable comprehensive research management
2023-08-29
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) has chosen Symplectic Elements from Digital Science’s flagship products to advance awareness of its world-class research.
ANSTO is the home to some of Australia’s most significant national infrastructure for research. Thousands of scientists from industry and academia benefit from gaining access to ANSTO’s ...
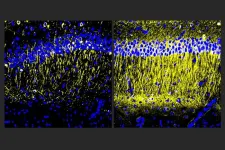
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer’s models
2023-08-29
Though drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer’s disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer’s mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
The target of the new “A11” molecule is a genetic transcription factor called PU.1. Prior research has shown that amid Alzheimer’s disease, PU.1 ...
Disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on American Indians
2023-08-29
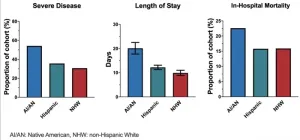
A study of COVID-19 patients at a New Mexico hospital finds that the virus hit American Indian patients particularly hard—even though Native American patients had fewer other illnesses or conditions than non-native patients. Douglas Perkins and colleagues analyzed data on 475 patients with COVID-19 infections from the University of New Mexico Hospital. The sample was 30.7% Native American, 47% Hispanic, and 18.5% non-Hispanic White. At admission, Native American patients were younger, more likely to need ...
Novel SwRI-developed antenna array wins 2023 R&D 100 Award
2023-08-29
SAN ANTONIO — August 29, 2023 —Novel Southwest Research Institute-developed direction-finding technology has won a prestigious R&D 100 Award. R&D World Magazine has recognized SwRI’s Wideband Conformal Continuous-Slot Antenna Array as one of the 100 most significant innovations for 2023.
“Southwest Research Institute strives to uncover innovative solutions to complex problems,” said SwRI President and CEO Adam L. Hamilton, P.E. “I am very proud of the work SwRI does and pleased to know this technology, which will provide significant support to naval operations, has been recognized as one of the most important innovations ...
Texas Biomed partners with Scancell to test novel COVID vaccine
2023-08-29
SAN ANTONIO (Aug. 29, 2023) – A DNA-based vaccine is very effective at protecting against COVID-19, according to a joint preclinical study by Scancell Ltd and Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) recently published in the Journal of Biotechnology and Biomedicine.
Unlike the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines that use messenger RNA (mRNA) to cue the immune system to produce antibodies, this vaccine platform uses sections of viral DNA to achieve a similar result.
“There is always a need to develop new, or improve on existing vaccines to ensure we have effective tools to counter emerging variants,” says Texas Biomed Innovation ...