(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — Recently, when customers began complaining that their vehicles with driver-assistance technologies were “phantom braking” or slamming on the brakes without any visible obstacles present, researchers at Michigan State University wanted to learn more about this phenomenon — why it happens and how to stop it.
“Frequent phantom braking incidents can erode confidence in autonomous driving technologies,” said Qiben Yan, an assistant professor in the College of Engineering. “If riders perceive the technology as unpredictable or unreliable, they’ll be less likely to embrace it.”
Autonomous vehicles have a vision system, composed of multiple cameras and radar, that uses radio waves to gather information the car leverages to navigate the world around it. In previous research, Yan and his team were able to show how the cameras in these vision systems can be deceived by hackers.
“We projected lights into the cameras of the vehicle, and the camera recognized this as a false object and hit the brakes; it is surprising how fake things can be created out of nowhere,” said Yan. “We were also able to make an object in front of the car disappear to the camera so that the vehicle couldn’t see an obstacle, and the vehicle hit the object.”
This new NSF grant — with Associate Professor Sijia Liu and MSU Research Foundation Professor Xiaoming Liu from MSU, and in collaboration with Virginia Tech — will help the researchers expand their knowledge by studying how cameras see these phantom attacks and identify ways to keep these vision systems more secure and resilient against nefarious attacks.
Yan and his team are using some ideas from the field of neuroscience that study how human eyes and brains are tricked by optical illusions.
“We borrowed some ideas from human perception studies to understand the AI systems behind the vision system,” said Yan. “We know that vision systems can be deceived, and we want to program the AI model to see the environment and interpret the information more accurately.”
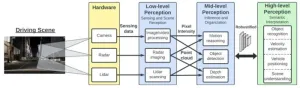
There are three levels of perception. Low-level perception means the vision system can see the scene in front of it, and mid-level perception recognizes what an object is and can determine how far away it is. In high-level perception, the system can recognize how fast an object is moving and how the object is part of the scene.
“We try to understand the evolution of perception from one level to the next,” said Yan. “Next, we want to develop a defense that ensures inherent security and to enhance the AI model that powers it.”
This research will help make autonomous vehicles smarter and safer in the future.
“Addressing the phantom braking issue is not just about refining the vision technologies, it’s about the overall viability, safety and success of autonomous vehicles in the future,” said Yan.
By Emilie Lorditch
Read on MSUToday.
###
Michigan State University has been advancing the common good with uncommon will for more than 165 years. One of the world's leading research universities, MSU pushes the boundaries of discovery to make a better, safer, healthier world for all while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 400 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
END
Using neuroscience to stop phantom braking
MSU has received a $1.2 million multiyear grant from the National Science Foundation to understand the security of autonomous vehicles’ vision systems
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sensitive parenting and preschool attendance may promote academic resilience in late preterm infants
2023-08-29
Late preterm infants, or infants born between 34 and 36-6/7 weeks gestation, are the majority of infants born preterm, and are at greater risk for academic delays compared to full term infants.
Certain factors, including a low level of maternal education, prenatal tobacco use, twins/multiple gestation and male sex increased the risk for deficits in math and reading by kindergarten for late preterm infants, a new study finds.
However, sensitive parenting and preschool enrollment are two possible ways to counter the risk of being born late preterm, and to promote academic resilience.
“Our findings highlight an opportunity for pediatric providers to offer prevention strategies ...
New imaging technique could provide clearer images for oncologists
2023-08-29
A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).
QPAT is an imaging modality that combines ultrasound, which is an imaging technique that uses sound waves to image features inside ...
Neptune's disappearing clouds linked to the solar cycle
2023-08-29
Astronomers have uncovered a link between Neptune's shifting cloud abundance and the 11-year solar cycle, in which the waxing and waning of the Sun's entangled magnetic fields drives solar activity.
This discovery is based on three decades of Neptune observations captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii, as well as data from the Lick Observatory in California.
The link between Neptune and solar activity is surprising to planetary scientists because Neptune is our solar system's farthest major planet and receives sunlight with about 0.1% ...
Liver-targeting drug reverses obesity, lowers cholesterol in mice
2023-08-29
A University of Massachusetts Amherst biomedical engineer has used a nanogel-based carrier designed in his lab to deliver a drug exclusively to the liver of obese mice, effectively reversing their diet-induced disease.
“The treated mice completely lost their gained weight, and we did not see any untoward side effects,” says S. Thai Thayumanavan, distinguished professor of chemistry and biomedical engineering. “Considering 100 million Americans have obesity and related cardiometabolic disorders, we became pretty excited about this work.”
Efforts ...
MIND Institute director calls for new approach to equity in autism, fragile X research
2023-08-29
UC Davis MIND Institute Director Leonard Abbeduto is calling for a major shift in the way research into autism and other neurodevelopmental disabilities is conducted. He co-authored a paper titled “Toward Equity in Research on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities” that was the basis for a special issue of the American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. The issue was published today.
Abbeduto, a distinguished professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, argues that researchers ...
Rapid shifts from drought to downpour occurring more often
2023-08-29
New research shows that wild swings from severe drought to heavy rains are becoming more common with climate change in many parts of the world and that feedback loops from the land itself are likely contributing to the trend.
The research looked at four decades of meteorological and hydrological data on a global level and found seven regional hotspots around the world where the trend was getting worse: eastern North America, Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, southern Australia, southern Africa, and southern South America.
“We are especially concerned with the sudden shift from drought to flood,” said coauthor Zong-Liang Yang, a professor at The University of Texas at Austin Jackson ...
Hemp helps to heal
2023-08-29
A few days ago, the federal government took the controversial decision to make the acquisition and possession of small amounts of cannabis exempt from punishment. Provided the German parliament approves the draft bill, the “Cannabis Act” will come into force next year. While some consider this move to be long overdue, others continue to warn strongly against the health risks of cannabis use.
The Jena researchers and their colleagues are now taking a different look at cannabis – at the traditional medicinal ...
Department of Energy announces $24 million for research on quantum networks
2023-08-29
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $24 million in funding for three collaborative projects in quantum network research.
Scientific research infrastructure linked with quantum networks is needed to realize distributed quantum computers. These quantum computers could simulate complex scientific processes inaccessible to computational platforms of today, integrate quantum sensors that promise measurements of unprecedented precision, and address previously inaccessible scientific questions of importance.
“Advances in quantum networking are enabling effective interconnections ...
A new fly model developed to find treatments for UBA5 deficiency, a rare epileptic brain disorder
2023-08-29
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy (DEE) refers to a group of neurodevelopmental conditions characterized by developmental delay, cognitive impairment, and seizures in children. In 2016, the first case linking variants in both the copies of UBA5 gene to DEE44 was reported. Since then, twelve distinct missense variants in the UBA5 gene have been identified in 25 patients. A recent study by Dr. Hugo J. Bellen and his team at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of ...
Statewide project to provide care and support to people living with dementia and their care partners
2023-08-29
INDIANAPOLIS—An Indiana University School of Medicine statewide project in collaboration with Indiana University Health was recently funded to support people living with dementia as well as their family care partners find more support and resources, thanks to a new $686,000 grant from the National Institute on Aging IMPACT Collaboratory.
The Aging Brain Care Virtual program will be the first study to test dementia collaborative care in Indiana University Health primary care. The project will utilize the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Using neuroscience to stop phantom brakingMSU has received a $1.2 million multiyear grant from the National Science Foundation to understand the security of autonomous vehicles’ vision systems