(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study suggest that a weighted lottery to allocate scarce resources is feasible and may result in more drug allocation to individuals who reside in disadvantaged neighborhoods and who identify as Black; however, Black individuals allocated the drug may be less likely to accept allocation and receive it.
Authors: Erin K. McCreary, Pharm.D., of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.2774)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.2774?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=090123
About JAMA Health Forum: JAMA Health Forum is an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
END
Weighted lottery to equitably allocate scarce supply of COVID-19 monoclonal antibody
JAMA Health Forum
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Telehealth vs in-clinic medication abortion services
2023-09-01
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that telehealth medication abortion services (tele-MAB) facilitates abortion care access for those further from brick-and mortar abortion facilities and, thus, may mitigate the impacts of travel logistics and costs. Additionally, tele-MAB may better meet the needs of those with prior abortion experience, perhaps due to greater familiarity with the abortion process.
Authors: Anna E. Fiastro, M.P.H., M.E.M., Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31900)
Editor’s ...
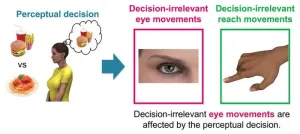
The eyes are a window into the deciding mind
2023-09-01
Researchers worldwide are seeking visible indicators of what is going on inside our minds as we think about issues and take decisions. They are searching for the ability to probe the invisible workings of the mind by monitoring subtle signals from the body. New insights from experiments at Tohoku University have revealed a link between eye movements and certain types of decision-making. Kazumichi Matsumiya and Shota Furukawa at the university's Graduate School of Information Sciences reported their findings in the journal Communications Biology.
"Our work has revealed that eye movements that are not ...
Three types of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation influence precipitation over the Yangtze river valley in various ways
2023-09-01
The Yangtze River Valley (YRV) is one of the most densely populated and economically developed regions in China. Summer precipitation over this region shows considerable intraseasonal variability with a period of 10–90 days, which can induce extreme precipitation events and lead to massive economic losses and human casualties.
The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO) is the intraseasonal variability active in the tropical Indian Ocean and western Pacific region. Over the last three decades, scientists have studied the influence of the BSISO, because it is an essential predictability source in extended-range forecasts.
A new study published in Atmospheric ...
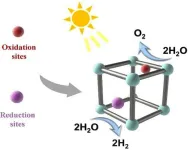
Roadmap drafted for research into metallic ‘sponges’ for clean hydrogen
2023-09-01
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) could deliver a major efficiency boost to the photocatalytic production of clean hydrogen. Chemical engineers have drafted a comprehensive overview of the state of their field and a plan for where it needs to focus.
Clean hydrogen production remains an energy-intensive and therefore costly proposition, inhibiting the battle against global warming. Metal organic frameworks—in effect tiny molecular ‘sponges’—look set to radically improve the efficiency of photocatalytic production of hydrogen due to their unique structural ...
Radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes receives $3.5 million from NIH
2023-09-01
The National Institutes of Health has provided $3.5 million for a large-scale clinical trial testing a radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes that, in an earlier study, put almost 70% of participants in remission without weight loss or medication.
The approach was developed by UVA Health’s Daniel J. Cox, PhD. It is built on the notion that educating people about how to make wise dietary and exercise choices can allow them to control their blood sugar and possibly even alter the course of the disease.
“Instead of focusing on reducing weight with diets ...
Breakthrough in atmospheric analysis: Chinese satellite delivers high spatial resolution ozone profiles
2023-09-01
A breakthrough in satellite observations has allowed scientists to obtain high spatial resolution ozone profiles, enhancing our understanding of ozone distribution and its impact on the atmosphere. The research, conducted by the research team led by Cheng Liu and Fei Zhao at the University of Science and Technology of China, utilized data from the Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument (EMI) on the Gaofen-5 satellite, the first Chinese ultraviolet-visible hyperspectral spectrometer.
Ozone plays a crucial role in the atmosphere, and understanding its vertical distribution is key to comprehending its horizontal and vertical transport, as well as its physical and chemical ...
Flowering for naught: 120 years with nothing to show
2023-09-01
A long-lived monocarpic species of bamboo, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, only flowers once every 120 years before it dies. The upcoming flowering event for this species does not bode well for its continued long-term survival, as most flowers are not producing viable seeds.
Flowering for some plants is a yearly occurrence, for others, it is a once-in-a-lifetime event. A widespread species of bamboo in Japan, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, takes this one-time flowering event and pushes it to the extreme: they flower once every 120 years before dying to make way for the next ...
TTUHSC secures National Academy of Inventors membership
2023-09-01
Since its inception in 2009 with 13 founding institutions, the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has grown to more than 4,600 individual members worldwide from more than 300 U.S. and international colleges and universities, government agencies and non-profit research institutes. That growth continued recently when the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) added its name to the NAI membership roster.
Lance R. McMahon, Ph.D., TTUHSC senior vice president for research and innovation, said the university’s new NAI membership and the appointment of several faculty members as senior members ...
Amsterdam UMC is building models to enable greater use of AI in the health care system
2023-09-01
80% of all patient data is unstructured. Notes from a conversation with a GP, the evaluation of a specialist in a university medical centre or even a recommendation from a pharmacist. While this 'unstructured’ data is no problem for the human eye, it presents an unsurmountable challenge to an AI-algorithm. One that is "preventing AI from reaching its full potential," in the view of Amsterdam UMC, Assistant Professor Iacer Calixto. To give AI the helping hand that it needs, Calixto is set to lead a project that will "tackle the important challenges ...
FAIR data and inclusive science to enable clean energy
2023-09-01
Fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy. The Sun and all stars are powered through fusion, which makes it the universe's preferred method of producing energy. Recent breakthroughs in fusion research have led to the US government's Bold Vision for Commercial Fusion Energy and the remarkable growth of the global fusion industry.
To accelerate the development of fusion-powered reactors on Earth, the US Department ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Weighted lottery to equitably allocate scarce supply of COVID-19 monoclonal antibodyJAMA Health Forum