(Press-News.org) Micro- and nanodisk lasers have recently emerged as promising optical sources and probes for various applications in the fields of nanophotonics and biomedicine. Their ability to achieve lasing at a deterministic wavelength and ultra-narrowband precision is critical for several applications in on-chip photonic communications, on-chip bioimaging, biochemical sensing, and quantum photonic information processing. However, the large-scale fabrication of such precise wavelength micro- and nanodisk lasers remains challenging. Current nanofabrication processes introduce randomness in the disk diameter, making it difficult to achieve deterministic wavelengths in laser batches.
Addressing this issue, a team of researchers from Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital’s Wellman Center for Photomedicine has developed an innovative photoelectrochemical (PEC) etching-based technique that facilitates precise tuning of the lasing wavelength of microdisk lasers with subnanometric accuracy. Their work is published in the Gold Open Access journal Advanced Photonics.
The new approach allows for the fabrication of micro- and nano-laser batches with precise and predetermined emission wavelengths. The key to this breakthrough lies in the use of PEC etching, which offers an efficient and scalable way to fine-tune the wavelength of microdisk lasers.
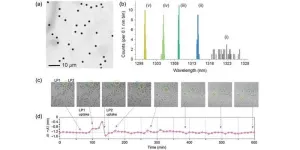
In their work, the team successfully obtained SiO2-capped indium gallium arsenide phosphide microdisks on indium phosphide pillar structures. Then they precisely tuned the lasing wavelengths of these microdisks to deterministic values, by performing photoelectrochemical etching in a diluted sulfuric acid solution. They also examined the mechanism and kinetics underlying the specific PEC etching. Finally, they transferred the wavelength-tuned microdisk arrays onto a polydimethylsiloxane substrate, producing free-standing, isolated laser particles with distinct lasing wavelengths. The resulting microdisks showed lasing emission with an ultranarrow bandwidth of less than 0.6 nm for on-pillar lasers and under 1.5 nm for the isolated particles.
This result opens doors to many new nanophotonic and biomedical applications. For instance, the free-standing microdisk lasers can serve as physical optical barcodes for heterogeneous biological samples, enabling the tagging of specific cell types and the targeting of specific molecules in multiplexed assays.
Cell-type specific tagging is currently performed using conventional biomarkers, such as organic fluorophores, quantum dots, and fluorescent beads, which have broad emission linewidths. As a result, only a few specific cell types can be tagged simultaneously. In contrast, microdisk lasers with their ultra-narrowband light emission would enable simultaneous identification of a larger number of cell types.
Accordingly, the team tested out and successfully demonstrated the precisely tuned microdisk laser particles as biomarkers by using them to tag live normal breast epithelial MCF10A cells in culture. With their ultranarrow bandwidth emission, these lasers can potentially revolutionize biosensing performed using well-established biomedical and optical techniques, such as cell dynamics imaging, flow cytometry, and multi-omics analyses.
The PEC etching-based technique marks a significant advancement of microdisk lasers. The scalable nature of the method, along with its sub-nm accuracy, opens up new possibilities for the myriad applications such lasers find in nanophotonic and biomedical devices as well as in the barcoding of specific cell populations and assay molecules.
For details, read the Gold Open Access article by D. Sarkar et al., “Precise photoelectrochemical tuning of semiconductor microdisk lasers,” Adv. Photon. 5(5), 056004 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.AP.5.5.056004.
END
New scalable, etching-based technique for precise tuning of microdisk lasers
Researchers have developed a photoelectrochemical technique that enables precise wavelength tuning of semiconductor lasers with sub-nanometer accuracy
2023-09-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Seismologists use deep learning for improved earthquake forecasting
2023-09-02
For more than 30 years, the models that researchers and government agencies use to forecast earthquake aftershocks have remained largely unchanged. While these older models work well with limited data, they struggle with the huge seismology datasets that are now available.
To address this limitation, a team of researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz and the Technical University of Munich created a new model that uses deep learning to forecast aftershocks: the Recurrent Earthquake foreCAST (RECAST). In a paper published today in Geophysical Research Letters, the scientists show how the deep learning model is more flexible ...
Software developed at UC Davis analyzes calcium ‘sparks’ that can contribute to arrhythmia
2023-09-01
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — A team of UC Davis and University of Oxford researchers have developed an innovative tool: SparkMaster 2. The open-source software allows scientists to analyze normal and abnormal calcium signals in cells automatically.
Calcium is a key signaling molecule in all cells, including muscles like the heart. The new software enables the automatic analysis of distinct patterns of calcium release in cells. This includes calcium "sparks," microscopic releases of calcium within cardiac cells associated ...
Could insights from ants help people build better transportation networks?
2023-09-01
Key takeaways
Ants can either forage for food as individuals or recruit other members of their colonies to help search for or carry food back to their nests.
UCLA biologists found that the strategies ants use to forage play a bigger role in how they build their nests than innate, evolutionary “blueprints” do.
When building nests, ants strike a balance between transportation efficiency and architectural constraints. Researchers say that observation could help humans design more efficient transportation systems tailored to specific needs.
Could ants’ nests hold the secret to reducing traffic congestion on the 405 Freeway?
In a new study, UCLA biologists ...
Invasive spotted lanternfly may not damage hardwood trees as previously thought
2023-09-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In 2012, when the spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula) arrived in the U.S. from its home in China, scientists, land managers, and growers were understandably concerned that the sap-feeding insect would damage native and commercial trees. New long-term research led by Penn State has discovered that hardwood trees, such as maple, willow and birch, may be less vulnerable than initially thought.
“Since the lanternfly was first introduced to the northeastern U.S., the question has been, ‘How at-risk are our forests?’ said Kelli Hoover, professor of entomology at Penn State. “So far, we haven't had a good answer. Our study is the first ...
$26M NIH grant addresses environmental influences on child health
2023-09-01
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Backed by a $26 million federal grant, researchers at three Michigan universities, a leading health care system, and a state agency will continue a long-term study of how exposure to environmental factors during pregnancy and early childhood can impact health for a lifetime.
The funding from the National Institutes of Health, or NIH, is for the second phase of a national research program called ECHO, which stands for the Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes, and includes a sample of mothers, infants and children from across the United States. The first phase began in 2016.
“This award shows the research ...
LDL not the be all, end all in heart disease, heart attacks and stroke
2023-09-01
Milwaukee, Wis. – Sept. 1, 2023 – Despite advances in treatment for high cholesterol, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S. Scientists at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) are investigating the role of a form of cholesterol called very-low-density lipoprotein – and their findings may lead to new treatment options in the future.
The research team is led by Ze Zheng, MBBS, PhD, MCW assistant professor of medicine (endocrinology and molecular medicine); co-leader of the MCW Cardiovascular Center’s Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis ...
Hot Jupiter blows its top
2023-09-01
A planet about 950 light years from Earth could be the Looney Tunes’ Yosemite Sam equivalent of planets, blowing its atmospheric ‘top’ in spectacular fashion.
The planet called HAT-P-32b is losing so much of its atmospheric helium that the trailing gas tails are among the largest structures yet known of an exoplanet, a planet outside our solar system, according to observations by astronomers.
Three-dimensional (3D) simulations on the Stampede2 supercomputer of the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) helped model the flow of the planet’s atmosphere, ...
Kidder receives American Chemical Society’s 2023 Mid-Career Award
2023-09-01
Michelle Kidder, a senior R&D staff scientist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has received the American Chemical Society’s Energy and Fuels Division’s Mid-Career Award for sustained and distinguished contributions to the field of energy and fuel chemistry. She was recognized for her scientific community service, leadership and contributions. Her research focuses on novel material development, methods and advanced characterizations for the separation and reaction chemistry of renewable energy resources including lignin and carbon dioxide.
Kidder, ...
Mukherjee elevated to senior member of IEEE
2023-09-01
Subho Mukherjee, an R&D associate in the Vehicle Power Electronics Research group at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elevated to the grade of senior member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, or IEEE. Senior IEEE members have made significant contributions to the profession and worked in the engineering field for 10 years or more.
As an electrical engineer, Mukherjee focuses on wireless power charging and developing wide bandgap semiconductor-based ...
SMART-BARN – a cutting-edge technology lab to study animal groups
2023-09-01
Researchers from the Cluster of Excellence Centre for the Advanced Study of Collective Behaviour (CASCB) and the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior have converted a former barn into a cutting-edge technology lab for complex behavioral analysis. In it, they can now study the intricate behaviour of animal groups. The barn also served as a prototype for the largest swarm behaviour lab at the University of Konstanz: the Imaging Hangar.
A major limitation in behavioural research is that scientists can either study animals under highly-controlled, yet often unrealistically simplified and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New scalable, etching-based technique for precise tuning of microdisk lasersResearchers have developed a photoelectrochemical technique that enables precise wavelength tuning of semiconductor lasers with sub-nanometer accuracy