(Press-News.org) Over the course of four weeks this summer, a motley crew of biologists, engineers, entrepreneurs and programmers gathered at predetermined sites within Windsor Nature Park, a 185-acre tropical rainforest located in the heart of Singapore. They’d traveled from all over the world to participate in a one-of-a-kind competition hosted by the XPRIZE Foundation, in which 13 teams would have three days to identify as many organisms within the forest as possible.
Up to 10 winning teams would equally split $2 million and advance to the 2024 finals, where they’d vie for the first-place prize of $5 million. But there was a catch: All observations and data collection had to be conducted remotely.
“The competition is specifically intended to spur the development of technology that allows us to monitor biodiversity within rainforests without disturbing the ecosystem,” said Niyomi House, a National Science Foundation postdoctoral fellow with the Florida Museum of Natural History.
House is a member of Team Waponi, which is led by Thomas Walla, a professor of biology at Colorado Mesa University, and is one of the few groups that made it to the semifinals in Singapore this summer. After a delay in which judges tallied the number of species and verified identifications, XPRIZE recently announced that Team Waponi is among the six finalists and will compete next year in Brazil’s Amazon Rainforest in the state of Amazonas.
The winning device that secured the team’s place in the finals involved a wireframe box, a drone and a saw.
“Our team invented a device called the Limelight, which attracts insects in the forest canopy,” House said. On the morning of June 3, members of Team Waponi carefully assembled their equipment and waited for noon, which would mark the start of their 24 hours they’d have to collect data.
When the clock started, drone operators piloted five Limelight devices into the canopy, gently placing each into the bough of a tree. As the sun descended, bulbs attached to the frame flicked on, illuminating a white canvas that served as both beacon and landing pad for insects attracted to the light. Cameras on either end of the screen photographed each visitor. Above this stage, a malaise trap captured insects as they flew upward, while an inverted pit trap below caught insects attempting to crawl away.
A third trap was stocked with a pungent lure to attract dung flies and an additional camera to photograph them. The Limelight devices were also equipped with bioacoustics recorders. The team was counting on these digital eyes and ears to detect more than members could with their own senses.
Before navigating back to the group, the drones collected plant samples using an extendable saw. The team’s time was cut short by five hours because of storms that dropped thick sheets of rain, during which the drones couldn’t operate. But when the skies cleared and the Limelights were retrieved, the devices were filled with hundreds of insects. That’s when the real work began.
“Each team had 48 hours to extract and sequence DNA, analyze the results and write a report,” House said. “The experience felt like completing an entire master’s degree in just two days.”
House and her teammate set about gleaning as much information as they could from each specimen, splitting their time between a field lab set up in a tent and a molecular lab at the nearby National University of Singapore.
Meanwhile, other members of the team ran each photograph through machine learning software, which identified insects based on their physical characteristics. A similar program was used to single out the various hoots, howls, caws and grunts captured by the bioacoustics monitor and match them to those of prerecorded animals.
When they added everything together, the team members had collectively identified hundreds of species, genera and families, all without stepping foot in the forest. The speed at which they could strip living things down to their component DNA base pairs and use that to decipher the identity of the organism they belonged to was a physical and technological feat.
“The way it’s currently done, the process of DNA extraction, amplification, cleaning and creating a genetic library is not easy. There are several reagents that have to go in at different times with specific temperatures, and it takes hour and hours of training to learn how to do it,” House said.
The main goal of the XPRIZE competitions is to test and extend the limits of existing technology. The foundation got its start in 1996 with a $10 million prize for the team that could design a suborbital aircraft capable of flying into space.
A few years ago, it would have been impossible to identify organisms across an entire ecosystem with ambient noise and trace amounts of DNA. Team members are in the process of adding even more bells and whistles to the Limelight before the competition’s final round, but regardless of the outcome, they intend to continue developing techniques that make biodiversity science and monitoring more accessible to everyone.
“My dream is to eliminate the complexity of DNA sequencing by creating a set of standard tools and kits people can use in different situations and a pipeline that tells them what’s available and how to access it,” House said.
END
Florida Museum researcher advances to finals in multimillion-dollar biodiversity competition
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The first book to combine mineral nutrition and plant disease gets updated
2023-09-05
Approximately 95% of the world’s food supply is directly or indirectly produced on soil, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Soil health is therefore critical to the health of all living organisms—especially plants. Equally as critical, resources that consider the overlap between soil’s mineral nutrition and plant diseases have been scarce, until members of the American Phytopathological Society (APS) recognized this gap.
APS PRESS has newly published an updated edition of the first book to successfully combine the two important plant science disciplines of nutrition and pathology. Mineral Nutrition and Plant Disease, ...
IKIDS child health research gets another boost in funding
2023-09-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Seven years after an initial $17.9 million award from the National Institutes of Health, the Illinois Kids Development Study at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign will receive approximately $13.7 million – awarded in two phases – to continue its work for another seven years. The money coming to Illinois is part of a national collaborative effort to explore how environmental exposures influence child development, cognition, growth and health.
IKIDS is part of Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes, a national initiative to study five ...
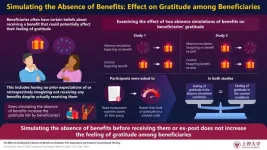
Does a “surprise” factor in gift-giving affect beneficiaries’ gratitude? Scientists answer
2023-09-05
Gratitude is a strong emotion, usually felt by a person who benefits from an intentional good deed of another person. Receiving gifts or benefits can instill a feeling of gratitude in people who receive them, i.e., beneficiaries, encouraging them to be more prosocial, while also helping to create a bond with their benefactors. This has led several researchers to examine the determinants of gratitude. Interestingly, beneficiaries often have preconceived beliefs about receiving a benefit. For instance, they may have no prior expectations of receiving a ...
Clarissa Campbell and Barbara Maier at CeMM receive ERC Starting Grants
2023-09-05
Two scientists at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences have received prestigious ERC Starting Grants from the European Commission: Clarissa Campbell and Barbara Maier. In Clarissa Campbell's laboratory, researchers are working to better understand the interplay between the immune system and metabolism. Barbara Maier and her team are researching the role of lymph nodes in the context of cancer.
(Vienna, 5 September 2023) The ERC grants are among the most prestigious and competitive research grants offered ...
Faster postal service linked to better voter turnout
2023-09-05
PULLMAN, Wash. – A more efficient U.S. Postal Service can increase voter turnout in all states regardless of their mail voting laws, according to a Washington State University study.
WSU researcher Michael Ritter analyzed election data from 2012 through 2020, when the pandemic encouraged many more people than usual to vote by mail. He found that in general more accessible mail voting laws, such as universal mail-in voting and no-excuse mail voting, increased the probability that individuals would vote. Restrictive laws, such as requiring ...
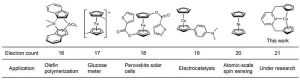
Scientists synthesize new organometallic “sandwich” compound capable of holding more electrons
2023-09-05
Organometallic compounds, molecules made up of metal atoms and organic molecules, are often used to accelerate chemical reactions and have played a significant role in advancing the field of chemistry.
Metallocenes, a type of organometallic compound, are known for their versatility and special "sandwich" structure. Their discovery was a significant contribution to the field of organometallic chemistry and led to the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973 to the scientists who discovered and explained their sandwich structure.
The ...
Study confirms it: Opposites don't actually attract
2023-09-05
Opposites don’t actually attract.
That’s the takeaway from a sweeping CU Boulder analysis of more than 130 traits and including millions of couples over more than a century.
“Our findings demonstrate that birds of a feather are indeed more likely to flock together,” said first author Tanya Horwitz, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience and the Institute for Behavioral Genetics (IBG).
The study, published Aug. 31 in the journal Nature Human Behaviour, confirms what individual studies have hinted at for decades, defying the age-old adage that “opposites ...
Poor water quality disproportionately affects socially vulnerable communities
2023-09-05
A new study published in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters examines the links between drinking water quality violations and social vulnerability in the United States, revealing that these violations disproportionately affect the most vulnerable communities. Approximately 70% of the population affected ranked in the highest social vulnerability category, with many different social parameters, beyond income, linked to different drinking water quality violations.
The study, led by researchers from the Jackson School of Geosciences, University of Texas in Austin, used new water quality data ...
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department use in British Columbia
2023-09-05
A new study showing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and mitigation strategies used to manage the virus on emergency department (ED) visits in British Columbia can help with future planning. The study is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221516.
"Evaluation of the effects of the pandemic and associated measures can provide a historical account and inform health care service planning for both postpandemic recovery and mitigation of potential consequences ...
THE LANCET PLANETARY HEALTH: Experts warn 'green growth' in high income countries is not happening, call for 'post-growth' climate policies to meet Paris targets
2023-09-05
Peer-reviewed / Empirical study
New study challenges political claims that some high-income countries have achieved “green growth”– revealing that under current growth-oriented strategies, emission reductions in these nations fall drastically short of meeting the climate goals and fairness requirements of the Paris Agreement.
If current trends continue, even the 11 high-income countries that have "decoupled" carbon emissions from GDP growth would on average take over 200 years to get their emissions close to zero, and would emit more than 27-times their fair share of the “global carbon budget” ...