New method enables efficient isolation of raccoon-borne food poisoning pathogen
2023-09-06
(Press-News.org)
Osaka, Japan – As cute as raccoons may look, their behaviors are troublesome, and so are their droppings. Known to contain Escherichia albertii—a harmful enteropathogen—raccoon feces challenge zoonotic researchers who grapple to isolate this bacterium for further study. Fortunately, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have come up with a novel culture medium for efficient isolation of E. albertii, making progress toward alleviating this particular raccoon-conveyed threat.
Due to global warming, wildlife habitats are overlapping with human residential areas, raising concerns about the transmission and spread of zoonotic diseases. In recent years, an emerging zoonotic pathogen called E. albertii—transmitted by wild animals such as raccoons—has garnered attention due to its remarkable similarities to several strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), including O157, and its potential for causing severe illness, particularly in children. However, characteristics of this bacterium, including its infection routes and antibiotic resistance status, remain unclear.
To identify the route of infection, it is essential to isolate and then investigate E. albertii from specimens of wild animals acting as vectors. However, the quantity of E. albertii in samples sourced from raccoons is often minuscule, making its extraction an ongoing challenge.
Addressing this issue, a research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki of the Graduate School of Veterinary Science at Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a novel culture medium that selectively promotes the growth of E. albertii from raccoon fecal samples. They succeeded in isolating E. albertii at a rate as high as 48%, even from samples with very low quantities of this bacterium.
Professor Yamasaki explained, “The selective enrichment medium developed in this study is expected to provide better insights into the epidemiology of E. albertii, facilitating improved control of food poisoning.”
Their findings were published in the Journal of Applied Microbiology.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-06
The research team led by Dr. Se-Jong Kim and Dr. Juwon Na of the Materials Data Management Center in the Materials Digital Platform Division together with the research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee of POSTECH has developed a technology that can automatically identify and quantify materials microstructure from microscopic images through human-in-the-loop machine learning. KIMS is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Microscopic imaging systems visualize material structure information at multiple ...
2023-09-06
Further conservation measures are required to protect Vietnamese reptiles, such as the psychedelic rock gecko (Cnemaspis psychedelica), from habitat loss and overharvesting, concludes a new report, published in the open-access scientific journal Nature Conservation.
Having identified areas of high reptile diversity and large numbers of endangered species, the study provides a list of the 50 most threatened species as a guide for further research and conservation action in Vietnam.
The study, based on the bachelor thesis of Lilli Stenger (University of Cologne, Germany), recommends IUCN CPSG’s ...
2023-09-06
A unique program that sees students at the Medical College of Georgia working as anesthesia technologists throughout their four years of medical school can influence more of them to pursue the specialty as a career, investigators report.
The MCG Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine’s nearly 100-year-old Externship Program is one of only five or six in the country and allows interested medical students to work nights, weekends and holidays, as a critical part of the anesthesia and operating room teams. Anesthesia techs are typically responsible for sterilizing, cleaning, assembling, calibrating, testing and troubleshooting various pieces of machinery in the operating ...
2023-09-06
WASHINGTON (September 6, 2023) – An annual survey of physical and sexual violence suffered by Californians documents for the first time the higher incidence of violence among non-binary and transgender people. One in 20 California adults has experienced physical violence (5%) in the past year, a decrease from 8% in 2022, according to The California Violence Experiences Study (CalVEX); but the reported rates for non-binary and transgender individuals were notably higher, 14% and 27%, respectively.
“The new data we have in this year’s report show that rates of violence have declined since levels seen during the pandemic, but these experiences remain too ...
2023-09-06
SALT LAKE CITY, Sept. 6, 2023 – Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ:MYGN), a leader in genetic testing and precision medicine, today revealed new nationwide survey results indicating widespread confusion and misconceptions about ovarian cancer screening among a majority of women.
The Myriad Genetics Cancer Risk survey shows that nearly three out of four women (71%) falsely believe annual pap smears include testing for ovarian cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the “only gynecologic cancer the Pap test screens for is cervical cancer.”
“Ovarian cancer is ...
2023-09-06
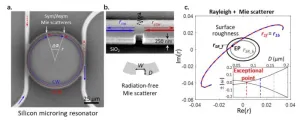
Non-Hermitian systems with their spectral degeneracies known as exceptional points (EPs) have been explored for lasing, controlling light transport, and enhancing a sensor’s response. A ring resonator can be brought to an EP by controlling the coupling between its frequency degenerate clockwise and counterclockwise traveling modes. This has been typically achieved by introducing two or more nano-tips into the resonator’s mode volume. While this method provides a route to study EP physics, the basic understanding of how the nano-tips’ shape and size symmetry impact the system’s non-Hermicity is missing, along with additional loss from both in-plane and out-of-plane ...
2023-09-06
A newly discovered way of optimising plant enzymes through bioengineering has increased knowledge of how plant material can be converted into biofuels, biochemicals and other high-value products.
The University of Adelaide-led study presents innovative ideas for how the walls of plant cells can be assembled, structured and remodelled by controlling specific enzymes’ catalytic function.
Fundamental plant cell properties – such as structure, integrity, cytoskeletal organisation and stability ...
2023-09-06
A multidisciplinary team of investigators from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center was awarded a $2.5 million Translational Team Science Award from the Department of Defense to develop a tailored treatment for glioblastoma, a deadly brain tumor with limited treatment options.
The team — including David Nathanson, associate professor of molecular and medical pharmacology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Benjamin Ellingson, director of the UCLA Brain Tumor Imaging Laboratory and professor of radiological ...
2023-09-06
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL SEPT. 5, 2023 AT 8 P.M. ET) – A new analysis of liver cancer has identified racial and ethnic differences and emerging trends for this highly fatal disease. The study, conducted by researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations, also identified potential targeted interventions to improve control and prevention.
Their extensive review, published Sept. 6 in the journal Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, examined 14,420 confirmed ...
2023-09-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Forest thinning is improving the robustness of older trees and enhancing native biodiversity on federal lands in eastern Oregon, evidence that collaborative efforts to restore forests are working, research by Oregon State University shows.
The study led by James Johnston of the OSU College of Forestry involved long-term monitoring and research partnerships between OSU, the U.S. Forest Service and local groups in Oregon’s Blue Mountains.
Published today in Forest Ecology and Management, the findings illustrate the collaboration’s success ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New method enables efficient isolation of raccoon-borne food poisoning pathogen