(Press-News.org) Oral health deteriorates in morbidly obese people on a diet in preparation for bariatric surgery and patients who have undergone the procedure, with increasing caries, gingivitis and periodontitis. This is the conclusion of a study conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in Brazil. Articles on the study are published in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation and Clinical Oral Investigations, stressing the importance of participation by a dentist in the assessment of bariatric patients.
The study was funded by FAPESP (projects 17/26400-6 and 16/10940-9), following 100 patients divided into two groups (dietary counseling and gastroplasty) at the Bariatric Clinic in Piracicaba, São Paulo state. The clinic performs some 50 such operations per month, mainly under the auspices of the SUS (“Sistema Único de Saúde”), Brazil’s national health service.
Questionnaires, oral examinations, saliva samples and cheek swabs were analyzed to determine dietary changes, weight loss, inflammatory markers, oral microbiota by sequencing, and dental and periodontal health before the operation, as well as three and six months after the operation or start of the diet.
“The patients were asked to floss and brush their teeth three times a day, but even so their oral health deteriorated significantly. The number of caries rose, and periodontal status worsened in a short period in both groups, but particularly in the gastroplasty group,” said oral physiologist Paula Midori Castelo Ferrua, a professor in the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at UNIFESP and last author of both articles.
Salivary markers showed impairment of acid buffering capacity, essential for maintaining pH and preventing demineralization of tooth enamel. Bacterial genome sequencing showed alterations of microbiota diversity, especially in the gastroplasty group, so that the proportion of microorganisms that cause periodontitis increased.
The diet of many patients was found to have improved, but profound dietary changes were believed to be the main cause of the deterioration in oral health, especially because more frequent daily meals were not accompanied by more frequent tooth cleaning, and more food was liquid or puréed in the first few months after surgery.
“There’s less fiber in the diet and no chewing is required, so the food sticks to the enamel and biofilm forms on the tooth surface. Without chewing, less saliva is secreted and acid buffering capacity decreases,” Castelo said.
Future improvements
More than 300,000 bariatric surgeries were performed in Brazil in the period 2017-22. They were paid for by the SUS and health insurance plans. The multidisciplinary teams responsible for these patients include physicians, physical therapists, nutritionists and psychologists. Dentists are not usually included, despite the oral health risks entailed by the drastic change in diet both before and after the operation.
The results of the study show that assessing the patient’s oral health before and after bariatric surgery is essential. They also point to next steps for researchers in the field, which should include determining the best preventive or therapeutic intervention to resolve oral health problems during the pre-operative diet and post-operative recovery period, testing well-established methods such as fluoride application, reinforcement of brushing and flossing, and analyzing financial viability and ease of implementation by the SUS.
“Specific oral health guidelines for people who seek treatment for morbid obesity will also be important in future,” Castelo said.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Oral health deteriorates before and after bariatric surgery, study shows
Researchers analyzed saliva, oral microbiota and dental health of volunteers who were preparing for gastroplasty and after the operation. The results showed an increase in caries and periodontitis, as well as alterations in salivary inflammatory markers
2023-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients with AML who received vitamin C/D supplements had fewer complications, but no overall survival benefit seen
2023-09-06
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who received vitamin C and D supplements while undergoing intensive chemotherapy had lower rates of complications, such as infections, bleeding, and inflammation, when compared with similar, previously treated patients who did not receive these supplements. Moreover, while the study showed no difference in survival between the two groups, a subgroup analysis showed that among patients with a genetic mutation known as NPM1 – found in about one in three patients with AML – the risk of death was nearly 50% lower among those ...
University of Colorado ophthalmologists administer novel treatment for single patient facing rare genetic condition
2023-09-06
Thirteen-year-old Grace Hoyt received potentially the best birthday gift ever this month when pediatric ophthalmologists at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Children’s Hospital Colorado administered the first treatment designed specifically to slow her vision loss associated with posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa (PCARP), a rare genetic condition that affects vision and the nervous system.
“It’s so incredible that she has this opportunity,” Susan Hoyt says of her daughter, who received the first treatment Aug. 24. “We’ve known that Grace is going to go blind, but to have ...
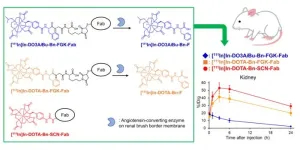
Novel molecular design for enhanced efficacy and safety in radiotheranostics
2023-09-06
Radiotheranostics embodies the convergence of diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals into a unified platform. In cancer treatment, radiotheranostic procedures typically involve the use of antibodies that bind to proteins abundantly found on the surface of cancerous cells. The antibodies are labeled with a suitable radioisotope, which facilitates imaging procedures used to diagnose cancer and can be used to target cancerous cells and bombard them with deadly radiation as a form of treatment.
Although radiolabeled antibodies show promise as a treatment for cancer, several hurdles impede their clinical translation. ...
Potential target for reversing drug resistance in ovarian cancer identified
2023-09-06
For the 314,000 people diagnosed with ovarian cancer each year, hope often comes in the form of platinum-based drugs such as cisplatin.
Cisplatin causes the death of quick-dividing tumour cells, so it is a potent first-line defence in the treatment of the often fatal disease.
However, over half of ovarian cancer patients develop recurrence and become resistant to cisplatin and other platinum-based chemotherapies, contributing to the five-year survival rate of 31%.
It is unclear why this resistance occurs, but a solution is urgently ...
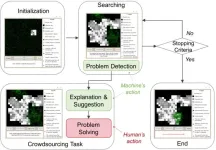
Human-AI collaboration improves source search outcomes
2023-09-06
When artificial intelligence robots that have been designed to use algorithms to complete source search tasks, such as search and rescue operations during a fire, encounter a disturbance, they are often unable to complete their task. Proposed solutions have ranged from trying to improve algorithms to introducing additional robots, but these AI-driven robots still encounter fatal problems.
Researchers have proposed a solution: a human-AI collaboration that takes advantages of the unique skills of the human brain to overcome challenges.
The paper was published in the Journal of Social ...
Teleneurology challenges met by training curriculum
2023-09-06
A new physician-training system in telehealth simulates key parts of traditional, in-person neurological exams that use little reflex hammers, pinpricks, and flashlights to test nerve function. The three-year program, which was designed by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, has trained at least 68 neurology residents since its rollout in 2020. Published online Aug. 3 in Neurology Education, a new analysis of the curriculum identifies challenges to translating in-person exam techniques ...
A secret for boosting hotel bookings: analyze online user reviews for your hotel and your competitors
2023-09-06
Researchers from Texas Christian University, University of South Carolina, and RealPage published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the impact of online reviews on hotel booking performance with a specific focus on the competitive effects of reviews.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “The Competitive Effects of Online Reviews on Hotel Demand” and is authored by Sanghoon Cho, Pelin Pekgun, Ramkumar Janakiraman, and Jian Wang.
Recent reports indicate that a majority of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations when deciding to book a hotel. A 2019 study ...
Rubber plumbing seals can leak additives into drinking water, study says
2023-09-06
As drinking water flows through pipes and into a glass, it runs against the rubber seals inside some plumbing devices. These parts contain additives that contribute to their flexibility and durability, but these potentially harmful compounds can leak into drinking water, according to a small-scale study in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters. The authors report that the released compounds, which are typically linked to tire pollution, also transformed into other unwanted byproducts.
To enhance rubber’s strength and durability, manufacturers typically mix in additives. Scientists have shown that tire dust ...
Mount Sinai announces partnership with the Brazilian Clinical Research Institute to advance cardiovascular disease research and medical education
2023-09-06
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai announced today that it has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Brazilian Clinical Research Institute (BCRI) to focus on advancing cardiovascular disease research, innovation, and medical education.
"This partnership is part of a broader initiative to expand Mount Sinai Heart’s reach globally, and Latin America is an important part of that goal," said Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Dr. Valentin Fuster Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine at Icahn Mount Sinai. "Our partnership ...
Recent advances in melon and gourd research
2023-09-06
As summer draws to a close, the long vines and tendrils of most melons and gourds in the Cucurbitaceae family snake their way along the ground. And they’re dotted with fruits, such as cucumbers or pumpkins. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into melons’ potential health impacts, pathogens and contaminants. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
“Nanoparticles Loaded with a Carotenoid-Rich Extract from Cantaloupe Melon Improved Hepatic Retinol Levels in a Diet-Induced Obesity Preclinical Model”
ACS ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Oral health deteriorates before and after bariatric surgery, study showsResearchers analyzed saliva, oral microbiota and dental health of volunteers who were preparing for gastroplasty and after the operation. The results showed an increase in caries and periodontitis, as well as alterations in salivary inflammatory markers