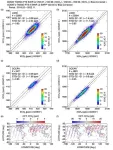
(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this dose-response meta-analysis that included nine randomized clinical trials and 2,980 patients, compared with placebo, gefapixant (45 mg orally twice daily) led to modest improvements in cough frequency, cough severity, and cough-specific quality of life but increased taste-related adverse events.
Authors: Imran Satia, M.D., Ph.D., of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.18035)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being released to coincide with presentation at the European Respiratory Society International Congress 2023.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.18035?guestAccessKey=7eeca61f-6e63-404e-b54e-fb61b407ac11&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=091123
END
Efficacy, tolerability of gefapixant for treatment of refractory or unexplained chronic cough
JAMA
2023-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Preschoolers show cultural differences in generosity, competitiveness
2023-09-11
RICHLAND, Wash. – In a set of sharing experiments, Spanish-speaking Latino preschoolers were more likely to choose options that would be more generous to others, even over a more equal sharing choice.
Their English-speaking peers in the Washington State University study more often chose the most competitive option, one that advantaged themselves over others. The most competitive among that group were English-speaking Latino children, a finding that the researchers believe may reflect their desire to transition ...
Scientists find evidence of sea star species hybridization
2023-09-11
New York, September 11, 2023 – Scientists have long suspected two species of sea stars—commonly referred to as starfish—along rocky European and North American coastlines of crossbreeding in the cool waters of the North Atlantic Ocean. Now, according to recently analyzed genomic data, hybrid starfish are living and thriving, from the shores of New England to the Canadian Maritimes.
A new study, published in the journal Molecular Ecology, presents genomic evidence of hybridization between two closely related species of sea stars– Asterias rubens, the common starfish, and Asterias forbesi, known as Forbes’ sea ...
How should clinicians prescribe opioids for cancer-related pain in patients who use cocaine or methamphetamines?
2023-09-11
Clinicians treating cancer-related pain must consider whether and how to prescribe opioids to patients who use nonmedical stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamines; however, no guidelines exist related to these common and challenging situations. In a new study, palliative care and addiction experts deemed it appropriate to continue opioids, increase monitoring, and avoid opioid tapering in such patients. The results are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Using opioids and nonmedical stimulants ...
Sorghum bran packs bigger punch than whole grain
2023-09-11
Sorghum bran has much higher levels of some essential amino acids and minerals needed for human health and development than a whole grain or dehulled sorghum flour, researchers from the University of Johannesburg have found.
Sorghum bran packs a calcium, magnesium, leucine and valine punch much higher than the whole grain flour. The climate-resilient gluten-free grain also holds its own on macro – and micronutrients compared to the biggest grains produced worldwide.
Dr Janet Adebo and Dr Hema Kesa investigated and compared the nutritional quality and functional properties of the different ...
Study on consistency of greenhouse gas concentrations between GOSAT and GOSAT-2
2023-09-11
1.Background and objectives
The Ministry of the Environment of Japan, the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency are jointly promoting the GOSAT series, a series of Earth observation satellites whose main purpose is to observe greenhouse gases from space; the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) launched in January 2009 and GOSAT-2 launched in October 2018 are currently in operation, and the Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle (GOSAT-GW) is planned to be launched in Japan’s FY2024. NIES is responsible for developing ...
Hospital admissions for COPD increased substantially, especially in women and younger people
2023-09-11
Annual hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Canada increased 69% since 2002, especially in females and people under age 65, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221051.
COPD affects the lungs and progresses, resulting in frequent hospitalization, burdening patients, families and health care systems. It has been viewed as a condition usually associated with male smokers.
"With increasing ...
Waterloo researchers make a significant step towards reliably processing quantum information
2023-09-11
Using laser light, researchers have developed the most robust method currently known to control individual qubits made of the chemical element barium. The ability to reliably control a qubit is an important achievement for realizing future functional quantum computers.
This new method, developed at the University of Waterloo’s Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC), uses a small glass waveguide to separate laser beams and focus them four microns apart, about four-hundredths of the width of a single human hair. The precision and extent to which each focused laser beam on its target qubit can be controlled in parallel ...
FLAURA2 results demonstrate osimertinib plus chemotherapy superior compared to osimertinib alone
2023-09-11
(Singapore – 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 11, 2023) – Osimertinib plus chemotherapy demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful progression-free survival benefit compared to osimertinib alone, according to research presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
The FLAURA2 study was led by Dr. Pasi A. Jänne from the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, Mass.
Osimertinib, a potent third-generation EGFR-TKI with central nervous system activity, has garnered attention for its targeted ...
MARS trial: decortication and chemotherapy associated with worse outcomes for patients with resectable mesothelioma
2023-09-11
(Singapore, September 11, 2023, 10:05 a.m. SGT) – Extended pleurectomy decortication combined with chemotherapy is associated with worse survival outcomes, a higher incidence of serious adverse events, and a diminished quality of life compared to platinum and pemetrexed chemotherapy alone, according to research presented today the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
The UK Multicentre Randomised Trial, known as MARS 2, conducted by a team led by Professor Eric ...
Large-scale investigation supports modified classification system for pulmonary adenocarcinomas
2023-09-11
(Singapore – 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 11, 2023) – A modified adenocarcinoma classification approach significantly enhances reproducibility and may be an improvement on the existing World Health Organization classification system, according to research unveiled at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
The study, led by Dr. Erik Thunnissen, Department of Pathology, Amsterdam UMC, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Efficacy, tolerability of gefapixant for treatment of refractory or unexplained chronic coughJAMA