(Press-News.org) September 12, 2023 — Since the 1980s, we have known that neurological soft signs (NSS) can distinguish people with schizophrenia from psychiatrically healthy individuals. NSS are subtle neurological impairments that principally manifest as decreased sensory integration (trouble receiving and responding to information transmitted to the brain through the senses) and difficulties with balance, rapid successive movements, and right–left orientation.
NSS doesn't always cause impairment of daily living, but identifying them could improve the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia and enhance understanding of the disease itself. Unfortunately, barriers to assessment have persisted for more than 40 years—rating systems for NSS are subjective, so it's difficult to reliably measure and compare deficits.
In a perspectives article published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry (HRP), part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer, John Torous, MD, MBI and colleagues of Harvard's Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and the Massachusetts Mental Health Center in Boston, discuss how smartphone sensing technology could be used to create standardized NSS assessments.
Advances in smartphones and digital phenotyping offer a means for more reliable scoring
In 2016, Dr. Torous and his colleagues were the first to define "digital phenotyping," the use of data from smart devices to identify behavior patterns that can detect disease. In the case of NSS, physicians can collect information from a smartphone's motion sensors, like those that adjust the screen display from portrait to landscape and react to gaming-related gestures, to detect behavior patterns as possible NSS markers. For example:
A test of balance: Patients stand with their arms held parallel to the floor and their eyes closed for one minute; patients could perform the same test with a smartphone attached to their sternums.
A test of motor coordination (like the tandem walk): Patients walk heel-to-toe in a straight line for 12 feet; the same test has been administered to patients with Parkinson's disease by having them put a smartphone in their pants pockets.
A test of complex motor acts: Ask the patient to reproduce a series of audible taps; alternatively, the smartphone could play a beat with the patient tapping along, and the patient could be asked to continue tapping the same pattern after the beat stops.
Smartphones and digital phenotyping have multiple advantages over traditional assessment
A smartphone makes objective measurements so it can quantitatively evaluate how well a patient does on a test rather than have the examiner decide whether the patient is impaired. In addition, using smartphones for NSS measurement could reduce the time necessary for neurological office visits since patients could complete aspects of the examination before or after a visit.
"Incorporating digital phenotyping into NSS assessment offers the potential to make measurement more scalable, accessible, and directly comparable across locations, cultures, and demographics," Dr. Torous and his colleagues note. Some tests may require use of a camera, but with proper security and privacy features in place the data could be safely employed.
"The rapid adoption of telehealth measures due to the COVID-19 pandemic increased patient buy-in and enhanced privacy considerations, making it an advantageous time to introduce smartphone sensing technology and tools to measure NSS," the authors conclude.
Read Article [Potential Role of Smartphone Technology in Advancing Work on Neurological Soft Signs with a Focus on Schizophrenia]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers, and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across health care. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
###
About HRP
Harvard Review of Psychiatry is the authoritative source for scholarly reviews and perspectives on a diverse range of important topics in psychiatry. Founded by the Harvard Medical School Department of Psychiatry, the journal is peer-reviewed and not industry sponsored. It is the property of President and Fellows of Harvard College and is affiliated with all of the departments of psychiatry at the Harvard teaching hospitals. Articles encompass all major issues in contemporary psychiatry, including (but not limited to) neuroscience, psychopharmacology, psychotherapy, history of psychiatry, and ethics.
In addition to scholarly reviews, perspectives articles, and columns, the journal includes a clinical challenge section that presents a case followed by discussion and debate from a panel of experts.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the health care, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
END
Smartphone technology expected to advance assessment of neurological soft signs in schizophrenia
Objective measurement could improve patient management and aid research into how distinct groups of signs might reflect different aspects of psychiatric illness and neurologic impairment
2023-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kessler Foundation receives $725,000 grant for study to accelerate functional recovery in multiple sclerosis
2023-09-12
East Hanover, NJ – September 12, 2023 – Carly Wender, PhD, associate research scientist in the Center for Neuropsychology and Neuroscience Research at Kessler Foundation received a three-year $725,499 grant from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society for her study, “A Novel Combinatory Approach to Maximize Functional Recovery of Learning and Memory in Multiple Sclerosis.”
Cognitive impairment is a common symptom in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) that can be particularly ...
Older adults with digestive diseases experience higher rates of loneliness, depression
2023-09-12
While life expectancy rates for older Americans are rising, nearly 40% of adults report living with a digestive disease of some kind.
“Many people don’t realize that these conditions are very common in ambulatory care,” said Michigan Medicine gastroenterologist Shirley Ann Cohen-Mekelburg, M.D., who specializes in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
“Ultimately, this creates an excess in health care spending in the United States. Not only are these conditions debilitating for the millions of people living with them, ...
Mount Sinai receives NIH grant to develop vaccines that can protect against many different types of coronaviruses
2023-09-12
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has awarded the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai a five-year, $13 million grant to bring together experts from multiple disciplines across five research institutions to create better vaccines against current as well as emerging coronaviruses.
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has infected 280 million people and caused more than five million deaths worldwide since late 2019. While considerable progress has been made to develop interventions (i.e., monoclonal antibodies, antivirals, vaccines) to treat and prevent COVID-19, ...
Setting the gold standard in diagnosis of lupus nephritis
2023-09-12
In the ever-perilous autoimmune disease world of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus), up to 60% of adult patients and 80% of children will develop lupus nephritis (LN), and up to half of those will move on to end-stage renal disease. LN occurs when the immune system wrongly attacks the kidneys, preventing them from doing their job, i.e., cleaning blood, balancing body fluids and controlling hormones that impact blood pressure.
Unfortunately, the most precise way to diagnose LN hasn’t been ...
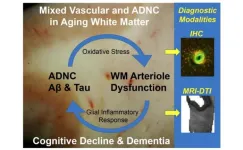
Contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-09-12
“The molecular mechanisms that mediate enhanced dysfunction of white matter parenchymal arterioles when vascular dysfunction and ADNC coincide remain elusive.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 12, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease.”
In their new editorial, researchers Zsolt Bagi, ...
Accelerating knowledge exchange in biodiversity genomics and bioinformatics
2023-09-12
Since its inception in 2021, the African BioGenome Project (AfricaBP), has made significant gains towards its ambitious goal of sequencing 100,000 endemic African species within the next 10 years. Recently, AfricaBP reported the successful implementation of the Open Institute in the journal Nature Biotechnology (https://rdcu.be/dlXYT), a pioneering biodiversity genomics and bioinformatics knowledge exchange programme.
The AfricaBP Open Institute’s framework will establish openly accessible workshops across Africa, crafted in close collaborations with local African Institutions. ...
Call: "Journalist in Residence“ program at Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA)
2023-09-12
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) is offering science journalists the opportunity for a paid three-month "Journalist in Residence“ program starting in April 2024. Applications are open until Oct. 31, 2023.
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) in Klosterneuburg – in the immediate vicinity of Vienna – is a Ph.D.-granting research institute. Opened in 2009, the Institute is dedicated to basic research in the natural sciences, mathematics and computer sciences. It has a total of 1000 employees and 75 different research ...
COVID-19 can trigger auto-immune disorders-related antibodies, causing thrombosis and other complications
2023-09-12
An article published in NPJ Aging, a Springer Nature journal, reveals that natural production of auto-antibodies increases with age and that infection by SARS-CoV-2 can exacerbate production of auto-antibodies relating to auto-immune diseases, helping to explain why aging increases the chances of developing severe COVID-19. The study also discovered some of the factors that associate the severe form of the disease with blood clotting disorders such as thrombosis.
“These findings open the door to a better ...
Alzheimer’s: An M.D./Ph.D. graduate student’s request for Yuhua Song as mentor leads to two NIH R01 awards totaling $5 million
2023-09-12
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In the summer of 2018, graduate student Hunter Dean from the Medical Scientist Training Program came to Yuhua Song, Ph.D., with a research idea. He wanted to pursue his doctoral research at the University of Alabama at Birmingham in Alzheimer’s disease — under the joint mentorship of Song, who had never worked in Alzheimer’s, and Erik Roberson, M.D., Ph.D., an Alzheimer’s expert in the UAB Department of Neurology and the Center for Neurodegeneration and Experimental Therapeutics, or CNET.
That collaboration brought Song, a professor in the UAB Department of ...
Recommendations for addressing health-related social needs in cancer care introduced at NCCN Policy Summit
2023-09-12
Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—presented new recommendations for screening and addressing health-related social needs (HRSN) in people with cancer during a policy summit in Washington, D.C. The event included a keynote address from Ellen Lukens, Deputy Administrator and Director, The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI), and other speakers representing a diverse group of patient advocates, providers, and policymakers.
The new recommendations for measuring and addressing HRSNs were ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Smartphone technology expected to advance assessment of neurological soft signs in schizophreniaObjective measurement could improve patient management and aid research into how distinct groups of signs might reflect different aspects of psychiatric illness and neurologic impairment