Economic evaluation of extended-release buprenorphine for persons with opioid use disorder
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-13
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: In this economic evaluation of extended-release buprenorphine compared with transmucosal buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder, extended-release buprenorphine was not associated with efficient allocation of limited resources when transmucosal buprenorphine was available. Future initiatives should aim to improve retention rates or decrease costs associated with extended-release buprenorphine.
Authors: Juliet M. Flam-Ross, B.A., of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in London, and Sabrina A. Assoumou, M.D., M.P.H., of the Boston Medical Center in Boston, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29583)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29583?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=091323
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Glue holds the world together. Without adhesives, much of modern human civilization — including our cellphones, cars, furniture, walls and the packages arriving on our doorstep — would simply fall apart.
The trouble with all those adhesives is that they are not sustainable. A team of chemists at Purdue University led by Jonathan Wilker, professor of chemistry in the College of Science and of materials engineering, aims to change that with a new, completely sustainable adhesive system. The team’s findings were released in a paper in Nature.
Additional Information
Shellfish ...
2023-09-13
DURHAM, N.C. -- Many of the bacteria that ravage crops and threaten our food supply use a common strategy to cause disease: they inject a cocktail of harmful proteins directly into the plant’s cells.
For 25 years, biologist Sheng-Yang He and his senior research associate Kinya Nomura have been puzzling over this set of molecules that plant pathogens use to cause diseases in hundreds of crops worldwide ranging from rice to apple trees.
Now, thanks to a team effort between three collaborating research groups, they may finally have an answer to how these molecules make plants sick -- and a way to disarm them.
The findings appear Sept. 13 in the journal Nature.
Researchers ...
2023-09-13
Researchers at Moorfields Eye Hospital and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that has the potential to not only identify sight-threatening eye diseases but also predict general health, including heart attacks, stroke, and Parkinson’s disease.
RETFound, one of the first AI foundation models in healthcare, and the first in ophthalmology, was developed using millions of eye scans from the NHS. The research team are making the system open-source: freely available to use by any institution worldwide, to act as a cornerstone for global efforts to detect and treat blindness using AI. ...
2023-09-13
Key takeaways
Social determinants of at-risk neighborhoods: Higher proportions of poverty and low per-capita income were most associated with higher rates of shooting incidents.
High levels of social stressors: The study found that fatal and non-fatal firearm assaults were clustered in neighborhoods with high levels of social stressors measured with the 2018 version of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Social Vulnerability Index (SVI).
A potential tool for directing anti-violence initiatives: The CDC’s SVI can help policymakers target neighborhoods at ...
2023-09-13
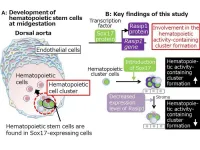
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have discovered that a gene called Rasip1 is intimately involved in the creation of blood cells
Tokyo, Japan – Blood has long been a symbol of life and health, so it may be surprising that some aspects of blood production, i.e., hematopoiesis, remain incompletely understood. One such mystery is the role of a protein called SOX17. Blood cells are generated by hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and SOX17 seems to be important to the development of HSCs because SOX17 is expressed where HSCs first develop. What exactly SOX17 does, however, has remained unclear.
Now, a research team at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) ...
2023-09-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new type of analysis suggests that droughts in Ohio were more severe from 2000 to 2019 than standard measurements have suggested.
Researchers at The Ohio State University developed impacts-based thresholds for drought in Ohio, looking specifically at how corn yield and streamflow were affected by various drought indicators, such as notable changes in soil moisture, crops, and even livestock losses in the state.
The results suggest this impacts-based approach could give Ohio farmers earlier and more accurate notice when drought conditions are approaching, said Steven Quiring, co-author of the study and a professor ...
2023-09-13
Men ages 50 to 60 have an 80 percent chance of having some degree of bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) due to an enlarged prostate – which causes multiple symptoms that can impact their lives physically and psychologically.
The bladder, an incredibly complex organ, has its own electrical system and can change its constituents and geometry through a growth and remodeling process. However, in bladders with BOO, the urethral resistance increases and forces the muscle cells within the bladder to generate larger pressures to void. Over time, the bladder adapts with a growth and remodeling response that causes changes in bladder size, tissue composition, ...
2023-09-13
The EU Horizon 2020 project B-GOOD, aiming at improving honey bee health and beekeeping sustainability, invites participants to the project’s closing conference in Bled, Slovenia this October. The upcoming scientific event will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, and information market stands to provide a comprehensive overview of the results and technologies developed during the project. The attendees will also be able to meet the consortium members of the project, ask questions and exchange ideas.
The event will take place on the 2nd of October 2023 immediately before the COLOSS ...
2023-09-13
New research suggests that owls in Texas have high rates of anticoagulant rodenticides (AR)—blood thinning rat poisons—in their systems. Jennifer Smith, a professor of integrative biology in the UTSA College of Sciences, co-authored a research article published recently in PLOS ONE, the world’s first multidisciplinary open access journal.
Eres Gomez, M.S. ’22, a UTSA graduate who had conducted research in the Smith Wildlife Lab as a student, was the article’s lead author. Heather Prestridge, a curator ...
2023-09-13
Acetone is an essential chemical industry input and is used in the manufacturing of a wide array of products, such as adhesives, antibiotics, electronic components, solvents and removers, inks and vitamins, among others. Its production is complex and hazardous. To simplify the process and make it safer and cheaper, researchers in Brazil and Germany have developed an innovative method that uses only light and photoactive iron chloride (FeCl3), an inexpensive chemical compound.
An article on the research, which was funded by FAPESP, is published in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Economic evaluation of extended-release buprenorphine for persons with opioid use disorder
JAMA Network Open