(Press-News.org) Europeans may be more willing to help Ukrainian refugees than those from Syria or Somalia in part because they consider Ukrainians less threatening
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290335
Article Title: Emotions, perceived threat, prejudice, and attitudes towards helping Ukrainian, Syrian, and Somali asylum seekers
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work.
END
Europeans may be more willing to help Ukrainian refugees than those from Syria or Somalia in part because they consider Ukrainians less threatening
2023-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
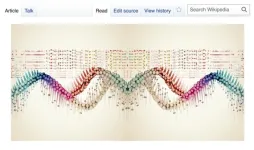
Wikipedia charts the history of science, per study analyzing evolution of CRISPR-related articles
2023-09-13
Wikipedia charts the history of science, per study analyzing evolution of CRISPR-related articles
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290827
Article Title: Wikipedia as a tool for contemporary history of science: A case study on CRISPR
Author Countries: France, Israel
Funding: Thanks to the Bettencourt Schueller Foundation long term partnership, this work was partly supported by the LPI Research Fellowship, Université de Paris, INSERM U1284, to RAv and OB. RAv’s work was supported in part at the Technion by a fellowship of "The Israel Academy of Science and Humanities”. In either ...
Jail admissions even for minor court debt are common, per analysis of US county-level data from Texas, Wisconsin and Oklahoma
2023-09-13
Jail admissions even for minor court debt are common, per analysis of US county-level data from Texas, Wisconsin and Oklahoma
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290397
Article Title: Forgotten but not gone: A multi-state analysis of modern-day debt imprisonment
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This study was supported by a grant from Arnold Ventures (https://www.arnoldventures.org). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, ...
The California rush hour is spreading and easing with reduced peak congestion following the COVID-19 pandemic, according to data from 3,500 traffic sensors
2023-09-13
The California rush hour is spreading and easing with reduced peak congestion following the COVID-19 pandemic, according to data from 3,500 traffic sensors
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290534
Article Title: Rush hour-and-a-half: Traffic is spreading out post-lockdown
Author Countries: USA
Funding: SZ: This work was supported in part by an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Award DGE 2040434. MWBC received no specific funding for this work. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, ...
Battery-free robots use origami to change shape in mid-air
2023-09-13
Researchers at the University of Washington have developed small robotic devices that can change how they move through the air by "snapping" into a folded position during their descent.
When these "microfliers" are dropped from a drone, they use a Miura-ori origami fold to switch from tumbling and dispersing outward through the air to dropping straight to the ground. To spread out the fliers, the researchers control the timing of each device's transition using a few methods: an onboard pressure ...
Owners of cats on vegan diets report healthier pets than owners of meat-eating cats
2023-09-13
In a survey of cat owners, those who fed their cats vegan diets tended to report better health outcomes for their pets than those who provided meat-based diets, though the differences were not statistically significant. Andrew Knight of the University of Winchester, UK, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on September 13.
Many pet foods contain cooked meat as the primary protein source, but a growing number of available products use alternative protein sources, such as plants or fungi. Some veterinary professionals ...
Wolves and dogs appear to remember where people hid food
2023-09-13
In a study involving several wolves and dogs, both animals performed better at finding hidden food if they had observed the food being hidden by a person—suggesting that they remembered where the food was, and did not rely solely on scent to find it. Sebastian Vetter of the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, Austria, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on September 13.
Many species transmit important information through social learning, where one individual learns by observing ...
A trained detection dog found sea turtle nests in Florida more accurately and efficiently than humans, indicating potential for dog-assisted nest monitoring
2023-09-13
A trained detection dog found sea turtle nests in Florida more accurately and efficiently than humans, indicating potential for dog-assisted nest monitoring
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290740
Article Title: Use of a scent-detection dog for sea turtle nest monitoring of three sea turtle species in Florida
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
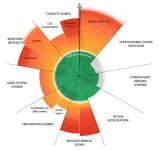
Six of nine planetary boundaries now exceeded
2023-09-13
A new study updates the planetary boundary framework and shows human activities are increasingly impacting the planet and, thereby, increasing the risk of triggering dramatic changes in overall Earth conditions.
For over 3 billion years, the interaction between life (represented by the planetary boundary, Biosphere Integrity) and climate have controlled the overall environmental conditions on Earth. Human activities, for example replacing nature with other land uses, changing the amount of water in rivers and in soil, the introduction of synthetic chemicals to the open environment, and the emission of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere ...
University secures £2.66M to develop personalized cancer treatment
2023-09-13
University of Liverpool researchers have secured £2.66m Medical Research Council funding to clinically test a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung cancer – one of the most deadly cancers.
Professor Christian Ottensmeier, and Professor Natalia Savelyeva from the Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology are collaborating with industry partner Genomics England and working closely with Touchlight Genetics Ltd to develop a vaccine therapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer who have not had sufficient benefit from standard immunotherapy.
Non-small ...
Natural compound found in plants inhibits deadly fungi
2023-09-13
A new study finds that a natural compound found in many plants inhibits the growth of drug-resistant Candida fungi — including its most virulent species, Candida auris, an emerging global health threat. The journal ACS Infectious Diseases published the discovery led by scientists at Emory University.
Laboratory-dish experiments showed that the natural compound, a water-soluble tannin known as PGG, blocks 90% of the growth in four different species of Candida fungi. The researchers also discovered how PGG inhibits the growth: It grabs up iron molecules, essentially starving the fungi of an essential nutrient.
By starving the fungi rather than attacking ...