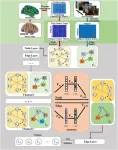
(Press-News.org) Developed in 2011, MXene is a two-dimensional nanomaterial with alternating metal and carbon layers, which has high electrical conductivity and can be combined with various metal compounds, making it a material that can be utilized in various industries such as semiconductors, electronic devices, and sensors. To properly utilize MXene, it is important to know the type and amount of molecules covered on the surface, and if the molecules covered on the surface are fluorine, the electrical conductivity of decreases and the efficiency of electromagnetic wave shielding decreases. However, since it is only 1 nm (nanometer - billionth of a meter) thick, it takes several days to analyze the molecules on the surface even with a high-performance electron microscope, so mass production has been impossible until now.
The research team led by Seung-Cheol Lee, director of the Indo-Korea Science and Technology Center(IKST) at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST), has developed a method to predict the distribution of molecules on the surface using the magnetoresistance property of MXene. By utilizing this method, it is possible to measure the molecular distribution of MXene with a simple measurement, enabling quality control in the production process, which is expected to open the way to mass production that was not possible until now.
The research team developed a two-dimensional material property prediction program based on the idea that electrical conductivity or magnetic properties change depending on the molecules attached to the surface. As a result, they calculated the magnetic transport properties of MXene and succeeded in analyzing the type and amount of molecules adsorbed on the surface of MXene at atmospheric pressure and room temperature without any additional devices.
By analyzing the surface of the MXene with the developed property prediction program, it was predicted that the Hall scattering factor, which affects magnetic transport, changes dramatically depending on the type of surface molecules. The Hall Scattering Factor is a physical constant that describes the charge-carrying properties of semiconductor materials, and the team found that even when the same MXene was prepared, the Hall Scattering Factor had a value of 2.49, the highest for fluorine, 0.5 for oxygen, and 1 for hydroxide, allowing them to analyze the distribution of the molecules.
The Hall scattering coefficient has different applications based on the value of 1. If the value is lower than 1, it can be applied to high-performance transistors, high-frequency generators, high-efficiency sensors, and photodetectors, and if the value is higher than 1, it can be applied to thermoelectric materials and magnetic sensors. Considering that the size of the maxin is a few nanometers or less, the size of the applicable device and the amount of power required can be dramatically reduced.
"Unlike previous studies that focused on the production and properties of pure MXene, this study is significant in that it provides a new method for surface molecular analysis to easily classify manufactured MXene," said Seung-Cheol Lee, director of IKIST. "By combining this result with experimental studies, we expect to be able to control the production process of MXene, which will be used to mass produce MXene with uniform quality."
IKST was established in 2010 and conducts research in the areas of theory, source code, and software for computational science. In particular, source code is a programming language that implements algorithms that can be modeled and simulated, and is considered an original research in the field of computational science, and the center conducts collaborative research with Indian universities and research institutes such as IIT Bombay to develop source code.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research, which was conducted as a KIST Major Project (2Z06950) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho), was selected as a Notable Article of the Year (2023 Hot Article Collection) of Nanoscale, an international journal in the field of nanoscience (IF:6.7, JCR top 16.7%) for its originality and scalability, and was published on June 28.
END
MXene, a dream new material, paves the way for mass production
IKST researchers develop analysis model using magnetic transport characteristics of molecules attached to the surface of MXene. Establishment of property prediction and classification system is expected to be utilized to produce uniform quality MXene.
2023-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What is the carbon footprint of a hospital bed?
2023-09-18
Researchers from the University of Waterloo completed the first-ever assessment of a Canadian hospital to reveal its total environmental footprint and specific carbon emission hotspots.
Studying a hospital in British Columbia during its 2019 fiscal year, the researchers identified energy and water use and purchasing of medical products as the hospital’s primary hotspots, accounting for over half of the yearly footprint, totalling 3500-5000 tons of CO2 equivalent. One hospital bed is roughly equivalent to the carbon footprint of five Canadian households.
The new method brings an unprecedented level of comprehensiveness and detail to hospital ...
Early treatment of child obesity is effective
2023-09-18
The early treatment of obesity in children is effective in both the short and long term, researchers from Karolinska Institutet report in a study published in The International Journal of Obesity.
The researchers followed over 170 young children in Sweden who had received treatment for diagnosed obesity. The children were recruited to the randomised controlled study when they were between four and six years old via children’s clinics in Region Stockholm.
The children and their parents were randomly assigned to one of three treatment conditions: standard treatment, parental support group, or parental support group with follow-up telephone ...
Study finds significant chemical exposures in women with cancer
2023-09-18
In a sign that exposure to certain endocrine-disrupting chemicals may be playing a role in cancers of the breast, ovary, skin and uterus, researchers have found that people who developed those cancers have significantly higher levels of these chemicals in their bodies.
While it does not prove that exposure to chemicals like PFAS (per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances) and phenols (including BPA) led to these cancer diagnoses, it is a strong signal that they may be playing a role and should be studied further.
The study showed that particularly for women, higher ...
Societal collapse is underway and museums can be unlikely heroes, suggests expert
2023-09-18
Museums and Societal Collapse: The Museum as Lifeboat presents evidence and theories around collapse and extinction, while locating the responsibility of museums in our changing world
Stressors like climate trauma, corporate deceit and political incompetence signal the threat of societal collapse, a new book asserts.
This claim lays the foundation for exploring arguments of ‘collapsology’ in new work by Robert R. Janes Ph.D., Museums and Societal Collapse: The Museum as Lifeboat. The book also contends with the unique role that can be played by museums during a mounting climate crisis.
“Social ...
Transfer of ageing: New drug class prevents key ageing mechanism in organ transplants
2023-09-18
(18 September 2023, Athens, Greece) A novel study has shown that Senolytics, a new class of drugs, have the potential to prevent the transfer of senescence*, a key mechanism of ageing, and the associated physical and cognitive impairments in recipients of older donor organs. 1
The pioneering research, presented today at the European Society for Organ Transplantation (ESOT) Congress 2023, opens promising avenues for expanding the organ donor pool and enhancing patient outcomes.
By transplanting older donor organs into younger ...
Ultrasound scans by doctors in emergency departments to diagnose deep vein thrombosis halve patients’ stay and may help to reduce over-crowding
2023-09-18
Barcelona, Spain: If doctors in hospital emergency departments are trained to carry out ultrasound on patients with suspected deep vein thrombosis (DVT), they can nearly halve the time the patients spend in these departments.
Dr Ossi Hannula, an emergency medicine specialist at the Wellbeing Services County of Central Finland, Jyväskylä, Finland, who presented the findings at the European Emergency Medicine Congress today (Monday), said his findings could help to reduce overcrowding in emergency departments ...
Brain-altering parasite turns ants into zombies at dawn and dusk
2023-09-17
Imagine coming-to, jaws gripping the top of a swaying blade of grass, unaware of how you got there. That's the reality for ants infected with the lancet liver fluke, a tiny parasitic flatworm. Liver flukes have a complicated, almost insanely conceived life cycle, which begins with the hijacking of the ant’s brain. The unsuspecting ant climbs up and clamps its powerful jaws onto the top of a blade of grass, making it more likely to be eaten by grazers such as cattle and deer.
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Plant ...
Neonatal kidney transplantation offers new hope in the organ shortage crisis, study shows
2023-09-17
(17 September 2023, Athens, Greece) New research, presented today at the European Society for Organ Transplantation (ESOT) Congress 2023, demonstrates that neonatal* kidney transplantation can offer a ‘game-changing’ solution to the pressing organ shortage crisis. 1
To assess the feasibility of neonatal organ donation, researchers analysed neonatal mortality in the United States and the long-term development of these kidneys after transplantation as well as the ethical and social considerations surrounding the procedure. 1
The study revealed that out of the 21,000 infants who lost their lives ...
Islet transplantation boosts long-term survival in kidney transplant recipients with type 1 diabetes
2023-09-17
(17 September 2023, Athens, Greece) Islet transplantation significantly reduces the risk of transplantation failure and enhances life expectancy in individuals with type 1 diabetes who undergo kidney transplantation, a new study has revealed. 1
This breakthrough research, presented today at the European Society for Organ Transplantation (ESOT) Congress 2023, compared the long-term outcomes of patients with type 1 diabetes who underwent kidney transplantation and received an islet transplantation*, with patients who underwent kidney transplantation and then managed their diabetes with insulin ...
Breakthrough model utilizes movie-watching FMRI and eye-tracking to predict cognitive scores
2023-09-16
In a recent article published in Volume 3 of the journal Psychoradiology, researchers from Northwestern Polytechnical University have unveiled the groundbreaking "Attention-CensNet" (A-CensNet), a fusion model that predicts cognitive scores by amalgamating movie-watching functional magnetic resonance imaging (mfMRI) and eye-tracking data. In this model, participants serve as nodes, mfMRI data are translated into node features, and eye-tracking details forge the connections between participants, creating graph edges. By employing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
[Press-News.org] MXene, a dream new material, paves the way for mass productionIKST researchers develop analysis model using magnetic transport characteristics of molecules attached to the surface of MXene. Establishment of property prediction and classification system is expected to be utilized to produce uniform quality MXene.