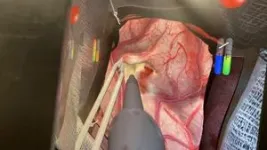
(Press-News.org) Virtual reality simulators can help learners improve their technical skills faster and with no risk to patients. In the field of neurosurgery, they allow medical students to practice complex operations before using a scalpel on a real patient. When combined with artificial intelligence, these tutoring systems can offer tailored feedback like a human instructor, identifying areas where the students need to improve and making suggestions on how to achieve expert performance.
A new study from the Neurosurgical Simulation and Artificial Intelligence Learning Centre at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, however, shows that human instruction is still necessary to detect and compensate for unintended, and sometimes negative, changes in neurosurgeon behaviour after virtual reality AI training.
In the study, 46 medical students performed a tumour removal procedure on a virtual reality simulator. Half of them were randomly selected to receive instruction from an AI-powered intelligent tutor called the Virtual Operative Assistant (VOA), which uses a machine learning algorithm to teach surgical techniques and provide personalized feedback. The other half served as a control group by receiving no feedback. The students’ work was then compared to performance benchmarks selected by a team of established neurosurgeons.
Comparing the results, AI-tutored students caused 55 per cent less damage to healthy tissues than the control group. AI-tutored students also showed a 59 per cent reduction in average distance between instruments in each hand and 46 per cent less maximum force applied, both important safety measures.
However, AI-tutored students also showed some negative outcomes. For example, their dominant hand movements had 50 per cent lower velocity and 45 per cent lower acceleration than the control group, making their operations less efficient. The speed at which they removed tumour tissue was also 29 per cent lower in the AI-tutored group than the control group.
These unintended outcomes underline the importance of human instructors in the learning process, to promote both safety and efficiency in students.
“AI systems are not perfect,” says Ali Fazlollahi, a medical student researcher at the Neurosurgical Simulation and Artificial Intelligence Learning Centre and the study’s first author. “Achieving mastery will still require some level of apprenticeship from an expert. Programs adopting AI will enable learners to monitor their competency and focus their intraoperative learning time with instructors more efficiently and on their individual tailored learning goals. We’re currently working towards finding an optimal hybrid mode of instruction in a crossover trial.”
Fazlollahi says his findings have implications beyond neurosurgery because many of the same principles are applied in other fields of skills’ training.
“This includes surgical education, not just neurosurgery, and also a range of other fields from aviation to military training and construction,” he says. “Using AI alone to design and run a technical skills curriculum can lead to unintended outcomes that will require oversight from human experts to ensure excellence in training and patient care.”
“Intelligent tutors powered by AI are becoming a valuable tool in the evaluation and training of the next generation of neurosurgeons,” says Dr. Rolando Del Maestro, the study’s senior author. “However, it is essential that surgical educators are an integral part of the development, application, and monitoring of these AI systems to maximize their ability to increase the mastery of neurosurgical skills and improve patient outcomes.”
This study, published in JAMA Network Open on Sept. 19, 2023, was funded by the Franco Di Giovanni Foundation, Brain Tumour Foundation of Canada Brain Tumour Research Grant, a Medical Education Research Grant from the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada, and the Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital.
The Neuro
The Neuro – The Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital – is a bilingual, world-leading destination for brain research and advanced patient care. Since its founding in 1934 by renowned neurosurgeon Dr. Wilder Penfield, The Neuro has grown to be the largest specialized neuroscience research and clinical center in Canada, and one of the largest in the world. The seamless integration of research, patient care, and training of the world’s top minds make The Neuro uniquely positioned to have a significant impact on the understanding and treatment of nervous system disorders. In 2016, The Neuro became the first institute in the world to fully embrace the Open Science philosophy, creating the Tanenbaum Open Science Institute. The Montreal Neurological Institute is a McGill University research and teaching institute. The Montreal Neurological Hospital is part of the Neuroscience Mission of the McGill University Health Centre.
END
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for hypertensive disorders in pregnant persons with blood pressure measurements throughout pregnancy. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are among the leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality in the U.S. The rate has been increasing from approximately 500 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 1993 to 1,021 cases per 10,000 deliveries in 2016 to 2017. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation is consistent with its 2017 recommendation statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
A team of Dana-Farber researchers has identified a potential new way to assess clinically valuable features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a form of kidney cancer, using image processing with deep learning. Their AI-based assessment tool evaluates two-dimensional pictures of a tumor sample on a pathology slide and identifies previously underappreciated features, such as tumor microheterogeneity, that could help predict whether a tumor will respond to immunotherapy.
Their results suggest that ...
An international study has revealed strong associations between oral health and survival among people diagnosed with head and neck cancer. Specifically, better oral health, as evidenced by the number of natural teeth and dental visits prior to the time of diagnosis, was associated with increased survival. Importantly, those who had more frequent dental visits were more likely to have their cancer diagnosed at an earlier, and less deadly, stage of the disease than those who had few or no dental visits.
The study, by researchers at UNC Lineberger ...
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that rehabilitation interventions in adults with post–COVID-19 condition are associated with improvements in functional exercise capacity, dyspnea, and quality of life, with a high probability of improvement compared with the current standard care. The certainty of evidence was moderate for functional exercise capacity and quality of life and low for other outcomes.
Authors: Dimitra V. Pouliopoulou, M.Sc., of Western University in London, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
About The Study: In this study of 3,635 female participants in the U.S., premenstrual disorders (PMDs) were associated with increased risks of early menopause and moderate or severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS). PMDs may be indicative of underlying physiology linked to early menopause and VMS, suggesting a phenotype observable during the reproductive years that may allow clinicians to target women at risk of earlier menopause and subsequent health risks later in the life course.
Authors: Yihui Yang, M.P.H., and Donghao Lu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden are the corresponding authors.
To ...
Brigham researchers found that patients prescribed amoxicillin-clavulanate had higher rates of gastrointestinal symptoms and yeast infections than those prescribed amoxicillin
Acute sinusitis is one of the most common causes for children to be put on antibiotic medications, with patients in the United States filing nearly 5 million antibiotic prescriptions every year to treat the condition. The drugs amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate make up most of those prescriptions, but there is a lack of consensus on which should be first-line ...
New research from Queen Mary University of London, published in iScience, shows an increased risk of blood clots in women who have any combination of a particular gene mutation, oestrogen use, or common medical conditions – specifically: obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and kidney disease.
Women with the Factor V Leiden (FVL) gene mutation who had been prescribed oestrogen had more than double the risk of blood clotting compared to women who did not have this mutation. And almost 20% of the women who carry FVL, ...
Researchers at IOCB Prague are the first to describe the causes of the behavior of one of the fundamental aromatic molecules, which fascinates the scientific world not only with its blue color but also with other unusual properties – azulene. Their current undertaking will influence the foundations of organic chemistry in the years to come and in practice will help harness the maximum potential of captured light energy. The article appeared in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Azulene has piqued the ...
A groundbreaking research study conducted by Hai-Lei Wei's research team at the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in China has revealed significant insights into the biosynthesis and modulation of plant immunity by a novel cyclic lipopeptide called medpeptin, produced by Pseudomonas mediterranea. The findings, published in Engineering, shed light on the intricate structure–function interactions of cyclic lipopeptides (CLPs) and open new avenues for the development of plant disease resistance strategies.
CLPs, multifunctional secondary metabolites produced by various bacteria, have emerged as key elicitors of plant ...
For over a generation, the MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences has been an essential resource for researchers and students of cognitive science and neuroscience. Today, the MIT Press proudly announces its intellectual successor—the Open Encyclopedia of Cognitive Science (OECS), a dynamic and openly accessible web reference poised to guide the next generation of exploration. Thanks to generous funding from James S. McDonnell Foundation and the Allen Institute for AI, the first set of articles will be published in 2024.
In ...