Real-time live tissue sensitivity assay for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
2023-09-19
(Press-News.org)
“This approach may allow clinicians to select the most effective therapeutic agents with real time in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 19, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on September 15, 2023, entitled, “Real time ex vivo chemosensitivity assay for pancreatic adenocarcinoma.”
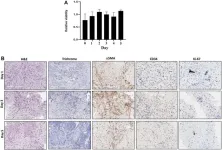
Patient-derived organoids (PDOs) and xenografts (PDXs) have been extensively studied for drug-screening. However, their usage is limited due to lengthy establishment time, high engraftment failure rates and different tumor microenvironment from original tumors. In this new study, researchers Dae Won Kim, Francisca Beato, Youngchul Kim, Alexandra F. Tassielli, Ruifan Dai, Jason W. Denbo, Pamela J. Hodul, Mokenge P. Malafa, and Jason B. Fleming from Moffitt Cancer Center developed real time-live tissue sensitivity assay (RT-LTSA) using fresh tumor samples to overcome these limitations.
“To overcome the major hurdles of the PDX-based assay, we developed real time LTSA (RT-LTSA) using fresh tumor samples. In this study, we report a reliable and reproducible RT-LTSA with resected fresh tumor samples to predict patients’ clinical response to chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer.”
Tissue slices from resected pancreatic cancer samples were placed in 96-well plates, and the slices were treated with chemotherapeutic agents. The correlation between the chemo-sensitivity of tissue slices and each patient’s clinical outcome was analyzed. The viability and tumor microenvironment of the tissue slices were well-preserved over 5 days. The drug sensitivity assay results were available within 5 days after tissue collection.
While all 4 patients who received RT-LTSA sensitive adjuvant regimens did not develop recurrence, 7 of 8 patients who received resistant adjuvant regimens developed recurrence. The researchers observed significantly improved disease-free survival in the patients who received RT-LTSA sensitive adjuvant regimens (median: not reached versus 10.6 months, P = 0.02) compared with the patient who received resistant regimens. A significant negative correlation between RT-LTSA value and relapse-free survival was observed (Somer’s D: −0.58; P = 0.016).
“RT-LTSA which maintains the tumor microenvironment and architecture as found in patients may reflect clinical outcome and could be used as a personalized strategy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Further, studies are warranted to verify the findings.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28508
Correspondence to: Jason B. Fleming
Email: jason.fleming@moffitt.org
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, sensitivity assay, chemotherapy
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28508
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-19
Empowering Employers
Last year, Deep Longevity launched SenoClock, a B2B platform that grants easy access to aging clocks and an anti-aging recommendation engine. SenoClock has gained popularity among longevity clinics and consumer health companies and is releasing a major update SenoClock Gold that’ll enable any organization to adopt the anti-aging paradigm to improve the quality of life of their workforce. SenoClock highlights the drivers of the aging process in its end-users, and now offers a dynamic view of their progress.
Forward-looking ...
2023-09-19
UCF Scientist Looking at Role of Fats to Curb Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients
BY SUHTLING WONG
Every three minutes, someone in the U.S. is diagnosed with leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloma – cancers of the blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.
Treatments for blood cancers often require hematopoietic stem cell transplants but such cells can launch a potentially deadly immunological attack on the patient’s organs called graft-vs-host ...
2023-09-19
ITHACA, N.Y.- Though human-made ponds both sequester and release greenhouse gases, when added up, they may be net emitters, according to two related studies by Cornell University researchers.
The studies begin to quantify the significant effects that both human-made and natural ponds have on the global greenhouse gas budget, measurements that aren’t well understood.
“Global climate models and predictions rely on accurate accounting of greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage,” said Meredith Holgerson, assistant professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Cornell and senior ...
2023-09-19
New research by Janelia scientists and collaborators at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill shows how a cluster of neurons in the fruit fly brain transforms memories about past rewards into actions, helping the fly navigate to find food.
Like other insects, flies turn into the wind, or upwind, to locate the source of attractive odors. The fly’s olfactory system detects and senses odors carried by the wind, guiding the fly to the reward.
In the fly, a brain region called the mushroom body processes and integrates olfactory information. Multiple compartments ...
2023-09-19
New Rochelle, NY, September 19, 2023–A special issue of the peer-reviewed journal Health Equity titled “How Stakeholders Are Working to Advance Health Equity" covers the following areas: changing mindsets, promoting antiracism in health delivery systems, and promoting antiracism in health policy. Click here to read the issue now.
Guest Editors of the special issue are Laurie Zephyrin, MD, MPH, MBA, Senior Vice President, Advancing Health Equity, The Commonwealth Fund; Claire-Cecile Pierre, MD, Associate Chief Medical Officer, Vice President of Community Health, ...
2023-09-19
Whether light and fluffy or thin and flexible, bread holds an important place in many cultures and cuisines. And despite millennia of baking experience, scientists are still striving to improve this staple food. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into the quality, healthfulness and preparation of bread. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
“Unraveling the Influence of Wheat Bran Chemical Composition, Lipolytic Enzyme Activities, and Phenolic Components on the Bread-Making Properties of Reconstituted Whole Wheat Flours”
ACS Food Science & Technology
Sept. 13, 2023
Whole-wheat bread contains ...
2023-09-19
Near-eye displays are emerging as the future of portable devices, providing individuals with immersive virtual reality experiences. The primary objectives in developing these displays are to create immersive experiences and ensure visual comfort. While a larger field of view (FOV) enhances immersion in virtual reality, addressing the Vergence-Accommodation-Conflict (VAC) is crucial for comfortable vision. Researchers have explored innovative approaches to tackle these challenges. A significant breakthrough in near-eye displays is the integration of light field technology. However, earlier light field displays in VR were limited by their ...
2023-09-19
Today, the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health was named one of 13 funded partners working alongside the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to establish the Outbreak Analytics and Disease Modeling Network (OADM) – an important step towards creating a nationwide outbreak resource to support more effective responses during public health emergencies.
Each funded partner will provide support in innovation, integration or implementation for outbreak analytics, disease modeling and forecasting. The Gillings ...
2023-09-19
The U.S. National Science Foundation, UK Research and Innovation, and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada have jointly funded a new global center to address the emerging opportunity and challenge of “green ammonia” to provide clean energy and support food production while mitigating climate change. The Global Nitrogen Innovation Center for Clean Energy and the Environment (NICCEE), spearheaded by the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (UMCES) with key partners in the U.S. (New ...
2023-09-19
Consumer confidence in driving hydrogen-fueled vehicles could be improved by having station operators adopt a predictive model that helps them anticipate maintenance needs, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Colorado State University (CSU).
Stations shutting down for unscheduled maintenance reduces hydrogen fueling availability to consumers and may slow adoption of these types of fuel cell electric vehicles, the researchers noted. The use of what is known as a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Real-time live tissue sensitivity assay for pancreatic adenocarcinoma





