(Press-News.org) A pair of independent studies, using recent James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations of carbon dioxide (CO2) ice on Jupiter’s moon Europa, indicate the CO2 originates from a source within the icy body’s subsurface ocean. The findings from both research groups provide new insights into the poorly known composition of Europa’s internal ocean. Beneath a crust of solid water ice, Jupiter’s moon Europa is thought to have a subsurface ocean of salty liquid water. Because of this, Europa is a prime target in the search for life elsewhere in the Solar System. Assessing this deep ocean’s potential habitability depends on its chemistry, including the abundance of biologically essential elements like carbon. Previous research has identified the presence of solid CO2 ice on Europa’s surface, but it has not been possible to establish whether the CO2 originated from the subsurface ocean, was delivered to the moon’s surface by meteorite impacts, or was produced on the surface through interactions with Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Determining the source of the CO2 could constrain the chemistry of Europa’s internal ocean.
In two separate studies, researchers analyze near-infrared spectroscopy of CO2 on Europa’s surface, obtained with JWST. In one study, Samantha Trumbo and Michael Brown used the JWST data to map the distribution of CO2 on Europa and found the highest abundance of CO2 is located in Tara Regio – a ~1,800 square kilometer region dominated by “chaos terrain,” geologically disrupted resurfaced materials. According to Tumbo and Brown, the amount of CO2 identified within this recently resurfaced region – some of the youngest terrain on Europa’s surface – indicates that it was derived from an internal source of carbon. This implies that the CO2 formed within Europa’s subsurface ocean and was brought to the surface on a geologically recent timescale. However, the authors say that formation of CO2 on the surface from ocean-derived organics or carbonates cannot be entirely ruled out. In either interpretation, the subsurface ocean contains carbon.
In an independent study of the same JWST data, Geronimo Villanueva and colleagues found that the CO2 on Europa’s surface is mixed with other compounds. Villanueva et al. also find the CO2 is concentrated in Tara Regio and interpret that as demonstrating that the carbon on the moon’s surface was sourced from within. The authors measured the ice’s 12C/13C isotopic ratio, but could not distinguish between an abiotic or biogenic source. Moreover, Villanueva et al. searched for plumes of volatile material breaching moon’s icy crust. Although previous studies have reported evidence of these features, the authors did not detect any plume activity during the JWST observations. They argue that plume activity on Europa could be infrequent, or sometimes does not contain the volatile gasses they included in their search. The results in both studies complement each other and reinforce the conclusion that Europa’s subsurface ocean contains abundant carbon.
END
Two studies indicate CO2 on Europa’s surface originated from within the moon’s internal ocean
2023-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global study reveals extensive impact of metal mining contamination on rivers and floodplains, suggesting need for new safeguards to address spike in demand for ‘green’ minerals
2023-09-21
A groundbreaking study, published today in Science, has provided new insights into the extensive impact of metal mining contamination on rivers and floodplains across the world, with an estimated 23 million people believed to be affected by potentially dangerous concentrations of toxic waste.
Led by Professors Mark Macklin and Chris Thomas, Directors of the Lincoln Centre for Water and Planetary Health at the University of Lincoln, UK – working with Dr Amogh Mudbhatkal from the University’s Department of Geography – the study offers a comprehensive understanding of the environmental and health challenges associated with metal mining activities.
Using ...
Regeneration across complete spinal cord injuries reverses paralysis
2023-09-21
When the spinal cords of mice and humans are partially damaged, the initial paralysis is followed by the extensive, spontaneous recovery of motor function. However, after a complete spinal cord injury, this natural repair of the spinal cord doesn’t occur and there is no recovery. Meaningful recovery after severe injuries requires strategies that promote the regeneration of nerve fibers, but the requisite conditions for these strategies to successfully restore motor function have remained elusive.
“Five years ago, we demonstrated that nerve fibers can be regenerated across anatomically complete spinal cord ...
The dance of organ positioning: a tango of three proteins
2023-09-21
In order to keep track of their environment, cells use cilia, antenna-like structures that can sense a variety of stimuli, including the flow of fluids outside the cell. Genetic defects that cause cilia to malfunction and lose their sensory abilities can result in disorders known as “ciliopathies”, including polycystic kidney diseases; but they can also disrupt the correct asymmetric positioning of internal organs during embryonic development – what is known as “organ laterality”.
An example of such asymmetry is the heart, which is typically ...
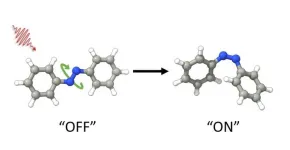
Using harmless light to change azobenzene molecules with new supera molecular complex
2023-09-21
New discovery allows scientists to change the shape of azobenzene molecules using visible light, which is more practical and safe than previously used ultraviolet light. Azobenzenes are incredibly versatile and have many potential uses, such as in making tiny machines and improving technology as well as making light controllable drugs. This molecule can switch between two different forms by light. However, the two forms are in equilibrium, which means that a mixture present that prevents optimal use for applications. Being able to control them with visible light and enrich only one form opens up new possibilities for these applications, making them more efficient ...
Scientists regenerate neurons that restore walking in mice after paralysis from spinal cord injury
2023-09-21
In a new study in mice, a team of researchers from UCLA, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, and Harvard University have uncovered a crucial component for restoring functional activity after spinal cord injury. The neuroscientists have shown that re-growing specific neurons back to their natural target regions led to recovery, while random regrowth was not effective.
In a 2018 study published in Nature, the team identified a treatment approach that triggers axons — the tiny fibers that link nerve cells and enable them to communicate — to regrow after spinal cord injury ...
Conversations with plants: Can we provide plants with advance warning of impending dangers?
2023-09-21
Imagine if humans could ‘talk’ to plants and warn them of approaching pest attacks or extreme weather.
A team of plant scientists at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University (SLCU) would like to turn this science fiction into reality using light-based messaging to ‘talk’ to plants.
Early lab experiments with tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) have demonstrated that they can activate the plant's natural defence mechanism (immune response) using light as a stimulus (messenger).
Light serves as a universal means of daily human communication, for example the signalling at traffic lights, pedestrian ...
Chicago’s West Side is air pollution hotspot
2023-09-21
Three independent state-of-the-art datasets reveal that the West Side has more nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution than the rest of the city
Depending on the month, residents in this area experience 16 to 32% higher NO2 concentrations on average
By identifying hotspots, residents and policymakers can be confident about where to prioritize immediate interventions
EVANSTON, Ill. — The western edge of Chicago — including the North and South Lawndale, East Garfield Park, Archer Heights and Brighton Park neighborhoods — experiences up to 32% higher concentrations of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) air pollution compared to the rest of the city, ...
Biophysical Society announces 2024 Society Fellows
2023-09-21
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Biophysical Society is proud to announce its 2024 Society Fellows. This award honors the Society’s distinguished members who have demonstrated excellence in science and contributed to the expansion of the field of biophysics. The Fellows will be honored at the Biophysical Society’s 68th Annual Meeting, being held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from February 10-14, 2024. The 2024 Fellows are:
Rommie E. Amaro, University of California, San Diego, USA, is named a Biophysical Society Fellow for her work on developing methods to enable the simulation of biological molecules in situ and ...
Wearable optical device shows promise for detecting postpartum hemorrhage
2023-09-21
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a wearable optical device for early detection of hemorrhage during labor or after childbirth. This serious heavy bleeding can be hard to detect before it becomes an emergency and accounts for almost 30% of maternal deaths globally and just over 10% of maternal deaths in the United States.
Studies have shown that early diagnosis and treatment for postpartum hemorrhage is the best way to prevent deaths. The new device is designed to be worn on the wrist, where it uses laser speckle imaging to continuously ...
David Huang, M.D., Ph.D., receives Lasker Award for transformative imaging technology
2023-09-21
PORTLAND, Oregon -- The United States’ most distinguished biomedical research award is being given to Oregon Health & Science University physician-scientist David Huang, M.D., Ph.D., for co-inventing an imaging technology that routinely helps prevent blindness and is increasingly used to diagnose and treat conditions of the heart, brain, skin and more.
Huang is receiving the 2023 Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award as a co-inventor of optical coherence tomography, or OCT, the Albert and ...