(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study using a behavioral experiment designed to mimic a real-world imposter scam among 644 older adults, a sizable number of older adults engaged without skepticism. The results suggest that many older adults, including those without cognitive impairment, are vulnerable to fraud and scams.
Authors: Lei Yu, Ph.D., of Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35319)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35319?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=092223
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Vulnerability of older adults to government impersonation scams
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiovascular disease burden, outcomes among American Indian and Alaska native Medicare beneficiaries
2023-09-22
About The Study: The results of this study of 220,000 American Indian and Alaska Native patients with Medicare insurance suggest a significant burden of cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic risk factors. These findings highlight the critical need for future efforts to prioritize the cardiovascular health of this population.
Authors: Lauren A. Eberly, M.D., M.P.H., of the Indian Health Service in Gallup, New Mexico, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Rapid and visual detection of monkey B virus based on recombinase polymerase amplification
2023-09-22
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/ZOONOSES-2023-0031
Announcing a new article publication for Zoonoses journal. Monkey B virus (BV) infection in humans and other macaque species has a mortality rate of approximately 80%. Because BV infects humans through bites, scratches, and other injuries inflicted by macaques, the simple and rapid diagnosis of BV in field laboratories is of great importance to protect veterinarians, laboratory researchers, and support personnels from the threat of infection.
Two recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assays with a closed vertical flow (VF) visualization strip (RPA-VF-UL27 and RPA-VF-US6) were developed that target ...
A promising drug candidate for ALS – prolongs lifespan and eases symptoms in rats and mice
2023-09-22
A research group at the University of Helsinki and its partners have found a promising drug candidate for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor CDNF prolongs the lifespan of and alleviates disease symptoms in rats and mice in animal studies.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rapidly progressing fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Specifically, a selective degeneration of motoneurons occurs in the spinal cord, leading to muscle atrophy and paralysis. Most patients with ...
Same genes behind heart muscle disorders in humans and Dobermanns
2023-09-22
Researchers have made a significant finding in determining the genetic background of dilated cardiomyopathy in Dobermanns. This research helps us understand the genetic risk factors related to fatal diseases of the heart muscle and the mechanisms underlying the disease, and offers new tools for their prevention.
Researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Folkhälsan Research Center, together with their international partners, have identified the genetic background of dilated cardiomyopathy, a disease that enlarges the heart muscle, in dogs and humans.
Based ...
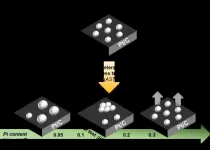
A teamwork to evaluate the influence of the cathode catalyst layer platinum loading on the durability of PEMFC
2023-09-22
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) hold promise as a replacement for fossil fueled engines in heavy-duty vehicles. Reducing the platinum content in catalysts is pivotal for scaling up in such applications. Yet, the degradation patterns of low platinum content catalysts remain poorly understood. A team of scientists conducted experiments to shed light on the degradation mechanisms associated with varying catalyst content, offering valuable insights. Their work is published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials on 11 Aug 2023.
In ...
Is there more to palm oil than deforestation?
2023-09-22
Palm oil is the world's most produced and consumed vegetable oil and everyone knows that its production can damage the environment. But do consumers have the full picture? In fact, replacing palm oil with rapeseed oil would require a four to five-fold increase in the amount of land needed. Research led by the University of Göttingen investigated the attitudes, beliefs and understanding about palm oil of the general public in Germany, and how this links to land use. The researchers show that people find it hard to know the consequences of their buying choices, even when extra information is supplied. The results were published in Sustainable ...
Researchers connect Alzheimer’s-associated genetic variants with brain cell function
2023-09-22
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Scientists studying Alzheimer’s disease (AD) have identified thousands of genetic variants in the genome in the development of this progressive neurodegenerative disease.
These variants are predominantly located in genomic regions that do not code for proteins, making it difficult to understand which variants confer individuals’ risk of AD. Non-coding variants were once thought to be “junk DNA” by scientists. In recent years, these variants have been appreciated for playing crucial roles in controlling gene expression across tissues and cell types. However, linking these non-coding variants to the genes they regulate and effects ...
New research reveals gut microbiota link to colitis: intestinal epithelial axin1 deficiency offers protective effects
2023-09-22
A groundbreaking study conducted by Jun Sun’s research team at the University of Illinois Chicago has revealed a new and critical role of Axin1 in regulating intestinal epithelial development and microbial homeostasis. The research, published in the journal Engineering, highlights the potential therapeutic strategies for human inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
IBD, a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the gastrointestinal tract, has been a significant health concern worldwide. The study focused on understanding the role of Axin1, a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin ...
Visualizing the current distribution inside fuel cells and achieving stable operation via non-destructive diagnostics using magnetic sensors
2023-09-22
Tsukuba, Japan—Fuel cells are attracting attention as a clean energy source technology because the cells do not produce carbon dioxide and emit only water during power generation. However, two contradictory phenomena can hamper their performance: flooding, wherein water remains inside the fuel cell and interferes with power generation, and dry-out, wherein an excess of water is removed and the polymer membrane, through which hydrogen ions permeate, dries out. To detect such issues, various devices and sensors have been used in analyses based on substantial amounts of data.
This research team has been investigating a method for detecting and controlling ...
Efficient fuel-molecule sieving using graphene
2023-09-22
Tsukuba, Japan—For realizing carbon neutrality, the demand for the development of direct methanol/formic acid-fuel cell technology has been increasing. In this technology, methanol or formic acid is used as an e-fuel for generating electricity. The fuel cells generate electricity via proton transfer; however, conventional proton-exchange membranes suffer from the "crossover phenomenon," where the fuel molecules are also transferred between anodes and cathodes. Thereafter, the fuel molecules are unnecessarily oxidized and the electrodes are deactivated. In this study, the researchers developed a new proton-exchange ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Vulnerability of older adults to government impersonation scamsJAMA Network Open