(Press-News.org)
In a groundbreaking study, a research team led by Changhu Xue and Xiangzhao Mao from the Ocean University of China has developed a remarkable double-layer polysaccharide hydrogel (DPH) that promises to revolutionize the field of intestine-targeted oral delivery of probiotics. The team’s findings, published in Engineering, demonstrate the potential of DPH to enhance the bioavailability, intestinal colonization, and overall effectiveness of probiotics in treating various diseases.
The research team’s study focused on addressing the challenges posed by the harsh gastrointestinal environment and the short retention time in the gastrointestinal tract, which significantly limit the efficacy of probiotics. By harnessing the unique properties of DPH, the team successfully encapsulated and delivered probiotics in a targeted manner within the body.
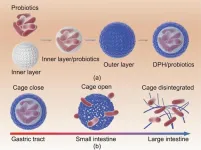
DPH, composed of a carboxymethyl cellulose (CMCL) supramolecular inner layer and a dialdehyde alginate (DAA) cross-linked carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) outer layer, exhibits a double-layer structure that plays a crucial role in protecting probiotics throughout the gastrointestinal journey. In the stomach, the cage-like structure of DPH remains closed, forming a barrier that shields the probiotics from gastric fluids. However, upon reaching the intestine, the cage structure opens and disintegrates, releasing the probiotics precisely where they are needed.
The results of the study are truly remarkable. Probiotics encapsulated by DPH demonstrated a staggering 100.1 times higher bioavailability and 10.6 times higher mucoadhesion compared to free probiotics in an animal model 48 hours post-treatment. Furthermore, DPH exhibited exceptional mucoadhesive properties, allowing for improved colonization in the intestinal tract and enhanced survival in the extreme conditions of the gastrointestinal tract while maintaining the viability and activity of the probiotics.
One of the key innovations of the DPH hydrogel is the dynamic crosslinking facilitated by DAA, which not only ensures the overall integrity of the hydrogels but also controls the timing of probiotic release. This breakthrough opens up new possibilities for delivering encapsulated substances, such as probiotics and proteins, to specific sites within the intestinal tract.
The potential applications of DPH extend beyond its role in enhancing the delivery of probiotics. The study also validated the structure, morphology, biocompatibility, controlled-release behavior, and bacterial competition of the DPH hydrogel, suggesting its potential as a versatile carrier for targeted delivery in various biomedical applications.
“The development of the double-layer polysaccharide hydrogel marks a significant milestone in the field of intestine-targeted oral delivery of probiotics,” said Shasha Zhao, editor of Engineering. “We anticipate that DPH will serve as a game-changer, offering a promising alternative to existing carriers and significantly improving the efficacy of probiotics in treating a wide range of diseases.”
These groundbreaking findings pave the way for further research and development in the field of targeted drug delivery and open up new possibilities for improving the effectiveness of probiotics in promoting gut health and treating various diseases.
The paper “A Double-Layer Polysaccharide Hydrogel (DPH) for the Enhanced Intestine-Targeted Oral Delivery of Probiotics”, authored by Wen-Can Huang, Wenjie Wang, Wei Wang, Yanan Hao, Changhu Xue, Xiangzhao Mao. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.05.024. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on Twitter (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringPortfolio).
About Engineering
Engineering (ISSN: 2095-8099 IF:12.8) is an international open-access journal that was launched by the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE) in 2015. Its aims are to provide a high-level platform where cutting-edge advancements in engineering R&D, current major research outputs, and key achievements can be disseminated and shared; to report progress in engineering science, discuss hot topics, areas of interest, challenges, and prospects in engineering development, and consider human and environmental well-being and ethics in engineering; to encourage engineering breakthroughs and innovations that are of profound economic and social importance, enabling them to reach advanced international standards and to become a new productive force, and thereby changing the world, benefiting humanity, and creating a better future.
END
New guidelines are needed to assure that research on human subjects performed on commercial spaceflights is conducted ethically, a panel of experts say in a commentary appearing in the September 28 issue of the journal Science.
Their paper is titled Ethically cleared to launch?
Private companies are expected to fly thousands of people into space in the coming decades. Those aboard will include workers and passengers who will have the opportunity to participate in research studies. Such research is not only essential to assure the safety of future space travelers but often also addresses critical issues of human health in general.
Buț ...
Large differences in flower characteristics between wildflowers with different pollinators are achieved by a few key genetic differences, according to a study by Carolyn Wessinger at the University of South Carolina, US, and colleagues, publishing September 28th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Plants that rely on animal pollinators, such as insects or birds, have evolved distinctive suites of flower characteristics — known as “pollination syndromes” — that are tailored to the pollinator. For example, most plants in the ...
To help resolve the scientific debate over whether it was a giant asteroid or volcanic eruptions that wiped out the dinosaurs and most other species 66 million years ago, Dartmouth researchers tried a new approach — they removed scientists from the debate and let the computers decide.
The researchers report in the journal Science a new modeling method powered by interconnected processors that can work through reams of geological and climate data without human input. They tasked nearly 130 processors with analyzing the fossil record in reverse to pinpoint the events and conditions that led to the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event that ...
HOUSTON – (Sept. 28, 2023) – The commercial spaceflight industry is expanding opportunities for scientific research in space, but the industry needs clear ethical guidelines before human research is ready for liftoff. In a new policy paper published in Science, a global, multidisciplinary team of bioethicists, health policy experts, space health researchers, commercial spaceflight professionals and government regulators outlines potential ethical concerns facing the future of commercial space research and provides guiding principles ...
A genome-wide survey of highly endangered staghorn coral in the Caribbean has identified 10 genomic regions associated with resilience against white band disease – an emergent infectious disease responsible for killing up to 95% of Caribbean Acropora species, including staghorn corals (A. cervicornis). The findings could be used as a conservation tool to improve disease resistance in the wild and nursery stocks of staghorn corals used to repopulate damaged coral reefs throughout Caribbean waters. Over the last several decades, Earth’s reef corals have experienced unprecedented declines. Increased anthropogenic ...
A previously uncharacterized adhesin protein specific to a human fungal pathogen first discovered in 2009 plays a crucial role in the fungus’s ability to colonize a variety of living and non-living surfaces, and in its virulence, according to a new study. “These findings [about Candida auris] offer insight into the genetics and molecular mechanisms by which [this fungus] mediates surface association, a trait critical to the increasing disease burden of this emerging pathogen,” write the authors. Since its first discovery in 2009, C. auris has become increasingly responsible for life-threatening infections in health care facilities worldwide. Outbreaks of ...
From long-frozen and potentially dangerous pathogens awakening in Arctic permafrost to emerging heat-related hazards in human pregnancy, ongoing climate change presents new challenges for human health. In this Special Issue, Science’s News Department offers a collection of five news stories highlighting several facets of the complex intersection between heat, disease, and human health and the researchers seeking to understand related emerging threats.
In one Feature, Science Correspondent Kai Kupferschmidt discusses ...
A novel approach to a question that’s been widely investigated reveals more insights about the environmental forcings associated with the end-Cretaceous mass extinction, suggesting that volcanism and other biological changes imparted stress on the global carbon cycle across the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K/Pg) boundary. In addition to providing new insights into the factors that contributed to extinction, the approach could be useful in disentangling other complex perturbations in the Earth system and their associated climatic and biological impacts. The end-Cretaceous mass ...
A global, multidisciplinary team of bioethicists, health policy experts, commercial spaceflight professionals and space health researchers, including Rachael Seidler from the University of Florida, has developed guiding principles and best practices to help ensure human research conducted in space is safe and inclusive.
The proposed ethical guidelines were released Friday in a policy paper published in Science and are the result of a workshop held at the Banbury Center of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory funded by the Translational ...
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (September 28, 2023) — Van Andel Institute Chief Scientific Officer Peter A. Jones, Ph.D., D.Sc. (hon), has received a seven-year, nearly $7.9 million grant from the National Cancer Institute’s Outstanding Investigator Award program. The funding will fuel his research into the epigenetic errors that drive cancer development — and help him find ways to fix them.
The award is a renewal of an earlier seven-year, $7.8 million Outstanding Investigator Award granted to Jones in 2017. The National Cancer Institute, a part of the National Institutes of Health, launched the Outstanding Investigator Award program in 2014 to support “investigators with ...