(Press-News.org)
A team of researchers from China has made a significant breakthrough in biomedical engineering by developing a novel adhesive that promises to revolutionize wound management and tissue repair. The research, published in Engineering, unveils a biocomposite adhesive that exhibits robust adhesion and real-time skin healing properties.
Adhesives have long been recognized as a valuable tool in biomedical engineering. However, current adhesive systems face challenges in achieving strong and durable adhesion, limiting their effectiveness in wound healing. Additionally, conventional chemical adhesives lack the ability to adapt to dynamic changes in the wound environment, hindering tissue regeneration.
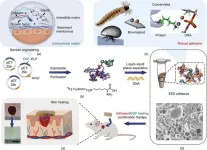
In response to these challenges, the Chinese research team engineered an extracellular matrix (ECM)-derived biocomposite adhesive that overcomes the limitations of existing adhesives. By harnessing liquid–liquid phase separation and leveraging supramolecular interactions between chimeric protein and natural DNA, the researchers achieved a reinforced adhesion performance in the biocomposite adhesive.
The newly developed adhesive demonstrates exceptional adhesion and sealing behaviors, surpassing its reported counterparts with a sheared adhesion strength of approximately 18 MPa. The engineered bioderived components not only enhance adhesion but also promote cell proliferation and migration, enabling real-time in situ skin regeneration.
The research team’s innovative approach involved actively introducing biological components and employing a rational design process to create the adhesive. Liquid–liquid phase separation, driven by electrostatic complexation between a chimeric epidermal growth factor (EGF), elastin-like protein, and natural DNA, facilitated the assembly of the adhesive. The resulting adhesive demonstrated exceptional adhesion on various substrates, including glass, ceramic, aluminum, steel, and soft tissues such as liver, muscle, and porcine skin.
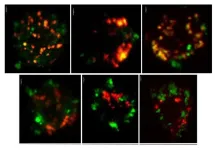
The adhesive’s remarkable adhesion strength of (18.9 ± 0.9) MPa on steel substrates and adhesion energy of (40.0 ± 5.3) J·m−2 on pigskin surpassed many reported adhesives. Furthermore, the adhesive exhibited hemostatic behavior, promoted cell proliferation and migration, remodeled the ECM, and accelerated in situ skin regeneration.
The potential applications of this novel adhesive extend beyond wound healing and tissue repair. The research team believes that the unique fabrication strategy holds great promise in the design of next-generation functionalized bioadhesives for broader applications, including bioelectronics and wearable health systems.
Nan Zhang, editor of the subject of chemical, metallurgical, and materials engineering of Engineering, stated that this work opens up novel avenues for functionalized bioadhesive engineering and biomedical translations. The adhesive, which has been engineered from ECM components, demonstrates biocompatibility and extraordinary biological functions, making it a promising candidate for biomedical adhesion and healing applications.
The paper “Engineering Protein Coacervates into a Robust Adhesive for Real-Time Skin Healing”, authored by Ming Li, Baimei Liu, Wei Xu, Lai Zhao, Zili Wang, Haonan He, Jingjing Li, Fan Wang, Chao Ma, Kai Liu, Hongjie Zhang. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.07.013. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on Twitter (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringPortfolio).
About Engineering
Engineering (ISSN: 2095-8099 IF:12.8) is an international open-access journal that was launched by the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE) in 2015. Its aims are to provide a high-level platform where cutting-edge advancements in engineering R&D, current major research outputs, and key achievements can be disseminated and shared; to report progress in engineering science, discuss hot topics, areas of interest, challenges, and prospects in engineering development, and consider human and environmental well-being and ethics in engineering; to encourage engineering breakthroughs and innovations that are of profound economic and social importance, enabling them to reach advanced international standards and to become a new productive force, and thereby changing the world, benefiting humanity, and creating a better future.
END
A research team led by Changjiang Wu at SINOPEC (Beijing) Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in China has made important progress in understanding the polymerization behavior and thermal properties of copolymers formed through ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins. The findings, published in the journal Engineering, shed light on the potential of utilizing different comonomers in olefin solution polymerization to obtain high-performance polyolefin materials.
Polyolefin elastomers (POEs) are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional properties. However, the high cost ...
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, and the Hospital for Special Surgery Research Institute have uncovered new details about how the immune system prevents the production of antibodies that can recognize and damage the body’s own, healthy tissues. The study, to be published September 29 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also reveals how this process is impaired in autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus ...
(WASHINGTON, Sept. 29, 2023) – Patients with multiple myeloma, a blood cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow, who also have diabetes have a reduced overall survival when compared to those without diabetes. In a subgroup analysis, this difference in survival due to diabetes was seen in white patients but not in Black patients, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes affects 13% of the U.S. population, and this prevalence is growing rapidly. Multiple myeloma is the second most common blood cancer in the U.S. and disproportionately ...
In a remarkable breakthrough in the field of Mathematical Science, Professor Kyudong Choi from the Department of Mathematical Sciences at UNIST has provided an irrefutable proof that certain spherical vortices exist in a stable state. This groundbreaking discovery holds significant implications for predicting weather anomalies and advancing weather prediction technologies.
A vortex is a rotating region of fluid, such as air or water, characterized by intense rotation. Common examples include typhoons and tornadoes frequently observed in news reports. Professor Choi’s mathematical proof establishes the stability of specific ...
The micro/nano metal pattern formation is a key step in the assembly of various devices. However, ex situ approaches of metal patterning limited their industrial applications due to the poor stability and dispersion of metal nanoparticles. The in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning may be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers. Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which can realize the in situ reduction of metal ions on the photoresist pattern. A team of scientists ...
The liver is a vital organ that plays a role in many essential functions, including digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. When the liver is damaged, it has the remarkable ability to regenerate itself. However, the process of liver regeneration is not fully understood.
A critical aspect of liver regeneration is removing dead tissue and necrotic lesions. In a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Feng et al. showed that monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMFs) play a crucial role in this process. MoMFs are a type of white blood cell that is recruited to the liver in response to injury. Once in the liver, MoMFs engulf dead cells ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The organisms that cause visceral leishmaniasis, a potentially deadly version of the parasitic disease that most often affects the skin to cause disfiguring disease, appear to have a secret weapon, new research suggests: They can infect non-immune cells and persist in those uncommon environments.
Researchers found the Leishmania donovani parasites in blood-related stem cells in the bone marrow of chronically infected mice – precursor cells that can regenerate all types of cells in the blood-forming system. The finding may help explain why some people who develop visceral leishmaniasis, which is ...
Cheaper, more efficient lithium-ion batteries could be produced by harnessing previously overlooked high pressures generated during the manufacturing process.
Scientists at the University of Birmingham have discovered that routine ball milling can cause high pressure effects on battery materials in just a matter of minutes, providing a vital additional variable in the process of synthesizing battery materials.
The research (part of the Faraday Institution funded CATMAT project), led by Dr Laura Driscoll, Dr Elizabeth Driscoll and Professor Peter Slater at the University of Birmingham is published in RSC Energy Environmental Science.
The use ...
September 29, 2023, Cincinnati, OH — A set of recommendations to address the known variation in outcomes at US congenital heart surgery centers has been endorsed by 15 collaborating societies led by the Congenital Heart Surgeons' Society (CHSS). The guidelines will appear in “Recommendations for Centers Performing Pediatric Heart Surgery in the United States," to be co-published in the World Journal for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery, Annals of Thoracic Surgery, and Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.
“In ...
Periodontal disease is one of the most common canine diseases, affecting at least 80% of dogs aged three and over. Periodontal disease begins as gingivitis, where gums become red and inflamed, and may bleed. Untreated, the disease can progress to periodontitis, where the alveolar bone is progressively damaged so that teeth may loosen or fall out. In turn, periodontitis is a risk factor for other diseases like cardiovascular and lung disease.
A major cause of periodontal disease is poor oral hygiene, ...