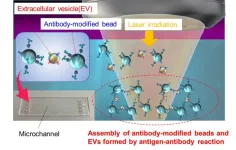
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles
Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes!
2023-10-06
(Press-News.org)
Osaka, Japan - Can particles as minuscule as viruses be detected accurately within a mere 5 minutes? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists say yes, with their innovative method for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of biological nanoparticles, opening doors for early diagnosis of a broad range of diseases.
Nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, with diameters of 50–150 nm, play essential roles in intercellular communication and have garnered attention as biomarkers for various diseases and drug delivery capsules. Consequently, the rapid and sensitive detection of nanoscale EVs from trace samples is of vital importance for early diagnosis of intractable diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's disease. However, the extraction of nanoscale EVs from cell culture media previously required a complex and time-consuming process involving ultracentrifugation.
A research team led by Director Professor Takuya Iida, Deputy Director Associate Professor Shiho Tokonami, and Assistant Director Professor Ikuhiko Nakase, from the Research Institute for Light-induced Acceleration System (RILACS) at Osaka Metropolitan University, has utilized the power of laser light to accelerate the reaction between nanoscale EVs derived from cancer cells and antibody-modified microparticles. The three-dimensional structure of the resulting aggregates was then analyzed using confocal microscopy. As a result, the researchers demonstrated the ability to measure, within 5 minutes, approximately 103–104 nanoscale EVs contained in a 500 nL sample.
Professor Iida concluded, “This research achievement provides a method for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of biological nanoparticles, offering a foundation for innovative analysis of cell-to-cell communication and early diagnosis of various diseases in the future.”
Their findings were published in Nanoscale Horizons.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is the third largest public university in Japan, formed by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in 2022. OMU upholds "Convergence of Knowledge" through 11 undergraduate schools, a college, and 15 graduate schools. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter: @OsakaMetUniv_en, or Facebook.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-06
Men who have been on parental leave have a significantly reduced risk of being hospitalized due to alcohol consumption. This is shown by a study published in Addiction from researchers at the Department of Public Health Sciences, Stockholm University.
The aim of the study was to assess whether fathers’ parental leave influences alcohol-related morbidity and mortality. In order to try to find out if that is the case, the researchers have investigated the effects of parental leave policy that was implemented in Sweden in 1995. The policy encouraged fathers to use parental leave by reserving 30 days of leave for their use alone and resulted in the proportion ...
2023-10-06
Utilizing soft, flexible materials such as cloth, paper, and silicone, soft robotic grippers is an essential device that acts like a robot's hand to perform functions such as safely grasping and releasing objects. Unlike conventional rigid material grippers, they are more flexible and safe, and are being researched for household robots that handle fragile objects such as eggs, or for logistics robots that need to carry various types of objects. However, its low load capacity makes it difficult to lift heavy objects, and its poor grasping stability makes it easy to lose the object even under mild external impact.
Dr. ...
2023-10-06
Associate Professor CAI Zhenyi and Professor WANG Junxian from the Department of Astronomy at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), through the study of the optical to extreme ultraviolet radiation generated by the accretion of supermassive black holes at the centers of quasars, have discovered that their spectral energy distribution is independent to the intrinsic brightness of quasars, overturning the traditional ...
2023-10-06
Intense tropical cyclones are one of the most devastating natural disasters in the world due to torrential rains, flooding, destructive winds, and coastal storm surges. New research co-authored by a University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa atmospheric scientist revealed that since the 1980s, Category 4 and 5 hurricanes (maximum wind speed greater than 131 miles per hour) have been arriving three to four days earlier with each passing decade of climate change. Their findings were published recently in Nature.
“When intense tropical cyclones occur earlier than usual, they cause unexpected problems for communities,” said Pao-Shin Chu, atmospheric ...
2023-10-06
PITTSBURGH, Oct. 4, 2023 – Former professional American football players who have medical and mental health conditions including depression, anxiety or sleep apnea are more likely to receive an unverified diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, compared to those without those conditions, report researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Harvard University and Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Sports Medicine today.
Receiving a CTE diagnosis that cannot be verified until after death could further exacerbate mental health conditions in former players due to the current lack of ...
2023-10-06
New study shows grasses are taking an evolutionary shortcut by continually borrowing genes from their neighbours to grow bigger, stronger and taller
The research, led by the University of Sheffield, is the first to show how frequently grasses exchange genes in the wild
The naturally occurring process observed in grasses, including in some of the crops we eat, may mirror methods used to make genetically modified crops
Understanding the rate is important to know the potential impact it can have on a plant’s ...
2023-10-06
Arcadia has made a major new philanthropic donation to the University of Cambridge, taking its total support for the Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme to over $138 million.
The Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme supports the large-scale restoration of Europe’s most treasured but endangered ecosystems, enriching biodiversity while revitalising local economies.
The work recognises humanity’s dependence on healthy, functioning ecosystems - for example in preventing urban flooding, and reducing the impacts ...
2023-10-06
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — A small segment of the U.S. population considers violence, including lethal violence, to be usually or always justified to advance political objectives. This is according to newly published research from the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program (VPRP).
The study provides a complex portrait of the attitudes and concerns about the state of democracy in the U.S. It also highlights the underlying beliefs that may inform the potential for violence.
The study was published Sept. 29, 2023, in Injury Epidemiology. A preprint, or version that had not yet been peer reviewed, was shared online ...
2023-10-06
SAN ANTONIO, Oct. 6, 2023 – Research led by Mays Cancer Center at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has discovered that altering certain molecular interactions could yield new strategies for treating prostate cancer and related diseases.
The study focuses on androgen receptors (AR), which are protein molecules that help direct the development of male sexual characteristics, essentially by turning genes on or off as necessary.
The researchers determined that an optimum level of ...
2023-10-06
New research being presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 Oct) shows that low muscle mass is associated with a two-fold risk of death from cardiovascular disease in individuals with diabetes.
This association is independent of frailty, glycaemic control and the microvascular complications retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels of the retina) and nephropathy (kidney disease), the analysis of data on US adults found.
Sarcopenia – age-related loss of muscle mass and strength – was known to be associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles
Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes!