(Press-News.org) Because metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) — highly porous metal complexes — are so structurally and chemically diverse, they could be used for many applications, such as drug delivery and environmental clean-up. But researchers still need to get a better understanding of how they function, especially when embedded in polymers. Reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, researchers have now developed and characterized nitric oxide (NO)-storing MOFs embedded in a thin film with novel antibacterial potential.
Studying the interactions between MOFs and polymers within membranes can be challenging and requires complex analytical methods and significant resources. In earlier studies, Russell E. Morris and colleagues examined the interface between a nickel-containing MOF and polyurethane. But the focused-ion-beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) method that they used can alter or damage both polymers and MOFs. So, the same researchers together with Zeiss Microscopy used a new FIB-SEM technique using cryogenics to increase stability of MOF composites.
To test this, they created three membranes in collaboration with researchers at Colorado State University containing a nickel MOF called CPO-27-Ni, a copper MOF called CuBTTri, or both. Next, using their cryogenic FIB-SEM technique, they saw particles of each MOF in greater detail than with other imaging methods. The images also showed that the metal complexes were distributed evenly throughout the membranes and did not overlap. The researchers then examined the ability of the films to release NO, a molecule with antibacterial properties that could have biomedical applications. In experiments, MOF-embedded membranes had different triggers and responses:
CPO-27-Ni released NO quickly, as a short burst, in response to moisture.
CuBTTri acted as a catalyst when exposed to a tripeptide, S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), a natural source of NO in the human body, and produced a sustained NO release in response.
Together, CPO-27-Ni and CuBTTri yielded a membrane with rapid and sustained NO delivery, when exposed sequentially to moisture and to GSNO.
The researchers say that the nickel and copper MOFs combined to create a composite material that achieved an optimal, two-stage NO delivery system. They suggest that this two-phase delivery might be useful in medical devices, providing both immediate antibacterial effects and long-term prevention of microbial fouling.
The authors acknowledge funding from the European Research Council grant ADOR, the EPSRC Light Element Analysis Facility Grant, and the EPSRC Strategic Equipment Resource Grant.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Oct. 11 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Metal-organic frameworks could someday deliver antibacterial nitric oxide
2023-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Significant development in mild cognitive impairment treatment revealed in Australia
2023-10-11
AUSTRALIA, Sydney – October 11, 2023 – Western Sydney University’s NICM Health Research Institute has led a world-first clinical trial in Australia that offers new hope in the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among older people. The trial’s results, published in Alzheimer's and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring, a journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, signal the efficacy and safety of Sailuotong (SLT), a novel herbal extract, as a potential treatment for MCI.
Trial ...
Rivers may not recover from drought for years
2023-10-11
Lack of rainfall is not the only measure of drought. New UC Riverside research shows that despite a series of storms, the impact of drought can persist in streams and rivers for up to 3.5 years.
There are two measures of drought in streams. One measure is the total water level, which is impacted by snowmelt and rainfall. Many researchers examine this measurement. Another measure is baseflow, which is the portion of streamflow fed by groundwater.
Fewer researchers examine baseflow droughts, and there was not previously an accurate way to measure them. Because baseflow is strongly tied to groundwater, and because the ...
Chronic kidney disease may be linked to sudden cardiac arrest in Hispanic/Latino adults
2023-10-11
Research Highlights:
Chronic kidney disease was strongly associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, in a new study.
Early identification and management of kidney disease may reduce risk of sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino people, researchers suggest.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023
DALLAS, October 11, 2023 — Chronic kidney disease may increase risk and predict sudden cardiac arrest among Hispanic/Latino adults, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American ...
Cardiac arrest: Hispanics, Latinos with kidney disease at high risk
2023-10-11
Hispanics and Latinos with chronic kidney disease are at significant risk for suffering from sudden cardiac arrest, according to a new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai.
During sudden cardiac arrest, the heart unexpectedly stops beating.
“Because people who experience sudden cardiac arrest have a survival rate of less than 10%, prevention is extremely important,” said Kyndaron Reinier, Ph.D., associate director of Epidemiology in the Center for Cardiac Arrest Prevention at the Smidt Heart Institute and lead author of the study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“This study highlights the importance for Hispanic ...
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays caught off Congo
2023-10-11
Tens of thousands of endangered sharks and rays are caught by small-scale fisheries off the Republic of the Congo each year, new research shows.
Scientists surveyed fish brought ashore at Songolo, which is home to more than 60% of the country's “artisanal” fishers (small boats, small engines, hand-hauled lines and nets).
In three years, the team – led by the University of Exeter in partnership with the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) Congo Program and the Republic of the Congo’s fisheries department – recorded more than 73,000 sharks and rays landed.
Most were juveniles, and 98% of individuals were of species listed as vulnerable, ...
Bouldering in south-central Madagascar: a new “rock-climbing” gecko species of the genus Paroedura
2023-10-11
Named after its habitat preference, Paroedura manongavato, from the Malagasy words “manonga” (to climb) and “vato” (rock), is a bouldering expert. Part of its “home range” is also very well-known to rock climbers for its massive granitic domes. “Its description represents another step into the crux (in climbing jargon, the most difficult section of a bouldering problem) of resolving the taxonomy of the recently revised P. bastardi group, where the new species belongs, and reaching a total of 25 described species in this genus, ...
Peregrine falcons set off false alarms to make prey easier to catch
2023-10-11
Predators must eat to survive — and to survive, prey must avoid being eaten. One theory, the Wolf-Mangel model, suggests predators could use false attacks to tire prey out or force them to take bigger risks, but this has been hard to show in practice. Now, scientists observing peregrine falcons have found evidence that they deliberately exhaust their prey to improve later hunting success.
“Although predators are imagined as clever in novels and movies, like the velociraptors in Jurassic Park, empirical biologists are generally not inclined to give much credence to such ideas,” ...
Make diagnosing serious geriatric diseases as easy as measuring blood sugar
2023-10-11
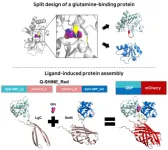
In 2023, life expectancy in Korea will be 83.6 years, the third highest among OECD countries, and it is steadily increasing every year. As the proportion of the elderly population increases, the social cost of treating various geriatric diseases is also increasing rapidly, and there is a growing interest in early diagnosis of diseases. Among the various diagnostic methods, researchers are actively conducting research on measuring glutamine as an indicator of geriatric diseases by finding that the concentration of glutamine in the cells and blood of patients with serious diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and dementia is significantly changed compared to normal people.
Dr. Seo, Moon-Hyeong ...
Commonly used herbicide is harmful to adolescent brain function
2023-10-11
Herbicides are the most used class of pesticides worldwide, with uses in agriculture, homes and industry. Exposures to two of the most popular herbicides were associated with worse brain function among adolescents, according to a study led by researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego.
In the Oct. 11, 2023 online issue of Environmental Health Perspectives, the researchers reported measuring metabolite concentrations of two commonly used herbicides — glyphosate and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) — and the insect repellent DEET in urine samples ...
New antibiotic drug developed by HKU Chemistry research team approved for clinical trials in humans
2023-10-11
A new antibiotic drug developed by a research team led by Professor Li Xuechen from the Department of Chemistry at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently gained approval from the authorities to undergo clinical trials in the Mainland.
The new drug, which has taken the research team ten years to develop and is named Kynomycin, received the "Notice of Approval for Drug Clinical Trials" from the National Medical Products Administration of China to be tested in human subjects.
The new antibiotic drug targets complex skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI) caused by bacteria. It ...