(Press-News.org) Filaments of dust and gas festoon this star-forming region in a new infrared image from MIRI.
One of the greatest strengths of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is its ability to give astronomers detailed views of areas where new stars are being born. The latest example, showcased here in a new image from Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), is NGC 346 – the brightest and largest star-forming region in the Small Magellanic Cloud.
The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, visible to the unaided eye in the southern constellation Tucana. This small companion galaxy is more primeval than the Milky Way in that it possesses fewer heavy elements, which are forged in stars through nuclear fusion and supernova explosions, compared to our own galaxy.
Since cosmic dust is formed from heavy elements like silicon and oxygen, scientists expected the SMC to lack significant amounts of dust. However the new MIRI image, as well as a previous image of NGC 346 from Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera released in January, show ample dust within this region.
In this representative-color image, blue tendrils trace emission from material that includes dusty silicates and sooty chemical molecules known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or PAHs. More diffuse red emission shines from warm dust heated by the brightest and most massive stars in the heart of the region. An arc at the center left may be a reflection of light from the star near the arc’s center. (Similar, fainter arcs appear associated with stars at lower left and upper right.) Lastly, bright patches and filaments mark areas with abundant numbers of protostars. The research team looked for the reddest stars, and found 1,001 pinpoint sources of light, most of them young stars still embedded in their dusty cocoons.
By combining Webb data in both the near-infrared and mid-infrared, astronomers are able to take a fuller census of the stars and protostars within this dynamic region. The results have implications for our understanding of galaxies that existed billions of years ago, during an era in the universe known as “cosmic noon,” when star formation was at its peak and heavy element concentrations were lower, as seen in the SMC.The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory.
Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
END
NASA’s Webb captures an ethereal view of NGC 346
2023-10-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New clinical trial tests innovative ways to preserve muscle mass during metastatic prostate cancer
2023-10-11
The National Cancer Institute awarded investigators at Huntsman Cancer Institute a grant totaling more than $3 million to conduct a clinical trial to see if combining creatine monohydrate supplementation and resistance exercise training helps preserve muscle in people who have metastatic prostate cancer. Loss of muscle mass is a major side effect of treatment for prostate cancer. Creatine monohydrate supplementation, a naturally occurring molecule in the body, helps combat fatigue and provides more energy, resulting in better workouts. Researchers hypothesize that taking creatine monohydrate ...
Isotope database will help Mexican communities better understand hydrology processes
2023-10-11
With a population of 127 million and a land mass about a fifth the size of the United States, Mexico has a large spectrum of climates and landscapes, ranging from mountains to coastal regions and from deserts to glaciers. Because of these variations, it is important for communities to understand precipitation patterns to plan appropriately for weather events and water resources management.
A team led by Ricardo Sánchez-Murillo, associate professor of earth and environmental sciences at The University of Texas at Arlington, has created a new isotope database that includes 608 monthly rain samples (spanning 2018-22) from 21 monitoring stations ...
Novel drug, NFX-179, inhibits MEK activity, prevents cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma development
2023-10-11
TAMPA, Fla. — Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer in the United States, impacting approximately 700,000 people each year. While medications exist to prevent the development of disease, they are associated with side effects, suggesting the need for new drugs that can be safely used to prevent it. In a new article published today in Science Translational Medicine, a team of Moffitt Cancer Center researchers, in collaboration with NFlection Therapeutics and researchers at Stanford University, reports the ...
MD Anderson hosts 2023 Leading Edge of Cancer Research Symposium
2023-10-11
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center will host its annual Leading Edge of Cancer Research Symposium Nov. 16-17, 2023, featuring presentations and discussions on genomics, immunity and inflammation, computational approaches for spatial biology, and emerging technologies that are driving the next wave of cancer breakthroughs.
The in-person symposium at MD Anderson will include keynote presentations from Paul Mischel, M.D., professor of Pathology at Stanford University, Andrea Schietinger, Ph.D., associate professor of Immunology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and Kevan Shokat, Ph.D., chair of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at University ...
NYU researchers reconstruct speech from brain activity, illuminates complex neural processes
2023-10-11
Speech production is a complex neural phenomenon that has left researchers explaining it tongue-tied. Separating out the complex web of neural regions controlling precise muscle movement in the mouth, jaw and tongue with the regions processing the auditory feedback of hearing your own voice is a complex problem, and one that has to be overcome for the next generation of speech-producing protheses.
Now, a team of researchers from New York University have made key discoveries that help untangle that web, and are using it to build vocal reconstruction technology that recreates the voices of patients ...
Oregon State to lead $2M federal push toward more-efficient, longer-lasting electrical components
2023-10-11
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering are spearheading a $2 million federal effort to explore new ways of developing electrical components that are better able to withstand extreme operating conditions, especially high temperatures.
The team will try to find novel, artificial-intelligence-based methods for designing and building long-lasting, high-efficiency electrical components for harsh-environment applications such as high-power radar and the aerospace, automotive and wireless communications industries.
“The semiconductor ...
Group led by University of Alaska Fairbanks gets $13.9 million to aid coastal climate resilience
2023-10-11
The National Science Foundation is funding a $13.9 million program led by the University of Alaska Fairbanks to help multiple communities respond to coastal erosion, flooding, permafrost thaw and other hazards attributed to climate change.
The four years of funding is part of the foundation’s Navigating the New Arctic program.
The funding supports AC³TION, a project led by the Alaska Coastal Cooperative at UAF in collaboration with the rural coastal communities, Arizona State University, the University of Northern Iowa and the University of Texas El Paso.
The group’s acronym stands for Alaska Coastal Cooperative for Co-producing Transformative Ideas and Opportunities ...
New study finds link between subjective and objective memory decline
2023-10-11
MINNEAPOLIS – Among people who report memory and thinking problems, some show no signs of a problem on standard tests, while others have subtle declines on their tests. A new study shows that people who have subtle problems with these tests may have an increased risk of developing mild cognitive impairment, which can be a precursor to dementia. The study is published in the October 11, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Several studies have found that people with subjective ...
New guidance issued on the determination of brain death
2023-10-11
MINNEAPOLIS – New guidance has been issued for clinicians on the determination of brain death, also known as death by neurologic criteria. A new consensus practice guideline, developed through a collaboration between the American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the Child Neurology Society (CNS), and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) is published in the October 11, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
This guideline updates the 2010 AAN ...
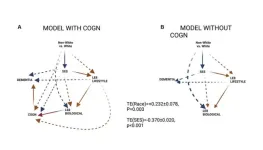
Insights on disparities in dementia from the UK Biobank study
2023-10-11
“The present study is among few to examine racial/ethnic disparities in dementia risk and their related pathways [...]. It is the first to do so in a UK population.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 11, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 18, entitled, “Pathways explaining racial/ethnic and socio-economic disparities in dementia incidence: the UK Biobank study.”
Pathways explaining racial/ethnic disparities ...