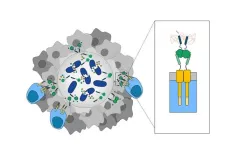
(Press-News.org) A new probiotic-guided chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T platform uses engineered bacteria to infiltrate and produce synthetic antigen targets, enabling CAR-T cells to find, identify, and destroy tumor cells in situ, according to a new study. The combined cell therapy platform expands the scope of CAR-T cell therapy to include difficult-to-target solid tumors. Immunotherapies using CAR-T cells have proven successful in treating some types of blood cancers. However, their efficacy against solid tumors remains elusive. A key challenge facing tumor-antigen targeting immunotherapies like CAR-T is the identification of suitable targets that are specifically and uniformly expressed on solid tumors. Solid tumors express heterogeneous and nonspecific antigens and are poorly infiltrated by T cells. As a result, the approach carries a high risk of fatal on-target, off-tumor toxicity, wherein CAR-T cells attack the targeted antigen on healthy vital tissues with potentially fatal effects. Previous studies have shown that, unlike CAR-T cells, some species of bacteria can selectively colonize the hostile microenvironments of immune-privileged tumor cores and can be engineered as antigen-independent platforms for therapeutic delivery. In this study, Rosa Vincent, Candice Gurbatri, and colleagues combine probiotic therapy with CAR-T cell therapy to create a two-stage probiotic-guided CAR-T cell (ProCAR) platform, whereby T cells are engineered to sense and respond to synthetic CAR targets that are delivered by solid tumor-colonizing probiotic bacteria. Using synthetic gene circuit engineering on a well-characterized non-pathogenic strain of E. coli, Vincent et al. created a probiotic that could infiltrate and cyclically release synthetic CAR targets directly to the tumor core, effectively “tagging” the tumor tissue. Then, generated CAR-T cells that were programed to recognize the probiotic-delivered synthetic antigen tags could be used to “home in” on the tagged solid tumors and kill tumor cells in situ. What’s more, the authors also engineered probiotics that co-release chemokines in addition to synthetic targets to further enhance CAR-T cell recruitment to the tumor, boosting therapeutic response. Vincent et al. demonstrate the platform in humanized and immunocompetent mouse models of leukemia, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer and show that it resulted in the safe reduction of tumor volume. “The study of Vincent et al. is an important proof-of-concept for a potential approach to treating heterogeneous, immunologically cold, and poorly infiltrated solid tumors,” write Eric Bressler and Wilson Wong in a related Perspective.
END
Engineered bacteria guide CAR-T cells to poorly infiltrated solid tumors
2023-10-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An electrical switch to control chemical reactions
2023-10-12
New pharmaceuticals, cleaner fuels, biodegradable plastics: in order to meet society’s needs, chemists have to develop new synthesis methods to obtain new products that do not exist in their natural state. A research group at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with Cardiff University, has discovered how to use an external electric field to control and accelerate a chemical reaction, like a ‘‘switch’’. This work, to be read in Science Advances, could have a considerable impact on the development of new molecules, enabling not only more environmentally friendly synthesis, but also very simple external control of a chemical reaction.
In ...
Gray whales experience major population swings as a result of Arctic conditions, research shows
2023-10-12
NEWPORT, Ore. – Dynamic and changing Arctic Ocean conditions likely caused three major mortality events in the eastern North Pacific gray whale population since the 1980s, a new study has found.
During each of these die-offs, including one that began in 2019 and is ongoing, the gray whale population was reduced by up to 25% over just a few years, said Joshua Stewart, an assistant professor with Oregon State University’s Marine Mammal Institute and the study’s lead author.
“These are extreme population swings that we did not expect to see in a large, long-lived species like gray whales,” Stewart said. “When the availability ...
Cell atlases of the human brain presented in Science
2023-10-12
In two parallel projects, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have been involved in creating the most comprehensive atlases of human brain cells to date. The two studies, which are published in Science, provide clues on different brain diseases and give hope for medical advancements in the future, such as new cancer drugs.
Knowing what cells constitute the healthy brain, where different cell types are located and how the brain develops from the embryo stage is fundamental to the ability to compare and better understand how diseases arise. There are at present advanced atlases of the ...
Coffee and cocoa plants at risk from pollinator loss
2023-10-12
Tropical crops such as coffee, cocoa, watermelon and mango may be at risk due to the loss of insect pollinators, finds a new study led by UCL and Natural History Museum researchers.
Published in Science Advances, the study explores the intricate interplay between climate change, land use change, and their impact on pollinator biodiversity, ultimately revealing significant implications for global crop pollination.
The study, which compiled data from 1,507 crop growing sites around the world and catalogued 3,080 insect pollinator species, exposes a concerning trend – the combined pressures ...
Scientists unveil detailed cell maps of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain
2023-10-12
A group of international scientists have mapped the genetic, cellular, and structural makeup of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain. This understanding of brain structure, achieved by funding through the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® Initiative, or The BRAIN Initiative®, allows for a deeper knowledge of the cellular basis of brain function and dysfunction, helping pave the way for a new generation of precision therapeutics for people with mental disorders and other disorders of the brain. The findings appear in a compendium of ...
Engineered bacteria paint targets on tumors for cancer-killing T cells to see
2023-10-12
New York, NY—October 12, 2023—For several years, researchers have been successfully using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells to target specific antigens found on blood cells as a cure for patients with leukemia and lymphoma. But solid tumors, like breast and colon cancers, have proven to be more difficult to home in on. Solid tumors contain a mix of cells that display different antigens on their surface-often shared with healthy cells in the body. Thus, identifying a consistent and safe target has impeded the success of most CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors at the first phase ...
How do tax proposals affect cancer health of tobacco users based on income, education?
2023-10-12
Tobacco is the leading cause of preventable death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and cigarette smoking causes three in 10 of all cancer deaths. Smoking also accounts for more than 30 percent of the difference in life expectancy among different socioeconomic groups.
Roberta Freitas-Lemos, research assistant professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, recently received a career development award to explore the ways in which nicotine tax policies can influence health disparities. The award of more than $680,000 over five years from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health is designed ...
NIH awards Mount Sinai researchers $12 million to personalize sickle cell treatment
2023-10-12
New York, NY (October 12, 2023) - The Mount Sinai Health System has received a $12,180,625 grant from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute to compare new treatment options for sickle cell disease and determine which work best for specific patients.
“Sickle cell traditionally has been a neglected disease, but it benefited from a flurry of innovation over the last decade and there are now three new medications approved for the disease,” says Jeffrey Glassberg, MD, Director of the Mount Sinai Sickle Cell Program.
“While this is welcome news, clinicians now have a new challenge. ...
Caution: Content warnings do not reduce stress, study shows
2023-10-12
Advocates for the use of trigger warnings suggest that they can help people avoid or emotionally prepare for encountering content related to a past trauma. But trigger warnings may not fulfill either of these functions, according to an analysis published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Instead, warnings appear to heighten the anticipatory anxiety a person may feel prior to viewing sensitive material while making them no less likely to consume that content, wrote Victoria M. E. Bridgland of ...
New catalyst could provide liquid hydrogen fuel of the future
2023-10-12
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden are investigating a car fuel comprised of a liquid that is converted to hydrogen by a solid catalyst. The used liquid is then emptied from the tank and charged with hydrogen, after which it can be used again in a circular system that is free from greenhouse gas emissions.
In two research articles, Lund researchers have demonstrated that the method works, and while it is still basic research, it has the potential to become an efficient energy-storage system in the future.
“Our catalyst is one of the most efficient around, at least if you look at publicly available research,” says Ola ...