(Press-News.org)
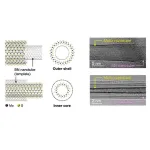
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have engineered a range of new single-walled transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) nanotubes with different compositions, chirality, and diameters by templating off boron-nitride nanotubes. They also realized ultra-thin nanotubes grown inside the template, and successfully tailored compositions to create a family of new nanotubes. The ability to synthesize a diverse range of structures offers unique insights into their growth mechanism and novel optical properties.
The carbon nanotube is a wonder of nanotechnology. Made by rolling up an atomically thin sheet of carbon atoms, it has exceptional mechanical strength and electrical conductivity amongst a range of other exotic optoelectronic properties, with potential applications in semiconductors beyond the silicon age.
The key features of carbon nanotubes come from subtle aspects of their structure. For example, like a piece of paper rolled up at an angle, nanotubes often have a chirality, a “handedness” in their structure that makes them different from their mirror image. That is also why scientists are looking ahead to materials beyond carbon, which might enable a wider range of structures. One spotlight is on transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) compounds, made of transition metals and Group 16 elements. Not only is there a whole family of them, TMDs have features which are not seen in carbon nanotubes, such as superconductivity and photovoltaic properties, where exposure to light generates a voltage or current.
To get to grips with the full potential of TMDs, however, scientists need to be able to make single-walled nanotubes in a variety of compositions, diameters, and chirality in a way that lets us study their individual properties. This has proven challenging: TMD nanotubes usually form in concentric multi-walled structures, where each layer might have different chirality. This makes it tricky to find out, for example, what kind of chirality gives rise to specific properties.
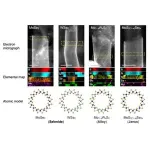
Now, a team led by Assistant Professor Yusuke Nakanishi from Tokyo Metropolitan University has come up with a way to do just that. By using boron-nitride nanotubes as a template, they could successfully grow a range of single-walled TMD nanotubes by adding the required elements through exposure to vapor. In previous work, they made single-walled molybdenum sulfide nanotubes. On looking at individual nanotubes in more detail, they have now distinguished a whole plethora of single-walled tubes of different diameters and chirality. Specifically, they measured the “chiral angles” of individual tubes which, taken together with their diameters, determine unique chiral structures. They discovered, for the first time, that the chiral angles of their nanotubes were randomly distributed: this means they have access to the whole range of possible angles, promising new insights into the relationship between chirality and electronic states, a key unsolved question in the field. There were also ultra-thin tubes only a few nanometers across grown inside the template, not outside, a unique platform for observing quantum mechanical effects.
By tweaking their recipe, the team has now also succeeded in switching both the metal and the chalcogen, making molybdenum selenide, tungsten selenide, and molybdenum tungsten sulfide alloy nanotubes. They even made nanotubes with one element on the outside, another on the inside, “Janus”-type nanotubes named after the two-faced god of Roman mythology. The team’s diverse new entries into the nanotube family promise bold new strides in not only our understanding of TMD nanotubes, but how exotic properties arise from their structures.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants (Grant Numbers JP23H01807, JP20H02572, JP21H05232, JP21H05234, JP22K04886, JP22H05468, JP22H01911, JP22H02573, JP21H05017, JP22H05469, JP23H00259, JP23K13635, JP23H00097, JP22H05441, JP21H05235, JPJSJRP20221202), the JST CREST Program (Grant Numbers JPMJCR17I5 and JPMJCR20B1) and the JST FOREST Program (Grant Number JPMJFR213X).
END
FINDINGS
In a recent study led by Ravi Salgia, M.D., Ph.D., the Arthur & Rosalie Kaplan Chair in Medical Oncology, a team of researchers from City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and other institutions found that nongenetic mechanisms are important in lung cancer patients who develop a resistance to one cancer therapy. Their findings were published in the October 13 issue of the journal Science Advances.
The team’s study explored resistance to the anti-cancer medication sotorasib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Sotorasib inhibits a specific mutation ...
London, Ont.,: Worldwide, millions of stroke survivors undergo prolonged cardiac monitoring, leading to the discovery of atrial fibrillation, or irregular heartbeats, in up to 1.5 million of these patients each year.
A new study, published in The Lancet Neurology, describes the knowledge on atrial fibrillation detected in patients who had a recent stroke. The publication suggests that atrial fibrillation detected post-stroke is not quite the same as the irregular heartbeats already known before a stroke.
The study, led by Western University professor Dr. Luciano Sposato, proposes that atrial fibrillation detected post-stroke exhibits distinct ...
New research has underscored how characteristics of “grit” and self-control are associated with better weight loss and weight maintenance outcomes in a study focusing on couples. And that these characteristics can change through behavioral interventions.
This research led by Amy Gorin, professor of psychological sciences and vice provost for health sciences and interdisciplinary initiatives; and Tricia Leahey, professor of allied health sciences in the College of Agriculture, Health and Natural ...
For the fourth time in five years, students at The University of Texas at Arlington have won a prestigious national award for noise control engineering.
Ross Everett and Bret Johnson, mechanical engineering students who graduated in May 2023, earned the Leo Beranek Student Medal for Excellence in the Study of Noise Control from the Institute of Noise Control Engineering of the USA for their work to decrease cabin noise in the autonomous rideshare cars owned by May Mobility that operate around UTA’s campus. The institute awards the medal annually to outstanding undergraduate and graduate ...
CHAPEL HILL, NC — A three-year clinical trial funded by the National Institutes of Health and Food Allergy Research and Education (FARE) has shown that the sublingual immunotherapy, or SLIT, is safe in peanut-allergic children ages 1 to 4, with a greater likelihood of desensitization and remission the earlier the treatment began.
Led by Edwin Kim, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the UNC School of Medicine, this is the first randomized, controlled trial to investigate – in this young age group – the efficacy and feasibility of SLIT, which ...
A long-term study by UC Davis Health researchers sheds new light on the relationship between autism traits and mental health in middle childhood. The paper, published in the journal Autism, finds that changes in core autism characteristics are related to whether children develop additional mental health challenges during their elementary school years.
“Our findings suggest that different aspects of a child’s development may affect each other over time,” explained Einat Waizbard-Bartov, a doctoral researcher in developmental psychology at the UC Davis MIND Institute and the lead author on the paper. “Core autism traits and ...
Professor Dan M. Frangopol is the winner of the EuroStruct2023 International Award of Merit presented by the EuroStruct Executive Committee in recognition of outstanding contributions to bridge and structural asset management and structural engineering.
Frangopol, the inaugural Fazlur R. Khan Endowed Chair of Structural Engineering and Architecture in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Lehigh, was presented with the award during EuroStruct 2023, the second Conference of the European ...
NEW YORK, NY--Does this sound like you? You wake up at the same time each morning, get the kids out the door, and rush to catch the subway to work. But at night, maybe you stay up until midnight doing laundry or 1 a.m. to catch up on the bills.
Lots of Americans—about one-third of us—are in the same situation and habitually get only five to six hours of sleep instead of the recommended seven to eight hours.
But even a mild chronic sleep deficit may heighten the risk of developing heart disease later in life: Surveys of thousands of people ...
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers conducted a statewide survey of all patients on breathing machines in hospitals and long-term care facilities and found that a significant percentage of them harbored two pathogens known to be life-threatening in those with compromised immune systems. One pathogen, Acinetobacter baumannii, was identified in nearly 31 percent of all patients on ventilators to assist with their breathing; Candida auris was identified in nearly 7 percent of patients on ventilators, according to the study which was published this week in the Journal ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: Friday, Oct. 13, 2023
CONTACT: NIAPressTeam@mail.nih.gov, 301-496-1752
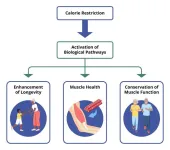
Reducing overall calorie intake may rejuvenate your muscles and activate biological pathways important for good health, according to researchers at the National Institutes of Health and their colleagues. Decreasing calories without depriving the body of essential vitamins and minerals, known as calorie restriction, has long been known to delay the progression of age-related diseases in animal models. This new study, published in Aging Cell, suggests the same ...