Sansbury receives funding for dissertation study
2023-10-16
(Press-News.org)
Amber B. Sansbury, a doctoral candidate in Mason's School of Education, received $24,576 from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services for the project: "Racial Identity Development of Young Black Children in Early Childhood Education: The Roles of Teachers and Families."
Colleen Vesely, Associate Professor, College of Education and Human Development (CEHD), is serving as Sansbury's adviser.
In this qualitative dissertation study, Sansbury will explore how family engagement vis-a-vis relationships between African American teachers and African American families supports racial socialization and young children's emergent racial identity.
This study is guided by the following research questions: 1) How do African American teachers and African American families build relationships to support African American children’s racial identity development? 2) How are these relationships reflected in African American teachers’ and African American families’ cultural values, race-related beliefs, and family-centered practices regarding their roles in racial identity development of African American young children?
The Educare model of Head Start provides high-quality instruction, intensive family engagement, and enriching learning environments with positive academic, behavioral, and social-emotional outcomes for children overall. A key component is the intensive family engagement that includes regular home visits, wraparound community and medical support, child development classes for families, and advocacy opportunities.
Sansbury is prioritizing family engagement by advancing how the field conceptualizes the race-related and cultural dimensions of family–school relationships for African American teachers and economically vulnerable African American parents in early care and education (ECE) settings specifically. A race-conscious model of family engagement is essential to understand how responsive relationships between African American parents and African American teachers might contribute to African American young children’s healthy racial identities by leveraging shared sociocultural assets.
Funding for this project began in Sept. 2023 and will end in Sept. 2024.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls 38,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the last half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity and commitment to accessibility. Learn more at http://www.gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-16
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the selection of the High Performance Data Facility (HPDF) hub, which will create a new scientific user facility specializing in advanced infrastructure for data-intensive science. The Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (JLab) will be the HPDF Hub Director and the lead infrastructure will be located at JLab. The project to build the Hub will be a partnership between JLab and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), and the two labs ...
2023-10-16
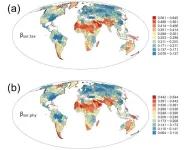
Beta-diversity serves as a crucial metric for gauging shifts in species composition over spatial or temporal scales, bridging the spectrum between localized (alpha) and broader regional (gamma) diversity. In the fields of ecology, biogeography and conservation biology, to elucidate the origins and sustenance of geographic beta-diversity patterns, we need to explore both the taxonomic and phylogenetic beta-diversity at different evolutionary depths.
In an article published in the KeAi journal Plant Diversity, using a ...
2023-10-16
Neurons, the main cells that make up our brain and spinal cord, are among the slowest cells to regenerate after an injury, and many neurons fail to regenerate entirely. While scientists have made progress in understanding neuronal regeneration, it remains unknown why some neurons regenerate and others do not.
Using single-cell RNA sequencing, a method that determines which genes are activated in individual cells, researchers from University of California San Diego School of Medicine have identified a new biomarker that can be used to predict whether ...
2023-10-16
Imagine the life of a yeast cell, floating around the kitchen in a spore that eventually lands on a bowl of grapes. Life is good: food for days, at least until someone notices the rotting fruit and throws them out. But then the sun shines through a window, the section of the counter where the bowl is sitting heats up, and suddenly life gets uncomfortable for the humble yeast. When temperatures get too high, the cells shut down their normal processes to ride out the stressful conditions and live to feast on grapes on another, cooler day.
This “heat ...
2023-10-16
About The Study: The results of this study including 121,000 Singaporean children ages 1 through 4 suggest that completion of a primary mRNA vaccine series provided protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Although incidence of hospitalization and severe illness is low in this age group, there is potential benefit of vaccination in preventing infection and potential sequelae.
Authors: Liang En Wee, M.R.C.P., M.P.H., of the National Centre for Infectious Diseases in Singapore, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
2023-10-16
About The Study: The findings of this study demonstrated that the incremental changes associated with dementia in regard to older adults’ long-term care and financial burden are substantial. Family care availability should be accounted for in a comprehensive assessment of predicting the effects of dementia.
Authors: Hwa Jung Choi, Ph.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.5482)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2023-10-16
Mass General Brigham investigators tested their approach using specimens from multiple cancer types, including liver, brain, tongue, skin, breast, bone and soft tissue
Their visual and quantitative technique, which combines an injected FDA-approved drug with high-speed cameras to detect changes occurring in a billionth of a second, had an accuracy of 97% across tumor types
Removing a patient’s tumor while sparing healthy tissue requires exquisite precision, but often surgeons must rely on their eyes and hands to determine where to cut. A team led ...
2023-10-16
One of the building blocks of ocean life can adapt to cope with the effects of climate change, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
The discovery holds promises for biotechnology developments that could counter the negative effects of changing environmental conditions, such as ocean warming and even the reduction in the productivity of crops.
Looking at eukaryotic phytoplankton, also referred to as microalgae, found over large parts of the ocean, the international team led by UEA’s Prof Thomas Mock discovered the algae have found a way to cope with nutrient starvation, which is predicted to ...
2023-10-16
Despite steps toward decreasing deforestation, uncontrolled wildfires are threatening environmental gains in Brazilian Amazonia, one of the world’s most critical carbon sinks and a region of high biological and cultural diversity.
An international team of scientists are raising the alarm in a letter published today in Nature Ecology & Evolution. ‘Increasing wildfires threaten progress on halting deforestation in Brazilian Amazonia’ is co-authored by researchers at the University of East Anglia (UEA) and the University of South Alabama, which led the study. Other contributors ...
2023-10-16
Most people think of dementia as something that affects a person’s brain. But a new study shows just how much damage it does to a person’s wallet and bank account too – as well as the higher demands it places on their family members.
In all, people diagnosed with dementia saw their out-of-pocket spending for health care more than double, and their net worth decline by more than 60%, within the first eight years of being diagnosed, the study finds.
Meanwhile, other people of similar ages and in similar health, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sansbury receives funding for dissertation study