(Press-News.org) Stress and depression are known to increase risk of heart attack, especially among women. They’ve also been linked to worse recovery. But does stress and depression contribute more to women with heart attacks with open arteries or blocked arteries? That’s what a new study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology aimed to find out.
Researchers found stress and depression were indeed common among women at the time of heart attack and for two months after. But they also found that women with heart attacks due to blockages (MI-CAD) in their coronary arteries had higher stress levels than those with heart attack with open arteries (MINOCA).
First author Anaïs Hausvater, MD, a cardiologist at the Sarah Ross Soter Center for Women’s Cardiovascular Research at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York, said the study highlights the need for greater focus on mental health among women with heart disease.
“We have identified a subset of high-risk patients who fail to improve [their stress] or get worse after their event,” she said. “It is important that clinicians, including cardiologists, screen their patients with heart disease for symptoms of stress, anxiety and depression.”
For the multicenter study, 486 female patients completed questionnaires measuring their perceived stress and depression symptoms at the time of their heart attack and again two months later. Researchers then compared the results over time and looked at differences between the two types of heart attacks.
While both groups had signs of stress and depression, women with heart attack and open arteries were less likely to report high levels of stress, both at the time of heart attack and after.
Hausvater said because little is known about what causes heart attack with open arteries or MINOCA, these patients are often left with few answers about why it happened to them and how they can prevent it from happening again.
“We have observed clinically that this can cause distress among our patients,” she said. “Prior studies have suggested that stress might contribute more to their disease, but we found this might not be true.”
One possible explanation is that younger patients might have different sources of stress, she added. Older women, who are more likely to have blocked arteries, may be coping with more financial stressors, as well as the illness or loss of aging partners.
Future studies from the group will focus on sex differences in psychosocial factors among men and women with heart attacks. Researchers are also working on a study that looks at stress interventions for women after heart attack.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org or follow @ACCinTouch.
The ACC’s family of JACC Journals rank among the top cardiovascular journals in the world for scientific impact. The flagship journal, the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) — and family of specialty journals consisting of JACC: Advances, JACC: Asia, JACC: Basic to Translational Science, JACC: CardioOncology, JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, JACC: Case Reports, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and JACC: Heart Failure — pride themselves on publishing the top peer-reviewed research on all aspects of cardiovascular disease. Learn more at JACC.org.
###
END
When walking on the sidewalk, a person is able to avoid puddles, other walkers, and cracks in the pavement. It may seem intuitive – and that's because it is.
There’s actually a biological component that allows humans and other mammals to navigate our complex environments. Central Pattern Generators (CPG) are neural networks that produce rhythmic patterns of control signals for limbs using simple environmental cues. When we quickly step away to avoid something blocking our path, that’s ...
Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.
The automotive, aerospace, clean energy and tool-and-die industries — any industry that needs complex and high-performance parts — could use additive manufacturing,” said Alex Plotkowski, materials scientist in ORNL’s Materials Science and Technology Division and the lead scientist of the experiment. Plotkowski and his ...
Findings from research to help the business world identify destructive ‘corporate psychopaths’ will be presented at the Chelmsford Science Festival on Monday, 23 October.
Dr Clive Boddy of Anglia Ruskin University, a pioneer in the field of corporate psychopathy, will discuss his research, published in the International Journal of Market Research, looking at how the financial industry can identify, manage and, if necessary, remove these individuals.
Around 1% of the adult population are ...
NEW ORLEANS, La. - Ochsner Health was named among the “Best Hospitals According to Patients & Health Care Providers” by WebMD, an online publication for health news and information.
The 2023 WebMD Choice Awards recognized a select group of 167 health systems with Elite Choice Awards, WebMD Patient Choice Awards, and Medscape Physician Choice Awards. Results were gathered via a survey of a national audience encompassing thousands of patients and healthcare clinicians to determine which hospitals they believe deliver the best quality and treatments. The awards program identifies the “best in class” ...
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon's Systems, Networking, and Energy Efficiency (Synergy) Lab will present several multi-year studies on their work around ubiquitous sensing at this week's ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp).
The works unveil several innovative systems and explain how the collected data can be converted to offer useful insights, all while ensuring the privacy of the individuals being monitored.
Led by School of Computer Science Associate Professor Yuvraj Agarwal, ...
Clinical stage artificial intelligence (AI) drug discovery company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) has been invited to present scientific data on its novel anti-cancer assets at three major upcoming cancer conferences -- the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) conference in Madrid Oct. 20-24, 2023; the Society of Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) conference Nov. 1-5, 2023 in San Diego; and the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) Dec. 5-9, 2023.
Small molecule oncology ...
SAN FRANCISCO — The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) today presented Philip G. Morgan, M.D., and Margaret M. Sedensky, M.D., with its 2023 Excellence in Research Award in recognition of their extensive research focused on understanding how anesthetics work and whether certain anesthetics are safe for children with mitochondrial disease. The award is presented annually for outstanding achievement in research that has had, or is likely to have, an important impact on the practice of anesthesiology.
Drs. Morgan and Sedensky are professors in the Department of Anesthesiology ...
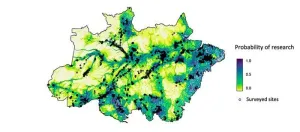
Many parts of the Brazilian Amazon are neglected in ecological research, for several reasons, according to an article published in the journal Current Biology. Authored by Joice Ferreira of the Federal University of Pará (UFP) and colleagues from many countries who also belong to the Synergize Consortium, the article identifies the areas missing from ecological research and the factors that have determined these gaps, pinpointing opportunities for the planning of new investments in research ...
A new kind of polymer membrane created by researchers at Georgia Tech could reshape how refineries process crude oil, dramatically reducing the energy and water required while extracting even more useful materials.
The so-called DUCKY polymers — more on the unusual name in a minute — are reported Oct. 16 in Nature Materials. And they’re just the beginning for the team of Georgia Tech chemists, chemical engineers, and materials scientists. They also have created artificial intelligence tools to predict the performance of these kinds of polymer membranes, which could accelerate development of new ones.
The implications are stark: ...
Gun violence is tied to poverty, unemployment, broken families, disengaged youth and racial segregation, according to a study by the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center at Rutgers.
Published in the Journal of Urban Health, the study found that people living in disadvantaged communities face gun violence at higher levels that are harmful to the health and well-being of whole neighborhoods.
“Many of America’s most disadvantaged neighborhoods are stuck in a vicious cycle of violence and collateral damage that is almost impossible to escape,” ...