(Press-News.org) A global team of scientists have announced the results of an unprecedented collaboration to search for the source of the largest ever seismic event recorded on Mars. The study, led by the University of Oxford, rules out a meteorite impact, suggesting instead that the quake was the result of enormous tectonic forces within Mars’ crust.
The quake, which had a magnitude of 4.7 and caused vibrations to reverberate through the planet for at least six hours, was recorded by NASA’s InSight lander on May 4 2022. Because its seismic signal was similar to previous quakes known to be caused by meteoroid impacts, the team believed that this event (dubbed ‘S1222a’) might have been caused by an impact as well, and launched an international search for a fresh crater.
Although Mars is smaller than Earth, it has a similar land surface area because it has no oceans. In order to survey this huge amount of ground – 144 million km2 – study lead Dr Benjamin Fernando of the University of Oxford sought contributions from the European Space Agency, the Chinese National Space Agency, the Indian Space Research Organisation, and the United Arab Emirates Space Agency. This is thought to be the first time that all missions in orbit around Mars have collaborated on a single project. Each group examined data from their satellites orbiting Mars to look for a new crater, or any other tell-tale signature of an impact (e.g. a dust cloud appearing in the hours after the quake).
After several months of searching, the team announced today that no fresh crater was found. They conclude that the event was instead caused by the release of enormous tectonic forces within Mars’ interior. The results, published today in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, indicate that the planet is much more seismically active than previously thought.
Dr Fernando said: ‘We still think that Mars doesn’t have any active plate tectonics today, so this event was likely caused by the release of stress within Mars’ crust. These stresses are the result of billions of years of evolution; including the cooling and shrinking of different parts of the planet at different rates. We still do not fully understand why some parts of the planet seem to have higher stresses than others, but results like these help us to investigate further. One day, this information may help us to understand where it would be safe for humans to live on Mars and where you might want to avoid!’
He added: ‘This project represents a huge international effort to help solve the mystery of S1222a, and I am incredibly grateful to all the missions who contributed. I hope this project serves as a template for productive international collaborations in deep space.’
Dr Daniela Tirsch, Science Coordinator for the High Resolution Stereo Camera on board the European Space Agency’s Mars Express Spacecraft said: ‘This experiment shows how important it is to maintain a diverse set of instruments at Mars, and we are very glad to have played our part in completing the multi-instrumental and international approach of this study.’
From China, Dr Jianjun Liu (National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences) added: ‘We are willing to collaborate with scientists around the world to share and apply this scientific data to get more knowledge about Mars, and are proud to have provided data from the colour imagers on Tianwen-1 to contribute to this effort.’
Dr Dimitra Atri, Group Leader for Mars at New York University Abu Dhabi and contributor of data from the UAE’s Hope Spacecraft, said: ‘This has been a great opportunity for me to collaborate with the InSight team, as well as with individuals from other major missions dedicated to the study of Mars. This really is the golden age of Mars exploration!’
S1222a was one of the last events recorded by InSight before its end of mission was declared in December 2022. The team are now moving forward by applying knowledge from this study to future work, including upcoming missions to the Moon and Titan’s Moon Saturn.
ENDS
NOTES TO EDITORS:
Media contact: Dr Benjamin Fernando, Department of Physics, University of Oxford: benjamin.fernando@physics.ox.ac.uk
The study ‘A tectonic origin for the largest marsquake observed by InSight’ will be published in Geophysical Research Letters at 14:01 BST/ 09:01 ET Tuesday 17 October 2023: https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL103619. To view a copy of the study under embargo contact Dr Benjamin Fernando, Department of Physics, University of Oxford: benjamin.fernando@physics.ox.ac.uk
Images of the InSight are available on request: benjamin.fernando@physics.ox.ac.uk
About InSight
InSight was a NASA mission dedicated to the study of the martian interior through geophysics, especially seismology (the study of Earthqukes).
It launched from California in May 2018 and landed on Mars in November of that year. The last data were returned in December 2022, after the spacecraft lost power due to increasing dust accumulation on its solar panels.
External partners to the InSight mission included the UK, France, Germany, and Switzerland. Within the UK, Imperial College London and the University of Oxford are lead institutions.
During its time on Mars, InSight recorded over 1,300 marsquake events. Of these, at least 8 were from meteoroid impact events. The largest two formed craters around 150m in diameter. If the S1222a event was formed by an impact, we would expect the crater to be at least 300m in diameter.
This project involved all other active missions currently orbiting Mars, who contributed their data and expertise. These include:
The MAVEN, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and Mars Odyssey spacecraft of NASA
The ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and Mars Express (MEX) spacecraft of ESA
The Emirates Mars Mission (Hope) of the United Arab Emirates Space Agency
The Tianwen-1 Mission of the Chinese National Space Agency
The Mangalyaan (MOM) mission of the Indian Space Research Organisation, which ended in September 2022. The MOM data were searched but no relevant images were taken before the end of mission
Additional Quotes
Dr Ernst Hauber, lead of the geoscience working group for the High Resolution Stereo Camera on the Mars Express mission, added: ‘This shows how important mission extensions, like the ones that Mars Express has received in the last few years, are to maintaining a diverse set of instruments in orbit which are complementary to each other.’
Dr Constantinos Charalambous of Imperial College London, a co-author on the study, said: ‘The absence of a crater in our image search for S1222a marks a significant milestone in interpreting seismic signals on Mars, crucial for distinguishing impact events from tectonic forces on the Red Planet.’
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the eighth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
END
International team reveals source of largest ever Mars quake
2023-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The dark side of the American lawn
2023-10-17
The American residential lawn is, for many, an iconic landscape and about half of homeowners in the US use fertilizer to keep their yards green and lush. Some proportion of the nitrogen in this fertilizer enters the broader environment, with negative consequences including algal blooms and deoxygenated waters. Peter Groffman and colleagues studied residential landscapes in the Baltimore, Maryland metropolitan area, which drains to the Chesapeake Bay, seeking to identify locations (hotspots) or times (hot moments) with disproportionately high rates of nitrogen export. The authors went to lawns in exurban, ...
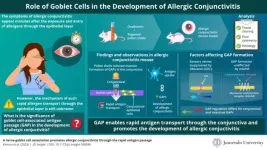
New study sheds light on the developmental mechanism of allergic conjunctivitis
2023-10-17
When it comes to eye allergies, the transition from allergen contact to bothersome symptoms has always been quick, appearing within a span of a few minutes. The initial stage of allergic conjunctivitis involves the penetration of allergen through the epithelial cell layer (cells covering the outer surface of the body). However, the exact mechanism underlying the rapid allergen transfer has remained a mystery so far.
Fortunately, in a new ground-breaking study published in the journal JCI Insight on October 11, 2023, researchers from Juntendo ...
Western University researchers reveal link between Alzheimer’s and sex hormones
2023-10-17
LONDON, ON., CA:
Alzheimer’s disease disproportionately affects women, who represent about two-thirds of those diagnosed with the late-onset type of the disease.
Previous research has shown Alzheimer’s is also more severe and progresses more rapidly in women, and women with Alzheimer’s experience a steeper cognitive decline – loss of memory, attention, and the ability to communicate and make decisions – compared to men with the disease.
The biological bases for these differences between men and women with Alzheimer’s disease are not well understood. ...
How to help save plants from extinction
2023-10-17
Now is the time to identify the conditions that cause plants to die. Doing so will allow us to better protect plants by choosing conservation targets more strategically, UC Riverside botanists argue in a new paper.
Published in the Oxford Academic journal Conservation Physiology, the paper demonstrates how scientists can learn the limits past which plants’ vital functions shut down, and makes the case that not doing so is a mistake in this era of increasing drought and wildfires.
“We can measure the amount of water loss plants ...
Kennedy Krieger receives $5 million grant to expand reach of its pediatric post-COVID-19 clinic and support school students
2023-10-17
BALTIMORE, October 17, 2023—Researchers at Kennedy Krieger Institute have received a $5 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), through the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), to expand access to comprehensive care for children and adolescents with long COVID-19, particularly among underserved populations.
During the five-year project, researchers at the Pediatric Post-COVID-19 Rehabilitation Clinic will receive up to $1 million annually to expand and strengthen its integrative services in Baltimore and the overall mid-Atlantic ...
Can lifestyle interventions benefit patients with advanced breast cancer?
2023-10-17
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Oct. 17, 2023) – Can lifestyle interventions such as exercise and intermittent fasting help patients with advanced breast cancer better tolerate side effects from treatment?
That is the question Tracy Crane, PhD, RDN, and Carmen Calfa, MD, at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and their collaborators will strive to answer with a $4-million, five-year grant from the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
Crane, co-lead of Cancer Control and director of Lifestyle Medicine, Prevention and ...
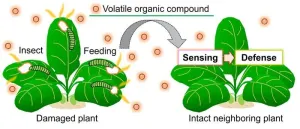
Unlocking nature's silent conversations: Real-time visualization of plant-plant communications through airborne volatiles
2023-10-17
Saitama, Japan: Plants emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere upon mechanical damages or insect attacks. Undamaged neighboring plants sense the released VOCs as danger cues to activate defense responses against upcoming threats (Figure 1). This phenomenon of airborne communication among plants through VOCs was first documented in 1983 and has since been observed in more than 30 different plant species. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying VOC perception to defense induction remain unclear.
Unveiling the Invisible Conversation
The ...
Critical step made for managing brushtail possums
2023-10-17
Researchers say mapping the genetic code of the brushtail possum will benefit those working to both conserve and control the animal.
In a five-year long study, just published in Nature Communications, an international group of researchers led by the University of Otago, has assembled the entire genetic code of the marsupial mammal.
The work also uncovered where and when their genes are expressed, and revealed surprising details about their population diversity, reproduction, and origins.
Study lead Associate Professor Tim Hore, of Otago’s Department of Anatomy, describes possums as “a fascinating animal that is loved ...
Surprising discovery about coral’s resilience could help reefs survive climate change
2023-10-17
The factors affecting coral’s resilience — its ability to adapt to and survive environmental changes — seem to be more nuanced than scientists believed.
In a study published Oct. 18 in the journal Global Change Biology, researchers reveal surprising findings about a species common to Caribbean waters. The discovery may help improve efforts to save corals from bleaching and other consequences of climate change.
A team led by Assistant Professor of Biological Sciences Carly Kenkel at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and ...
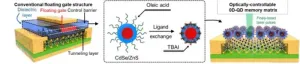
Ushering in the era of light-powered 'multi-level memories'
2023-10-17
We live in an era of data deluge. The data centers that are operated to store and process this flood of data use a lot of electricity, which has been called a major contributor to environmental pollution. To overcome this situation, polygonal computing systems with lower power consumption and higher computation speed are being researched, but they are not able to handle the huge demand for data processing because they operate with electrical signals, just like conventional binary computing systems.
The Korea Institute of Science ...