(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Climate change and the rapid increase in frequency of extreme weather events around the globe – such as wildfires and floods – reinforces the reality that these events are not only not random but, rather, interconnected. Interlinked climate behavior, or teleconnections, isn’t a well understood field but will be necessary to fully comprehend how our climate system works.
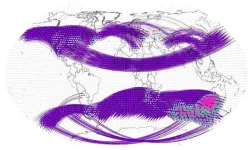
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, a team of researchers affiliated with Beijing Normal University and Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications in China and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany describes a climate network analysis method to explore the intensity, distribution, and evolution of teleconnections.
“Teleconnections describe how climate events in one part of the world can affect weather thousands of kilometers away,” said co-author Jingfang Fan of Beijing Normal University and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. “Think of it as a domino effect on a global scale.”
And then there’s global warming – the Earth is becoming hotter. “Within just five years, we may see temperatures rising to levels that global scientists have been warning us about,” said Fan. “It’s like the planet is running a fever that’s steadily getting worse.”
Climate networks are akin to maps where data points are marked as locations, and the connections between them reveal similarities.
The researchers’ climate network analysis method combines the directions and distribution patterns of teleconnections to evaluate their intensity and to identify sensitive regions using global daily surface air temperature data. Their method relies on advanced data processing and mathematical algorithms to find meaningful insights.
“Our work uncovered patterns in climate events driven mainly by atmospheric Rossby waves, which are large inertial planetary waves that naturally occur in rotating fluids and cause movement within the atmosphere,” said Fan.
The team identified areas significantly affected by these interconnected events, within regions like southeastern Australia and South Africa, which are particularly sensitive. One fascinating discovery they made is that these interconnections are becoming stronger over time, from 1948 to 2021, possibly due to a mix of climate change, human activities, and other factors. The extent and intensity of the impact of teleconnections has increased more prominently in the Southern Hemisphere during the past 37 years.
This work provides a new way to measure and explore climate teleconnections. The researchers plan to use this knowledge to pinpoint which regions may be at a higher risk in the future and to devise strategies to address these challenges.
“The next step is like weather forecasting – but on steroids,” said Fan. “Using what we’ve learned, we plan to predict how climate events will unfold and connect. We’re diving deep to explore why these events happen and how various climate ‘tipping points’ within our climate system might be linked.”
###
The article “Exploring the intensity, distribution, and evolution of teleconnections using climate network analysis” is authored by Shang Wang, Jun Meng, and Jingfang Fan. It will appear in Chaos on Oct. 17, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0153677). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0153677.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Chaos is devoted to increasing the understanding of nonlinear phenomena in all areas of science and engineering and describing their manifestations in a manner comprehensible to researchers from a broad spectrum of disciplines. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/cha.
###
END
Climate network analysis helps pinpoint regions at higher risk of extreme weather
Tracking climate behavior could connect the dots between major weather events and help with forecasting on a global scale
2023-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Race and ethnicity and prehospital use of opioid or ketamine analgesia in acute traumatic injury
2023-10-17
About The Study: The results of this study of over 4.7 million patient encounters across the U.S. during a 3-year period suggest that patients from racial and ethnic minority groups with acute traumatic injuries do not have their pain treated equitably in the prehospital setting.
Authors: Eli Carrillo, M.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38070)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the risk of dementia
2023-10-17
About The Study: In this study of 109,000 individuals born between 1933 and 1952 and followed up in old age, adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) was associated with an increased risk of dementia. Policy makers, caregivers, patients, and clinicians may wish to monitor reliably for ADHD in old age.
Authors: Stephen Z. Levine, Ph.D., of the University of Haifa in Haifa, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38088)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
AI models identify biodiversity from animal sounds in tropical rainforests
2023-10-17
Tropical forests are among the most important habitats on our planet. They are characterised by extremely high species diversity and play an eminent role in the global carbon cycle and the world climate. However, many tropical forest areas have been deforested and overexploitation continues day by day.
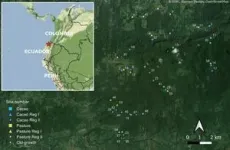
Reforested areas in the tropics are therefore becoming increasingly important for the climate and biodiversity. How well biodiversity develops on such areas can be monitored very well with an automated analysis of animal sounds. This was reported by researchers in the journal Nature Communications.
Recordings on Former Cocoa Plantations and Pastures
As part of the DFG research group ...
Recognizing clinical signs of hyperthyroidism leads to appropriate treatments, reduces adverse impact on health
2023-10-17
(Boston)—Untreated hyperthyroidism, conditions where there is excess thyroid hormone present, can adversely affect health, leading to increased risks for abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure, osteoporosis, adverse pregnancy outcomes, metabolic abnormalities and increased mortality risk. Hyperthyroidism can occur due to several different etiologies, including Graves’ disease, toxic (overactive) thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis. It is important to recognize, correctly diagnose, and appropriately treat the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism to minimize its impacts on health.
In a new review article in the Journal ...
Adults with ADHD are at increased risk for developing dementia
2023-10-17
Adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are nearly three times more likely to develop dementia than adults without ADHD, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, coauthored by Michal Schnaider Beeri, director of the Herbert and Jacqueline Krieger Klein Alzheimer’s Research Center at Rutgers Brain Health Institute (BHI) was published in JAMA Network Open. It followed more than 100,000 older adults in Israel over 17 years to examine if adults with ADHD are at increased risk for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Although more than 3 percent of the adult population in the United States has ADHD, there is limited research ...
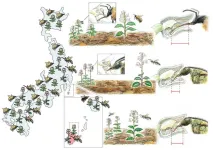
Orchid without bumblebee on island finds wasp, loses self
2023-10-17
Because the bumblebee that an orchid relies on for pollination does not exist on a remote island, the plant gets pollinated by an island wasp. Kobe University researchers found that this came at the cost of being hybridized with another orchid species adapted to being pollinated by the wasp. The finding showcases how plants in ecological relationships adapt to changing circumstances.
Remote islands have been exciting study grounds for biologists since at least the days of Darwin. When studying ecological relationships between different species, the differences between mainland and island ...
Ocean circulation, ice melt and increasing tourism could all be contributing to Arctic microplastics
2023-10-17
Scientists measured microplastic concentrations in the highly productive Barents Sea and suggest that ocean circulation, ice melt, tourism, inadequate waste management, shipping and fishing are all likely contributors.
Numerous studies have shown that global microplastic quantities in the marine environment are increasing, even in remote locations such as the Arctic.
The Barents Sea, which adjoins the Arctic Ocean, is one of the most productive oceanic areas in the world and home to an enormous diversity of organisms.
It is also a key route for Atlantic ...
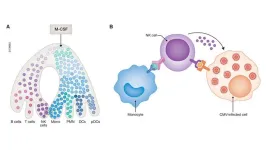
Boosting weak immune system: scientists find an unusual weapon against virus
2023-10-17
Some viruses can be dormant throughout a person’s life and cause no harm but become dangerous when the immune system is weakened. One of such viruses is human cytomegalovirus (CMV). Harmless to the general public but life-threatening to patients with a supressed immune system.
“Patients undergoing bone marrow transplantations have their blood and immune system fully replaced by that of the donor. In the first months after transplantation they are defenseless. They can either catch CMV or have virus reactivated that was dormant in the patient. At the moment, there is no ideal treatment. The available ones work ...
Depression, anxiety common among college students
2023-10-17
Depression and anxiety among college students is a growing public health problem. And new research from the University of Georgia suggests the problem may be worse for students who aren’t the same race as most of their peers.
The new study found that students who were not the majority race at a predominantly white college reported significantly higher rates of depression than their white peers.
At the mostly white university, more than half of the students who self-identified as races other than white reported feelings of mild depression. An additional 17% said they were experiencing moderate to severe depression.
Students at the predominantly ...
Research finds water quality in Gulf of Mexico improves when adding social costs to carbon emissions
2023-10-17
DURHAM, N.H.—U.S. Climate policies can offer options for putting climate change efforts into place that solve environmental problems like excessive carbon dioxide in the atmosphere created by greenhouse gas emissions. Research led by the University of New Hampshire took a closer look at what would happen to agriculture if there was an extra cost, or so-called social cost, added to fossil fuels, which are essential for making fertilizer used in farming. They found that while CO2 emissions would decline by as much as 50%, the cost of fertilizer would rise leading to a significant benefit on water quality by lessening fertilizer runoff contributing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] Climate network analysis helps pinpoint regions at higher risk of extreme weatherTracking climate behavior could connect the dots between major weather events and help with forecasting on a global scale