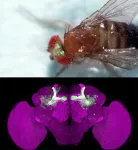
Thermosensation is critical for the survival of animals, but the mechanisms by which this is modulated by nutritional status remain unclear
Behavioral and live brain imaging studies reveal why food-sated fruit flies prefer to stay at relatively higher temperatures compared to hungry flies
2023-10-17
(Press-News.org)
Thermosensation is critical for the survival of animals, but the mechanisms by which this is modulated by nutritional status remain unclear; here, behavioral and live brain imaging studies reveal why food-sated fruit flies prefer to stay at relatively higher temperatures compared to hungry flies.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002332
Article Title: Independent insulin signaling modulators govern hot avoidance under different feeding states
Author Countries: Taiwan
Funding: This work was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council (112-2311-B-182-002-MY3 and 109-2326-B-182-001-MY3) to C-LW, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPD1M0301-3, CMRPD1M0761-3, and BMRPC75) to C-LW. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-17
Different strains of E.coli can outcompete one another to take over the gut, a new study reveals.
Publishing their findings today in PLOS Biology, scientists reveal that a particular strain, known as MDR ST131, can readily colonise new hosts, even if those hosts are already have E.coli in their healthy gut.
The international team, led by experts at the University of Birmingham, used a mouse model to help understand why strains of E.coli that live in a healthy gut are rapidly overtaken of when challenged with a multi-drug resistant strain.
Lead author Professor Alan McNally, from ...
2023-10-17
Sleeping patterns and stress hormones could be the key to understanding how and when people with epilepsy are likely to experience seizures, a new study reveals.
Researchers used mathematical modelling to understand the impact of different physiological processes, such as sleep and changes in concentration of the stress-hormone cortisol, on key signatures of epilepsy – known as epileptiform discharges (ED).
Epilepsy is a serious neurological disorder characterised by a tendency to have recurrent, spontaneous seizures. Classically, seizures were assumed to occur at random, until the discovery of ED activity with timescales that vary from hours and days through to months.
The scientists ...
2023-10-17
The Dompé Foundation is offering 16 scholarships to support neuroscience and neurobiology students enrolled at US universities for the academic year 2023/2024. This funding opportunity, which honors the legacy of the only female Italian Nobel laureate in Medicine, is intended for promising candidates from any nationality that have already been admitted to a Master’s, PhD or post-doc program. With a total budget of up to about 1 million USD, the Foundation has doubled from the previous two years its funding for the US project, ...
2023-10-17
Continuing the temperature trend from this summer, September 2023 was the hottest September on record, according to scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS). The month also set the record for the highest temperature anomaly – the largest difference from the long-term average.
This visualization shows global temperature anomalies along with the underlying seasonal cycle. Temperatures advance from January through December left to right, rising during warmer months and falling during cooler months. The color of each line represents the year, with colder purples for the 1960s and warmer oranges and yellows for more recent ...
2023-10-17
One of the biggest challenges for earthquake early warning systems (EEW) is the lack of seismic stations located offshore of heavily populated coastlines, where some of the world’s most seismically active regions are located. In a new study published in The Seismic Record, researchers show how unused telecommunications fiber optic cable can be transformed for offshore EEW.
Jiuxun Yin, a Caltech researcher now at SLB, and colleagues used 50 kilometers of a submarine telecom cable running between the United States and Chile, sampling ...
2023-10-17
A team of researchers at the Texas A&M University School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) has received a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to research metabolism in people with Down syndrome.
By targeting genes that affect metabolism, the team may be able to develop drug therapies for physical and mental symptoms of the condition, like muscle loss, accelerated aging, and lower cognitive function, thereby improving the quality of life for people with Down syndrome.
The new grant will also make Dr. Weston Porter, a professor in the VMBS Department of Veterinary Physiology & Pharmacology and lead researcher ...
2023-10-17
In a world that relies on high-speed internet and seamless communication, the absence of a reliable fiber connection can be a significant hurdle. Fortunately, a cutting-edge technology known as free-space optical communication (FSO) offers a flexible solution for field-deployable high-speed wireless communication in areas where fiber connections are unavailable.
FSO has garnered attention for its versatility across various scales of operation. On a global level, it plays a crucial role in establishing high-speed satellite internet projects like Starlink, ensuring global connectivity. At the ground level, ...
2023-10-17
BATON ROUGE – The Obesity Society – the leading professional society focused on obesity science, treatment and prevention – has named Pennington Biomedical’s Dr. Leanne Redman as the recipient of the 2023 TOPS Research Achievement Award. The award, which is funded by the Take Off Pounds Sensibly, or TOPS, Foundation, was presented to Dr. Redman on Monday, Oct. 16, in recognition of her contributions to research in the field of obesity.
Considered by many to be the top award for obesity research, Dr. ...
2023-10-17
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Anyone who has ever tried to pack a family-sized amount of luggage into a sedan-sized trunk knows this is a hard problem. Robots struggle with dense packing tasks, too.
For the robot, solving the packing problem involves satisfying many constraints, such as stacking luggage so suitcases don’t topple out of the trunk, heavy objects aren’t placed on top of lighter ones, and collisions between the robotic arm and the car’s bumper are avoided.
Some traditional methods tackle this problem sequentially, guessing a partial solution ...
2023-10-17
Glioblastoma is the most common type of brain tumor that affects adults and, unfortunately, still remains incurable. In a new study, researchers have demonstrated that a specific mitochondrial protein plays an important role in glioblastoma, and can therefore be used as a potential target to reduce tumors.
“Glioblastoma is notorious for its lethality. One of the major challenges is that it spreads invasively throughout the brain. We’re interested in understanding what drives this process in order to identify new therapeutic strategies,” said Brendan Harley (RBTE leader/EIRH), the Robert W. Schaefer Professor of Chemical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Thermosensation is critical for the survival of animals, but the mechanisms by which this is modulated by nutritional status remain unclear
Behavioral and live brain imaging studies reveal why food-sated fruit flies prefer to stay at relatively higher temperatures compared to hungry flies






